Two clashing ideas about disorder inside black holes now point to the same strange conclusions, and it could reshape the foundations of how we think about space and time
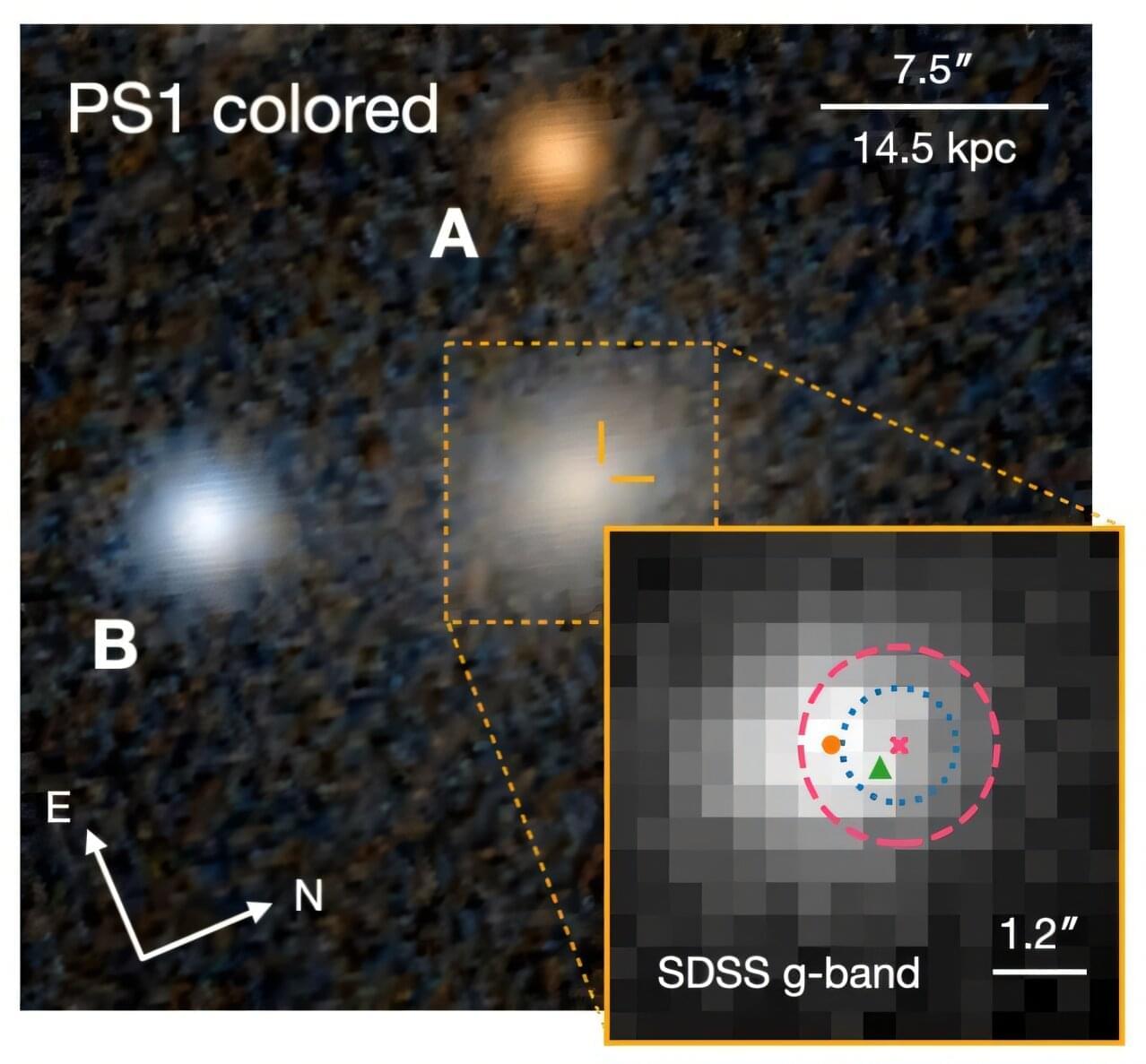



An international team of astronomers has investigated a short-lived optical flare designated AT2022zod. As a result, they found evidence indicating that this flare is an unusual tidal disruption event. The findings were presented in a research paper published Dec. 1 on the arXiv pre-print server.
When a star passes close enough to a supermassive black hole and is pulled apart by the black hole’s tidal forces, it triggers the process of disruption, which is known as a tidal disruption event (TDE). Afterward, the tidally disrupted stellar debris starts raining down on the black hole, and radiation emerges from the innermost region of accreting debris, which is an indicator of the presence of a TDE.

“Novae are more than fireworks in our galaxy — they are laboratories for extreme physics,” said Dr. Laura Chomiuk.
What can imaging supernovae (plural for supernova) explosions teach astronomers about their behavior and physical characteristics? This is what a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated the mechanisms behind the thermonuclear eruptions that supernovae cause. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand supernovae, as they are hypothesized to be responsible for spreading the chemical elements and molecules needed for life throughout the universe.
For the study, the researchers used the Georgia State University CHARA Array to observe exploding supernovae from two separate white dwarfs: nova V1674 Her and nova V1405 Cas, which are located approximately 16,200 and 5,500 light-years from Earth, and were observed days 2 & 3 and days 53, 55, & 67 after first light of eruption, also known as t0, respectively. For nova V1674 Her, the researchers observed outflows during days 2 & 3, while they observed this same behavior for nova V1405 Cas during days 53, 55, & 67. The researchers note these contrasting observations challenge longstanding hypotheses regarding supernovae behavior during their eruption periods.
An exploration of ten spooky aspects of the multiverse and our universe within it.
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
Music:
Cylinder Eight by Chris Zabriskie is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.…
Source: http://chriszabriskie.com/cylinders/
Artist: http://chriszabriskie.com/
Cylinder Five by Chris Zabriskie is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.…
Source: http://chriszabriskie.com/cylinders/
Artist: http://chriszabriskie.com/
Darkest Child by Kevin MacLeod is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)

Astronomers from the University of California (UC), Berkeley and elsewhere have performed spectroscopic and photometric study of a peculiar supernova designated SN 2021ukt, which underwent a transition from Type IIn to Type Ib. Results of the new study, presented Nov. 28 on the arXiv pre-print server, shed more light on the nature of this supernova.


An international team led by the University of Oxford has identified one of the largest rotating structures ever reported: a ‘razor-thin’ string of galaxies embedded in a giant spinning cosmic filament, 140 million light-years away. The findings, published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, could offer valuable new insights into how galaxies formed in the early Universe.
Cosmic filaments are the largest known structures in the Universe: vast, thread-like formations of galaxies and dark matter that form a cosmic scaffolding. They also act as ‘highways’ along which matter and momentum flow into galaxies. Nearby filaments containing many galaxies spinning in the same direction-and where the whole structure appears to be rotating – are ideal systems to explore how galaxies gained the spin and gas they have today. They can also provide a way to test theories about how cosmic rotation builds up over tens of millions of light-years.
What makes this structure exceptional is not just its size, but the combination of spin alignment and rotational motion. You can liken it to the teacups ride at a theme park. Each galaxy is like a spinning teacup, but the whole platform-the cosmic filament-is rotating too.

Astronomers have observed the longest-ever gamma-ray burst — a powerful, extragalactic explosion that lasted over seven hours. Rapid follow-up observations with the U.S. Department of Energy-fabricated Dark Energy Camera and the International Gemini Observatory, funded in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation and operated by NSF NOIRLab, provided crucial information about the possible origin of this extraordinary event and the galaxy that hosts it.
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are among the most powerful explosions in the Universe, second only to the Big Bang. The majority of these bursts are observed to flash and fade within a few seconds to minutes. But on 2 July 2025, astronomers were alerted to a GRB source that was exhibiting repeating bursts and would end up lasting over seven hours. This event, dubbed GRB 250702B, is the longest gamma-ray burst humans have ever witnessed.
GRB 250702B was first identified by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope (Fermi). Shortly after space-based telescopes detected the initial bursts in gamma-rays and pinpointed its on-sky location in X-rays, astronomers around the world launched campaigns to observe the event in additional wavelengths of light.