When quantum computers become powerful enough, they could theoretically crack the encryption algorithms that keep us safe. The race is on to find new ones.



The research community is excited about the potential of DNA to function as long-term archival storage. That’s largely because it’s extremely dense, chemically stable for tens of thousands of years, and comes in a format we’re unlikely to forget how to read. While there has been some interesting progress, efforts have mostly stayed in the research community because of the high costs and extremely slow read and write speeds. These are problems that need to be solved before DNA-based storage can be practical.
So we were surprised to hear that storage giant Seagate had entered into a collaboration with a DNA-based storage company called Catalog. To find out how close the company’s technology is to being useful, we talked to Catalog’s CEO, Hyunjun Park indicated that Catalog’s approach is counterintuitive on two levels: It doesn’t store data the way you’d expect, and it isn’t focusing on archival storage at all.

A phenomenon that often accompanies technological innovations involves how they tend to become smaller with their improvement over time. From televisions and communication devices like telephones to computers and microchip components, many of the technologies we use every day occupy a fraction of the space in our homes and offices that their predecessors did just decades ago.
In keeping with this trend, it is no surprise that a new tech developed by scientists at Sandia National Laboratories, in cooperation with the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light, may soon replace cumbersome technologies than once required an entire room to operate, thanks to an ultrathin invention that could change the future of computation, encryption, and a host of other technologies.
At the heart of the invention and its function is a peculiar phenomenon that has perplexed physicists for decades, known as quantum entanglement.

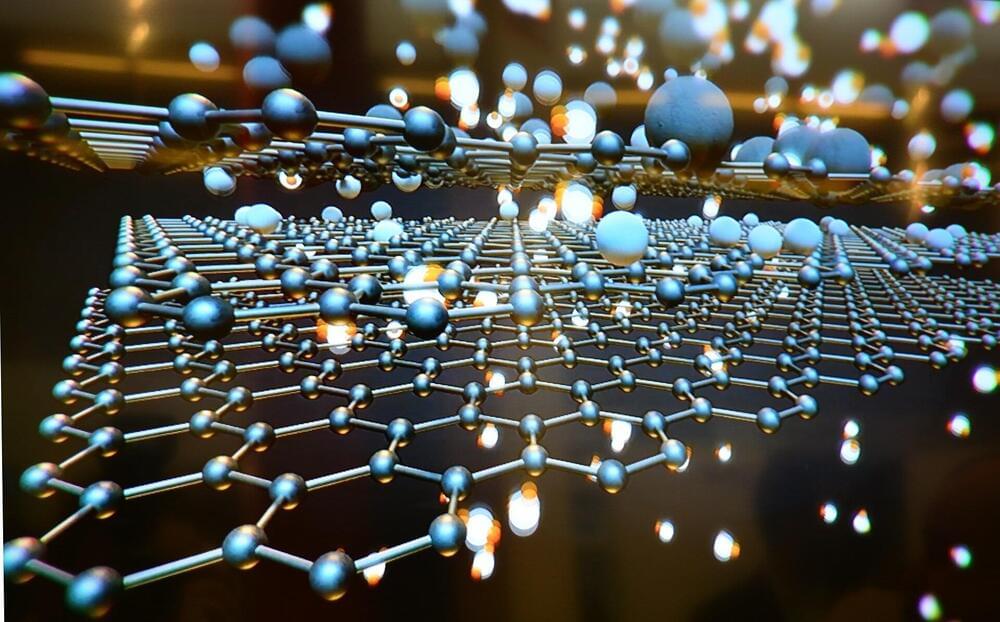
U.S. and European physicists have demonstrated a new method for predicting whether metallic compounds are likely to host topological states that arise from strong electron interactions.
Physicists from Rice University, leading the research and collaborating with physicists from Stony Brook University, Austria’s Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien), Los Alamos National Laboratory, Spain’s Donostia International Physics Center and Germany’s Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, unveiled their new design principle in a study published online today in Nature Physics.
The team includes scientists at Rice, TU Wien and Los Alamos who discovered the first strongly correlated topological semimetal in 2017. That system and others the new design principle seeks to identify are broadly sought by the quantum computing industry because topological states have immutable features that cannot be erased or lost to quantum decoherence.
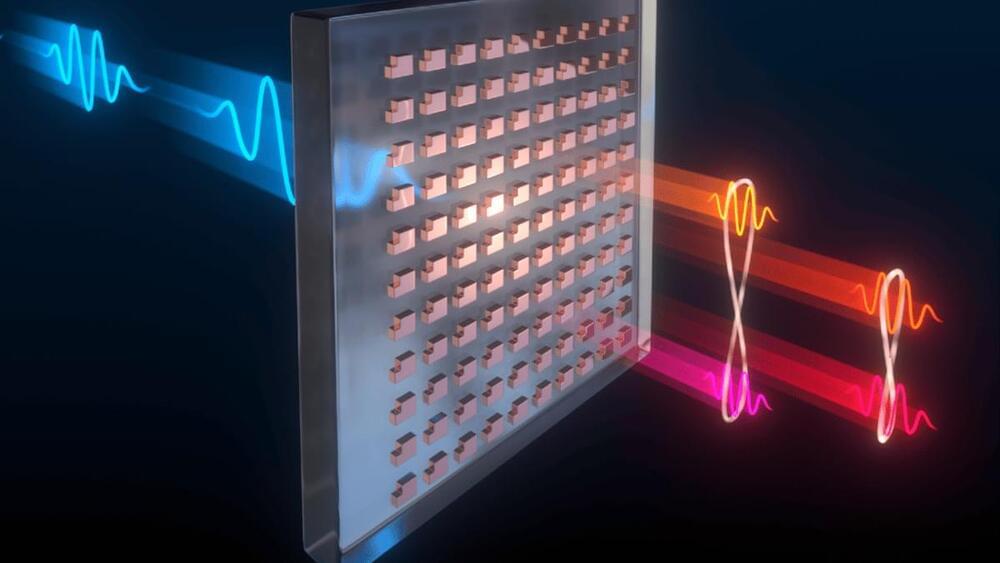
Scientists at Sandia National Laboratories and the Max Planck Institute have developed a way to produce a web of quantum entangled photons using a far more simple setup than usual. The key is a precisely patterned surface 100 times thinner than paper, which could replace a roomful of optical equipment.
Quantum entanglement is the bizarre-sounding phenomenon where two particles can become so entwined together that manipulating one will instantly affect its partner, no matter how far apart they may be. This forms the basis for emerging technologies like quantum computing and quantum encryption.
The problem is, generating entangled groups of photons can be tricky, and is usually done with large arrays of lasers, specialized crystals, and other optical equipment. But the Sandia and Max Planck team has a much simpler setup – a metasurface.
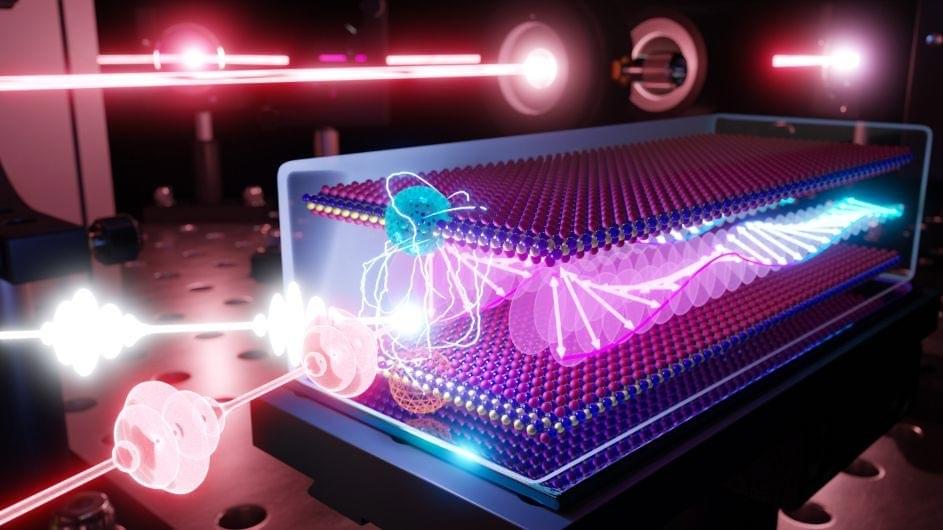
New research reveals that spinning quasiparticles, or magnons, light up when paired with a light-emitting quasiparticle, or exciton, with potential quantum information applications.
All magnets contain spinning quasiparticles called magnons. This is true of all magnets from the simple souvenirs hanging on your refrigerator to the discs that give your computer memory storage to the powerful versions used in research labs. The direction one magnon spins can influence that of its neighbor, which in turn affects the spin of its neighbor, and so on, yielding what are known as spin waves. Spin waves can potentially transmit information more efficiently than electricity, and magnons can serve as “quantum interconnects” that “glue” quantum bits together into powerful computers.
Although magnons have enormous potential, they are often difficult to detect without bulky pieces of lab equipment. According to Columbia researcher Xiaoyang Zhu, such setups are fine for conducting experiments, but not for developing devices, such as magnonic devices and so-called spintronics. However, seeing magnons can be made much simpler with the right material: a magnetic semiconductor called chromium sulfide bromide (CrSBr) that can be peeled into atom.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=DGbZ9J2nlNA&feature=share
TWITTER https://twitter.com/Transhumanian.
PATREON https://www.patreon.com/transhumania.
BITCOIN 14ZMLNppEdZCN4bu8FB1BwDaxbWteQKs8i.
BITCOIN CASH 1LhXJjN4FrfJh8LywR3dLG2uGXSaZjey9f.
ETHEREUM 0x1f89b261562C8D4C14aA01590EB42b2378572164
LITECOIN LdB94n8sTUXBto5ZKt82YhEsEmxomFGz3j.
CHAINLINK 0xDF560E12fF416eC2D4BAECC66E323C56af2f6666.

Two big players in computing and research are trying to lay the groundwork for a future quantum internet.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is teaming up with Harvard University to test and develop strategies for networking together quantum technologies. Their partnership was announced today, and is a continuation of AWS’ goals to create a communications channel between the quantum computers that it is also working on in parallel.
During the three-year research alliance, funding from Amazon will support research projects at Harvard that focus on quantum memory, integrated photonics, and quantum materials, and help upgrade infrastructure in Harvard’s Center for Nanoscale Systems.

You need to wait till 2023 to get them though.
Lenovo has unveiled its T1 Glasses at its Tech Life 2022 event and promises to place a full HD video-watching experience right inside your pockets, a company press release stated.
Mobile computing devices have exploded in the past few years as gaming has become more intense, and various video streaming platforms have gathered steam. The computing power of smartphones and tablets has increased manifold. Whether you want to ambush other people in an online shooting game or sit back and watch a documentary in high-definition, a device in your pocket can help you do that with ease.