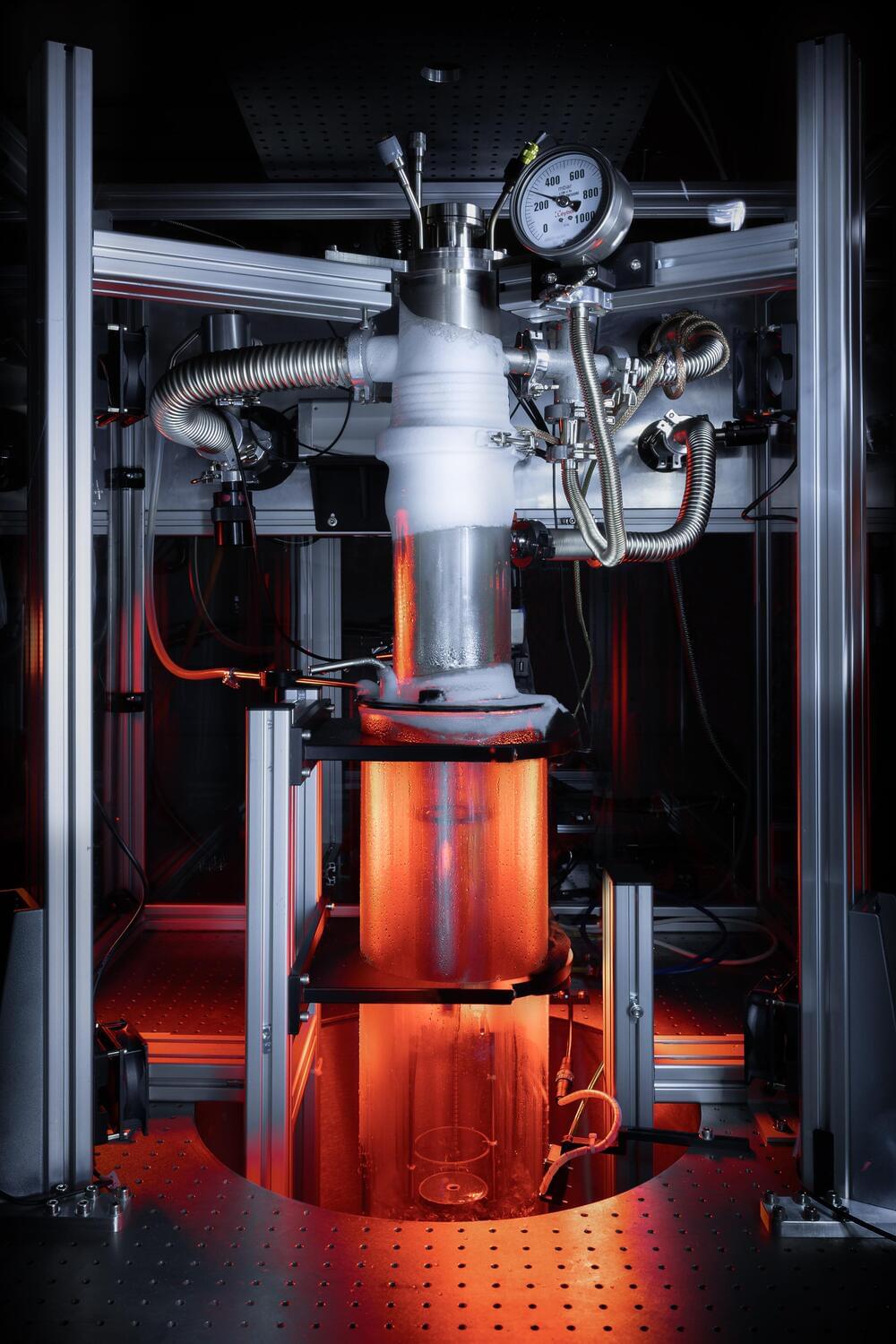
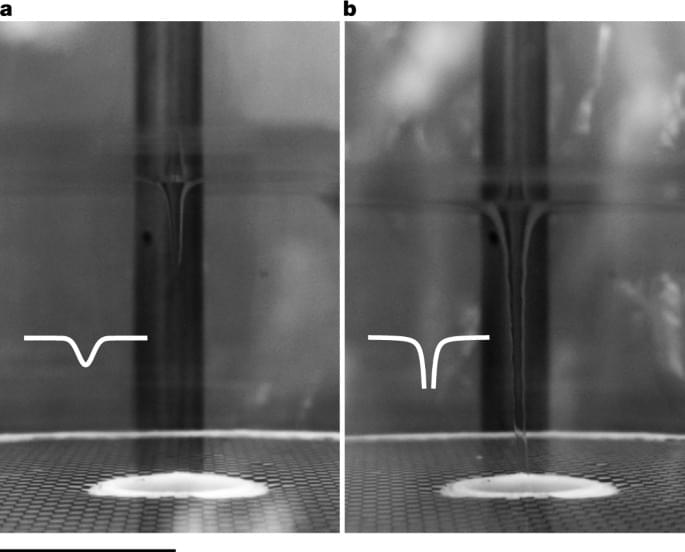
Scientists have for the first time created a giant quantum vortex to mimic a black hole in superfluid helium that has allowed them to see in greater detail how analog black holes behave and interact with their surroundings.

Journey into the enigmatic depths of a black hole, with beloved physicist Carlo Rovelli. Buy Carlo’s book here: https://geni.us/nNB6xAsBecome one of our YouTu…
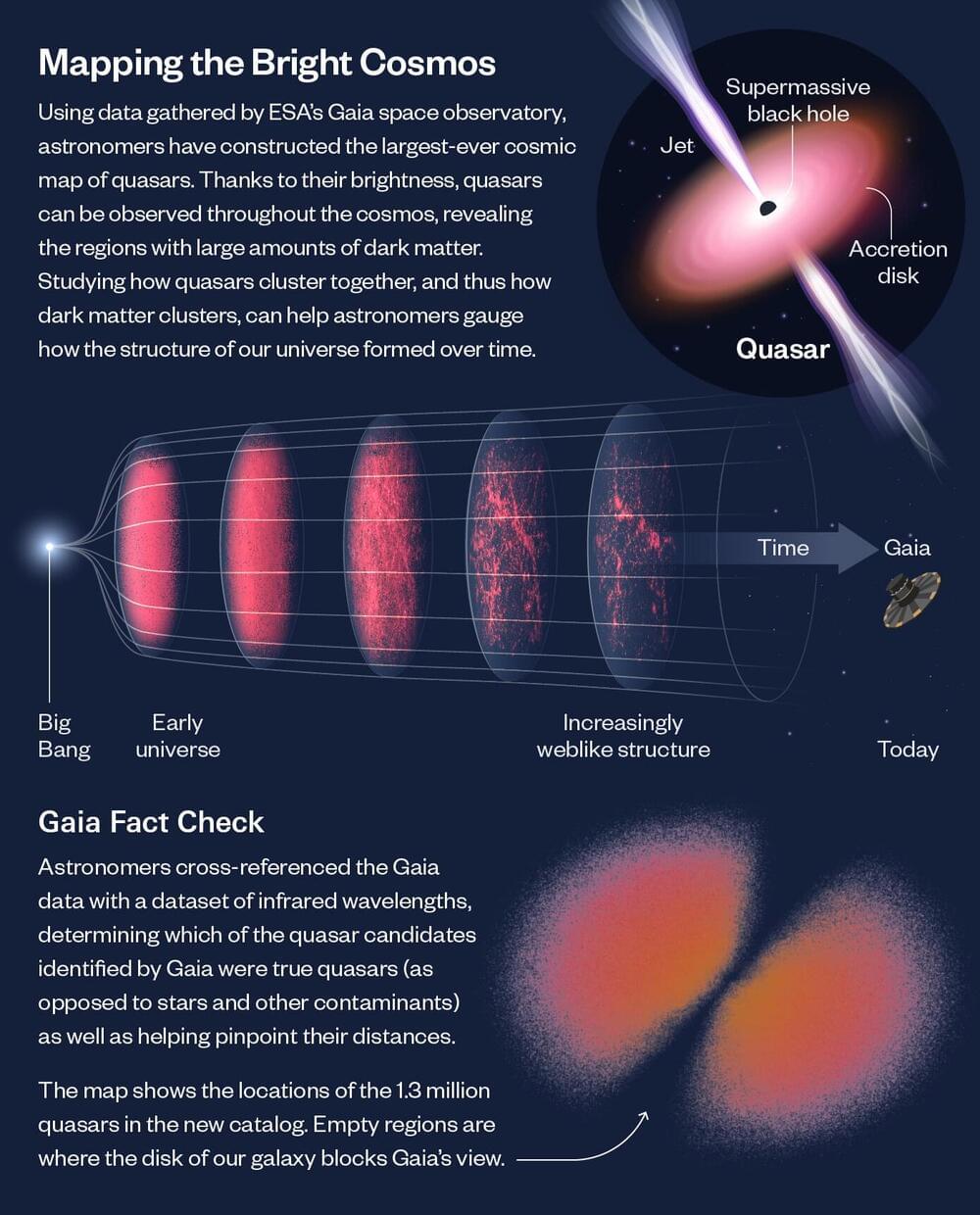
The new map includes around 1.3 million quasars from across the visible universe and could help scientists better understand the properties of dark matter.
Astronomers have charted the largest-ever volume of the universe with a new map of active supermassive black holes living at the centers of galaxies. Called quasars, the gas-gobbling black holes are, ironically, some of the universe’s brightest objects.
The new map logs the location of about 1.3 million quasars in space and time, the furthest of which shone bright when the universe was only 1.5 billion years old. (For comparison, the universe is now 13.7 billion years old.)

It takes more than a galaxy merger to make a black hole grow and new stars form: machine learning shows cold gas is needed too to initiate rapid growth — new research finds.
When they are active, supermassive black holes play a crucial role in the way galaxies evolve. Until now, growth was thought to be triggered by the violent collision of two galaxies followed by their merger, however new research led by the University of Bath suggests galaxy mergers alone are not enough to fuel a black hole — a reservoir of cold gas at the centre the host galaxy is needed too.
The new study, published this week in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society is believed to be the first to use machine learning to classify galaxy mergers with the specific aim of exploring the relationship between galaxy mergers, supermassive black-hole accretion and star formation. Until now, mergers were classified (often incorrectly) through human observation alone.

At some point, theoretical physics shades into science fiction. This is a beautiful little book, by a celebrated physicist and writer, about a phenomenon that is permitted by equations but might not actually exist. Or perhaps white holes do exist, and are everywhere: we just haven’t noticed them yet. No such controversy exists about black holes, wh…

Dive into the captivating story of Gz9p3, an ancient galaxy that’s challenging our understanding of the cosmos. Revealed by the James Webb Space Telescope, this galactic giant, observed just 510 million years after the Big Bang, is reshaping our views on early universe galactic formation. Join us as we explore the mysteries and wonders of Gz9p3, a window into the universe’s dawn.
Chapters:
00:00 Introduction.
00:54 Unveiling Gz9p3: A Glimpse into the Past.
03:16 Cosmic Collisions: Sculpting Galaxies.
05:03 Rethinking Early Universe Cosmology.
06:25 Outro.
07:13 Enjoy.
Best Telescopes for beginners:
Celestron 70mm Travel Scope.
https://amzn.to/3jBi3yY
Celestron 114LCM Computerized Newtonian Telescope.
https://amzn.to/3VzNUgU
Celestron – StarSense Explorer LT 80AZ
https://amzn.to/3jBRmds.
Visit our website for up-to-the-minute updates:
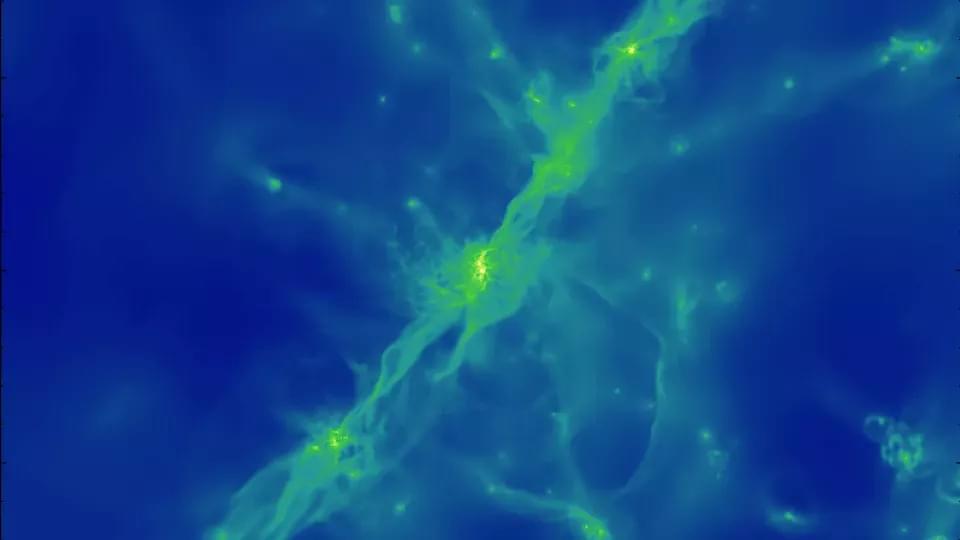
Astronomers can use supercomputers to simulate the formation of galaxies from the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago to the present day. But there are a number of sources of error. An international research team, led by researchers in Lund, has spent a hundred million computer hours over eight years trying to correct these.
The last decade has seen major advances in computer simulations that can realistically calculate how galaxies form. These cosmological simulations are crucial to our understanding of where galaxies, stars and planets come from. However, the predictions from such models are affected by limitations in the resolution of the simulations, as well as assumptions about a number of factors, such as how stars live and die and the evolution of the interstellar medium.
To minimise the sources of error and produce more accurate simulations, 160 researchers from 60 higher education institutions – led by Santi Roca-Fàbrega at Lund University, Ji-hoon Kim at Seoul National University and Joel R. Primack at the University of California – have collaborated and now present the results of the largest comparison of simulations done ever.