If you’ve ever tried to carry on a conversation in a noisy room, you’ll be able to relate to the scientists and engineers trying to “hear” the signals from experimental quantum computing devices called qubits. These basic units of quantum computers are early in their development and remain temperamental, subject to all manner of interference. Stray “noise” can masquerade as a functioning qubit or even render it inoperable.
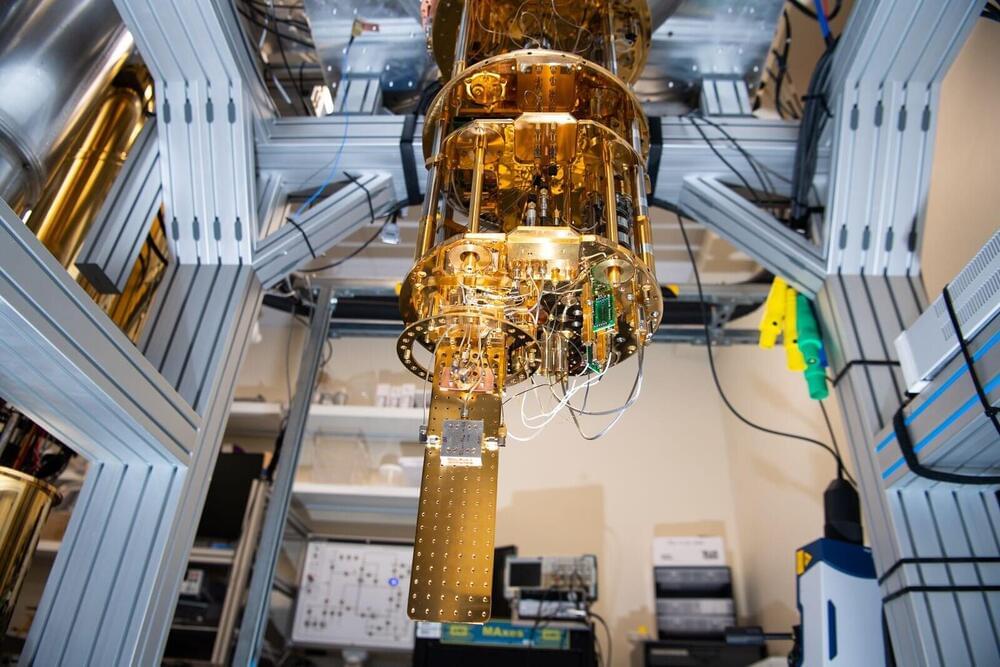
That’s why physicist Christian Boutan and his Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) colleagues were in celebration mode recently as they showed off PNNL’s first functional superconducting qubit. It’s not much to look at. Its case—the size of a pack of chewing gum—is connected to wires that transmit signals to a nearby panel of custom radiofrequency receivers. But most important, it’s nestled within a shiny gold cocoon called a dilution refrigerator and shielded from stray electrical signals. When the refrigerator is running, it is among the coldest places on Earth, so very close to absolute zero, less than 6 millikelvin (about −460 degrees F).
The extreme cold and isolation transform the sensitive superconducting device into a functional qubit and slow down the movement of atoms that would destroy the qubit state. Then, the researchers listen for a characteristic signal, a blip on their radiofrequency receivers. The blip is akin to radar signals that the military uses to detect the presence of aircraft. Just as traditional radar systems transmit radio waves and then listen for returning waves, the physicists at PNNL have used a low-temperature detection technique to “hear” the presence of a qubit by broadcasting carefully crafted signals and decoding the returning message.