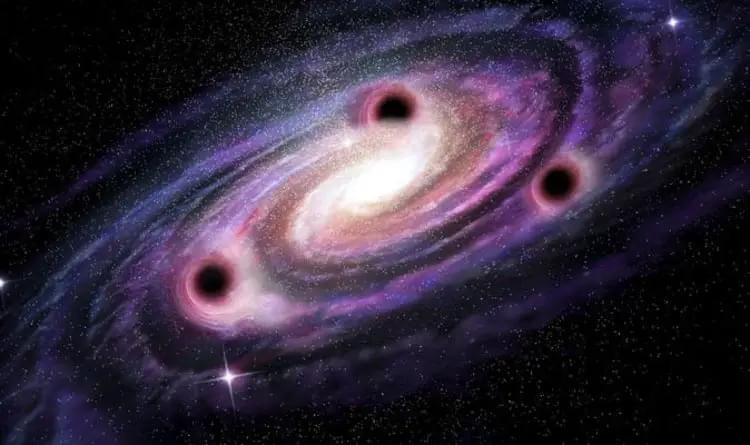
In the study, an international team of astronomers identified three supermassive black holes lurking near the center of galaxy NGC 6,240, which has been visibly disturbed by the gravitational effects of a triple merger. Because NGC 6,240 is so close—just 300 million light-years away—astronomers had previously assumed that its odd shape was the product of a typical merger between two galaxies. They believed that these two galaxies collided as they increased to hundreds of miles per second, and that they are still combining. Therefore, the researchers expected to find two supermassive black holes hiding near the center of the cosmic collision.
Instead, the team discovered three supermassive black holes, each weighing more than 90 million Suns, when they used 3D mapping techniques to peer into the core of NGC 6240. (To put this into perspective, Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, is roughly 4 million solar masses in weight.) Furthermore, the three massive black holes of NGC 6,240 are confined to an area that is less than 3,000 light-years across, or less than 1% of the galaxy in which they are found.
“Up until now, such a concentration of three supermassive black holes had never been discovered in the universe,” said study co-author Peter Weilbacher of the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam in a press release. This is the first time that scientists have seen a group of supermassive black holes packed into such a small area, despite the fact that they have previously discovered three distinct galaxies and the black holes that are connected to them on a collision course.