Searches for dark matter particles have come up empty so far, driving theorists to get more creative with their ideas.



Our universe is filled with galaxies, in all directions as far as our instruments can see. Some researchers estimate that there are as many as 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe. At first glance, these galaxies might appear to be randomly scattered across space, but they’re not. Careful mapping has shown that they are distributed across the surfaces of giant cosmic “bubbles” up to several hundred million light-years across. Inside these bubbles, few galaxies are found, so those regions are called cosmic voids. NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will allow us to measure these voids with new precision, which can tell us about the history of the universe’s expansion.
“Roman’s ability to observe wide areas of the sky to great depths, spotting an abundance of faint and distant galaxies, will revolutionize the study of cosmic voids,” said Giovanni Verza of the Flatiron Institute and New York University, lead author on a paper published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Cosmic recipe The cosmos is made of three key components: normal matter, dark matter, and dark energy. The gravity of normal and dark matter tries to slow the expansion of the universe, while dark energy opposes gravity to speed up the universe’s expansion. The nature of both dark matter and dark energy is currently unknown. Scientists are trying to understand them by studying their effects on things we can observe, such as the distribution of galaxies across space.


Rocky planets like our Earth may be far more common than previously thought, according to new research published in the journal Science Advances. It suggests that when our solar system formed, a nearby supernova (the massive explosion of a star near the end of its life) bathed it in cosmic rays containing the radioactive ingredients to make rocky, dry worlds. This mechanism could be ubiquitous across the galaxy.
Earth-like planets are thought to form from planetesimals (objects made of rock and ice) that were dried out early in the solar system’s history. This process required a lot of heat, which came primarily from the radioactive decay of short-lived radionuclides (SLRs), such as aluminum-26. Previous analysis of meteorites, which are ancient records of the early solar system, confirmed the abundance of SLRs at this time.
Flaws in previous models However, models that explain supernovae as the sole source of these SLRs cannot accurately match the quantity of the nucleotides found in meteorites. To deliver enough radioactive material, the supernova would have to be so close to the early solar system that it would have destroyed the disk of dust and gas where the planets were forming.
Professor John Donoghue explains why quantum physics and gravity actually work perfectly together. He tackles quadratic gravity, effective field theory, and random dynamics, arguing that grand unification and naturalness aren’t required for a theory of everything.
As a listener of TOE you can get a special 20% off discount to The Economist and all it has to offer! Visit https://www.economist.com/toe.
SUPPORT:
Support me on Substack: https://curtjaimungal.substack.com/su…
JOIN MY SUBSTACK (Personal Writings): https://curtjaimungal.substack.com LISTEN ON SPOTIFY: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9… TIMESTAMPS:
LINKS MENTIONED:
SOCIALS:
Guests do not pay to appear. Theories of Everything receives revenue solely from viewer donations, platform ads, and clearly labelled sponsors; no guest or associated entity has ever given compensation, directly or through intermediaries. #science.
Support me on Crypto: https://commerce.coinbase.com/checkou…
Support me on PayPal: https://www.paypal.com/donate?hosted_…
JOIN MY SUBSTACK (Personal Writings): https://curtjaimungal.substack.com.
LISTEN ON SPOTIFY: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9…
TIMESTAMPS:
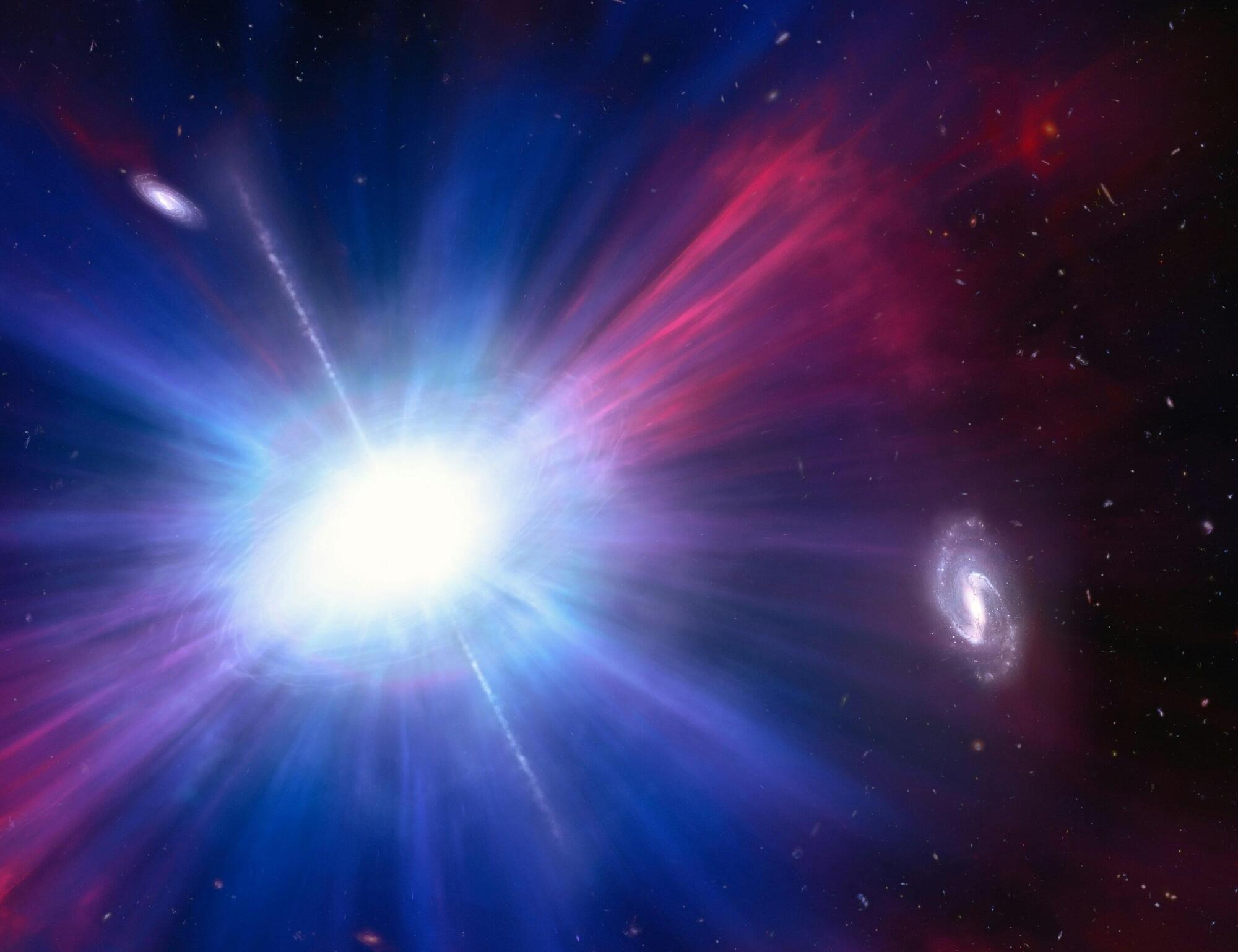

An international team of astronomers has achieved a first in probing the early universe, using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), detecting a supernova—the explosive death of a massive star—at an unprecedented cosmic distance.
The explosion, designated SN in GRB 250314A, occurred when the universe was only about 730 million years old, placing it deep in the era of reionization. This remarkable discovery provides a direct look at the final moments of a massive star from a time when the first stars and galaxies were just beginning to form.
The event, which has been reported on in the recently published academic paper JWST reveals a supernova following a gamma-ray burst at z ≃ 7.3, (Astronomy & Astrophysics, 704, December 2025), was initially flagged by a bright burst of high-energy radiation, known as a long-duration Gamma-Ray Burst (GRB), detected by the space-based multi-band astronomical Variable Objects Monitor (SVOM) on March 14, 2025. Follow-up observations with the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO/VLT) confirmed the extreme distance.

When black holes collide, the impact radiates into space like the sound of a bell in the form of gravitational waves. But after the waves, there comes a second reverberation—a murmur that physicists have theorized but never observed.
An international collaboration has for the first time simulated in detail what these whispers—called late-time gravitational wave tails —might “sound” like.
“So far, we’ve only seen tails in simplified models, not in full simulations of numerical relativity,” said Leo Stein, University of Mississippi associate professor of physics and astronomy and co-author of the study. “These are the first fully numerical simulations where we saw tails clearly.”


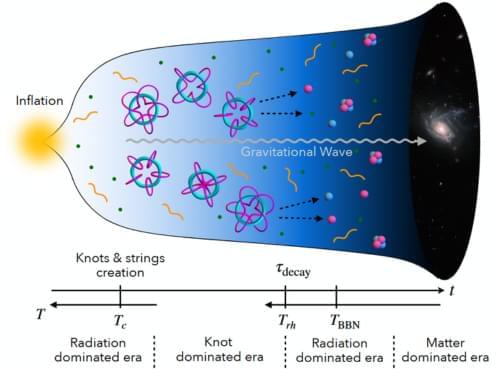
Knotted structures once imagined by Lord Kelvin may actually have shaped the universe’s earliest moments, according to new research showing how two powerful symmetries could have created stable “cosmic knots” after the Big Bang. These exotic objects may have briefly dominated the young cosmos, unraveled through quantum tunneling, and produced heavy right-handed neutrinos whose decays tipped the balance toward matter over antimatter.
In 1867, Lord Kelvin pictured atoms as tiny knots in an invisible medium called the ether. That picture turned out to be wrong, since atoms are built from subatomic particles rather than twists in space. Yet his discarded idea of knotted structures may still help explain one of the deepest questions in science: why anything in the universe exists at all.
A team of physicists in Japan has now shown that knotted structures can naturally appear in a realistic particle physics model that also addresses several major mysteries, including the origins of neutrino masses, dark matter, and the strong CP problem. Their study, published in Physical Review Letters, suggests that such “cosmic knots” could have formed in the violently changing early universe, briefly taken over as a dominant form of energy, and then collapsed in a way that slightly favored matter over antimatter. As they formed and decayed, these knots would have stirred spacetime itself, producing a distinctive pattern of gravitational waves that future detectors might be able to pick up, which is rare for a problem that is usually very difficult to test directly.