Google takes on the cause of rehabilitating old hardware with Chrome OS Flex.
ChromeOS Flex is designed to make obsolete computers functional to do work in the 21st century.


Researchers at the SketchX, University of Surrey have recently developed a meta learning-based model that allows users to retrieve images of specific items simply by sketching them on a tablet, smartphone, or on other smart devices. This framework was outlined in a paper set to be presented at the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), one of the top three flagship computer vision conferences along with CVPR and ICCV.
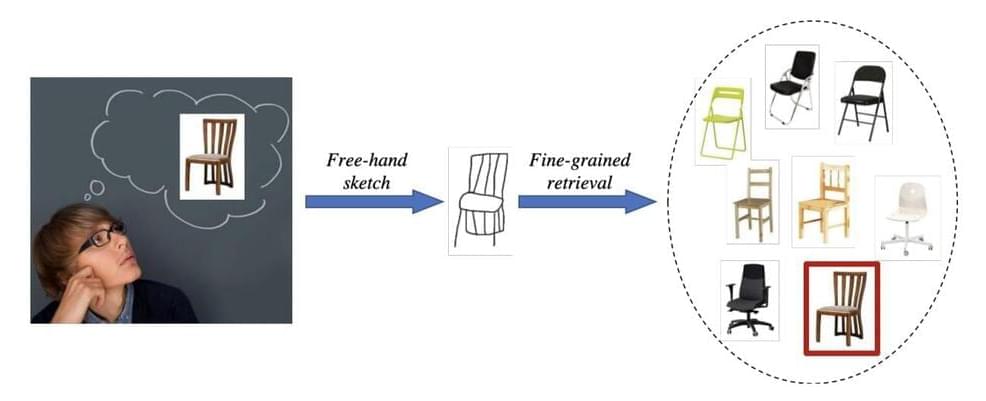
Researchers at the SketchX, University of Surrey have recently developed a meta learning-based model that allows users to retrieve images of specific items simply by sketching them on a tablet, smartphone, or on other smart devices. This framework was outlined in a paper set to be presented at the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), one of the top three flagship computer vision conferences along with CVPR and ICCV.
“This is the latest along the line of work on ‘fine-grained image retrieval,’ a problem that my research lab (SketchX, which I direct and founded back in 2012) pioneered back in 2015, with a paper published in CVPR 2015 titled ‘Sketch Me That Shoe,’” Yi-Zhe Song, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “The idea behind our paper is that it is often hard or impossible to conduct image retrieval at a fine-grained level, (e.g., finding a particular type of shoe at Christmas, but not any shoe).”
In the past, some researchers tried to devise models that can retrieve images based on text or voice descriptions. Text might be easier for users to produce, yet it was found only to work at a coarse level. In other words, it can become ambiguous and ineffective when trying to describe details.

We live in an increasingly connected world, a fact underscored by the swift spread of the coronavirus around the globe. Underlying this connectivity are complex networks—global air transportation, the internet, power grids, financial systems and ecological networks, to name just a few. The need to ensure the proper functioning of these systems also is increasing, but control is difficult.
Now a Northwestern University research team has discovered a ubiquitous property of a complex network and developed a novel computational method that is the first to systematically exploit that property to control the whole network using only local information. The method considers the computational time and information communication costs to produce the optimal choice.
The same connections that provide functionality in networks also can serve as conduits for the propagation of failures and instabilities. In such dynamic networks, gathering and processing all the information necessary to make a better decision can take too much time. The goal is to diagnose a problem and take action before it leads to a system-wide issue. This may mean having less information but being timely.

Swave Photonics has designed holographic chips on a proprietary diffractive optics technology to “bring the metaverse to life.”
Can virtual reality become indistinguishable from actual reality? Swave Photonics, a spinoff of Imec and Vrije Universiteit Brussel, has designed holographic chips on a proprietary diffractive optics technology to “bring the metaverse to life.” The Leuven, Belgium–based startup has raised €7 million in seed funding to accelerate the development of its multi-patented Holographic eXtended Reality (HXR) technology.
“Our vision is to empower people to visualize the impossible, collaborate, and accomplish more,” Théodore Marescaux, CEO and founder of Swave Photonics, told EE Times Europe. “With our HXR technology, we want to make that extended reality practically indistinguishable from the real world.”
What does it mean to project images that are indistinguishable from reality? “It means a very wide field of view, colors, high dynamic range, the ability to move your head around an object and see it from different angles, and the ability to focus,” he said.

A new miracle drug could increase the human lifespan by up to 200 years. Dr. Andrew Steele, a British computational biologist recently published a new book on the longevity of human life. In the book, the doctor argues that it is completely feasible for humans to live beyond our standard 100-year lifespan thanks to a new type of drug.

Intel ((INTC) — Get Intel Corporation Report ) is the bearer of additional bad news.
The chip giant will give an extra blow to consumers and businesses concerned about the health of the economy. For several weeks in fact, consumers have seen their bills for groceries and other products increase. The price of gasoline at the pump has jumped when they go to fill up their car.
And the situation is not getting any better since inflation remains at its highest for forty years, which should push the Federal Reserve to be even more aggressive in raising rates. However, economists have already warned that this monetary policy would plunge the economy into recession.
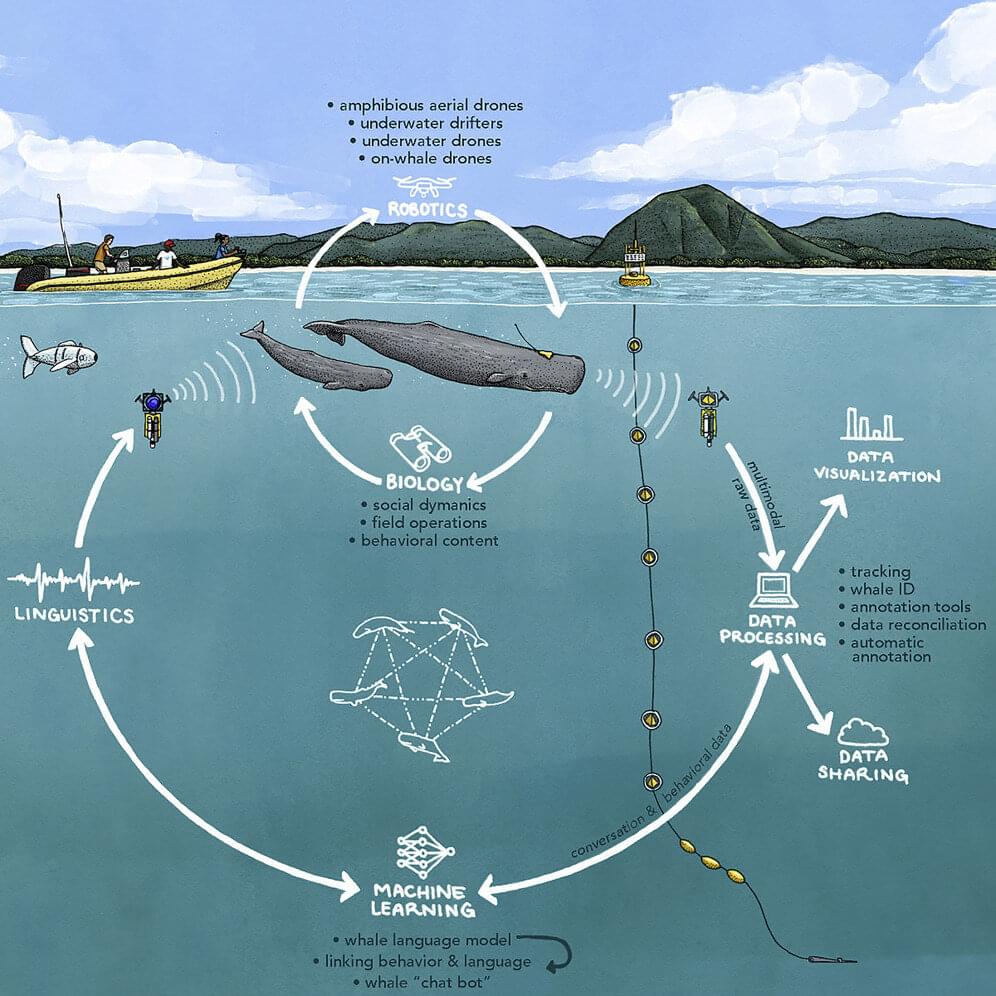
In the 2016 sci-fi movie “Arrival,” a linguist and a theoretical physicist race against time to communicate with endangered extraterrestrial heptapods wishing to share their wisdom and technologies with the human race so it will survive and one day return the favor.
At the University of California, Berkeley, a real and more down-to-earth mission to decode an unknown form of communication is underway. Linguist Gasper Begus and computer scientist Shafi Goldwasser are part of an international team of researchers attempting interspecies communication with sperm whales by deciphering their deafening, 200-plus decibel clicking sounds, or codas.
They are among the key members of the Cetacean Translation Initiative (CETI), a newly launched, five-year multidisciplinary project aimed at cracking sperm whales’ Morse code-like communications off the Caribbean island of Dominica, to gain a deeper knowledge of the ocean’s brainiest predators and to preserve their habitat from further human disruption.