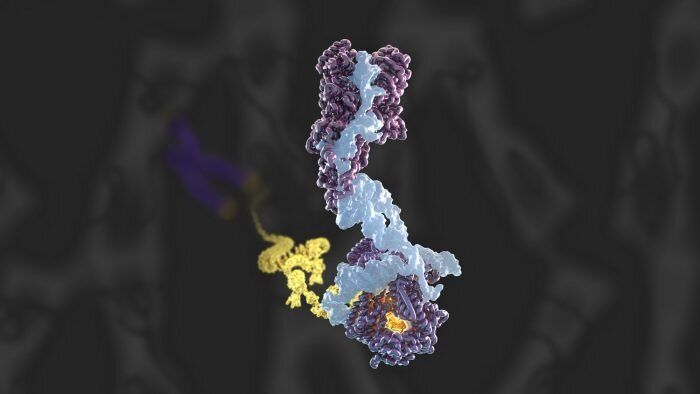
Telomeres are large nucleoproteins structures that cap the ends of chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. When a cell divides, a small portion of the telomere is lost due to the inherently incomplete process of genome replication. If left unchecked, over time the telomeres will reach a critically short length and the cell will face genomic instability, deterioration or death. To offset this shortening, an essential enzyme called telomerase rebuilds the telomeres by synthesizing new telomeric DNA repeats at chromosome ends. Kelly Nguyen’s group, in the LMB’s Structural Studies Division, has solved the first complete atomic model of this enzyme and discovered a histone dimer as novel telomerase subunits.
Telomeres act as a barrier to protect the genetic information from progressive degradation arising from incomplete DNA replication. Additionally, telomeres distinguish the natural chromosome ends from DNA double-strand breaks, thereby avoiding an illicit DNA damage response and preventing intrachromosomal fusion. This makes telomeres essential for the preservation of genome and chromosome stability. In previous research, Kelly had discovered the architecture and composition of human telomerase holoenzyme at 8 Å (Ångströms) resolution using cryo-EM. However, to understand the molecular mechanism governing telomerase mediated telomere maintenance, a high-resolution structure of the complex was required.
To conduct this study, Kelly’s group, in collaboration with Kathleen Collins at the University of California, Berkeley, and Rhiju Das at Stanford University, prepared telomerase by extracting it from cultured human cells, before imaging using cryo-EM—resulting in the collection of almost 44000 images. This data was analyzed using RELION—a complex computer program developed at the LMB—in order to achieve the 3.4−3.8 Å structure of telomerase. From this Kelly and members of her group, George Ghanim, Adam Fountain, and Marike van Roon, were able to build the first complete atomic model of telomerase, with 12 protein subunits and telomerase RNA. By completing the structure to such a high resolution, the group was not only able to illuminate how common RNA and protein motifs work together, but also to highlight new interactions.