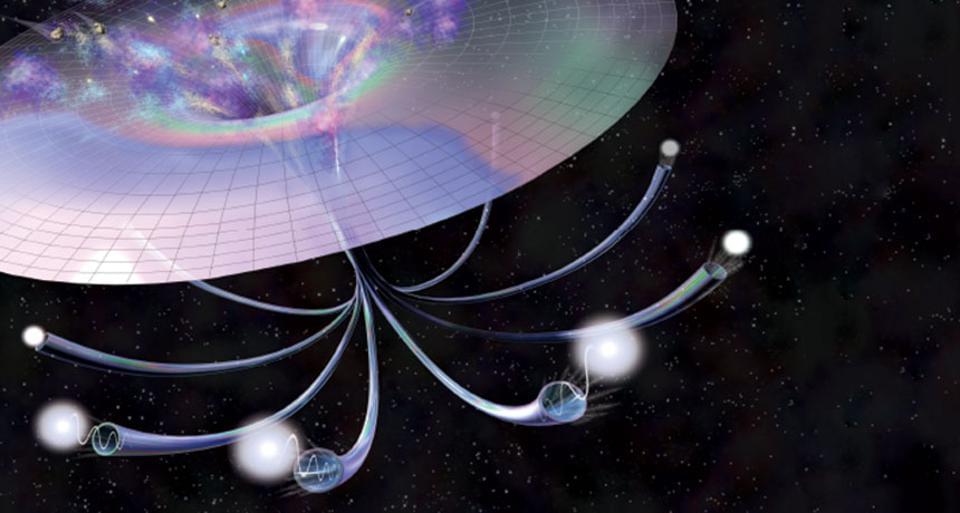
On the other side of a black hole is the other side. It’s not two dimensional like the artists renderings. The question is… what’s inside of it?


Experiments from Artemis I are headed to the moon an asteroid and beyond. See this mission overview which delves into the ten cubesat secondary payloads and the manikin experiments flying on Artemis I.
Worm-hole generators by the pound mass: https://greengregs.com/
For gardening in your Lunar habitat Galactic Gregs has teamed up with True Leaf Market to bring you a great selection of seed for your planting. Check it out: http://www.pntrac.com/t/TUJGRklGSkJGTU1IS0hCRkpIRk1K
Awesome deals for long term food supplies for those long missions to deep space (or prepping in case your spaceship crashes: See the Special Deals at My Patriot Supply: www.PrepWithGreg.com.
To try out our new course (and many others on math and science), go to https://brilliant.org/sabine. You can get started for free, and the first 200 will get 20% off the annual premium subscription.
Physicists have many theories for the beginning of our universe: A big bang, a big bounce, a black hole, a network, a collision of membranes, a gas of strings, and the list goes on. What does this mean? It means we don’t know how the universe began. And the reason isn’t just that we’re lacking data, the reason is that science is reaching its limits when we try to understand the initial condition of the entire universe.
💌 Sign up for my weekly science newsletter. It’s free! ➜ http://sabinehossenfelder.com/
👉 Support me on Patreon ➜ https://www.patreon.com/Sabine.
📖 My new book “Existential Physics” is now on sale ➜ http://existentialphysics.com/
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC1yNl2E66ZzKApQdRuTQ4tw/join.
The Poplawski paper about how the universe might have been born from a black hole is here: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10714-021-02790-7
00:00 Intro.
00:25 The Big Bang Theory.
03:47 Why So Many Other Theories?
04:53 The Problem With Cosmology.
07:30 The Importance of Simplicity.
10:57 Stories of Creation.
15:35 Sponsor Message
This isn’t what we see. What we observe is that more distant galaxies have a dimmer surface brightness than closer ones. The amount of dimming is proportional to the amount of redshift the galaxy has. You might think this proves that all those distant galaxies are speeding away from us, but it actually doesn’t. If those distant galaxies were speeding away, you’d have two dimming effects. The red shift and the ever-increasing distance. The Tolman test predicts that in a simple expanding universe, the surface brightness of galaxies should diminish proportional to both redshift and distance. We only see the effects of redshift.
This fact has led some to propose a static universe where light spontaneously loses energy over time. It’s the so-called tired light hypothesis, and it’s very popular among big bang opponents. If the universe is static and light is tired, then the Tolman test predicts exactly what we observe. Hence no big bang.
Back in 2014, Eric Lerner et al. published a paper making exactly this point. It caused a flurry of “Big Bang Dead!” articles in the popular media. The latest claims about Webb killing the big bang began with a popular article by the same Eric Lerner. So here we are. In fairness, back in 2014, the Hubble observations supported Lerner’s claim, and so do the latest Webb observations. But what Lerner conveniently omitted from his paper is that the Hubble and Webb observations also support the LCDM model.
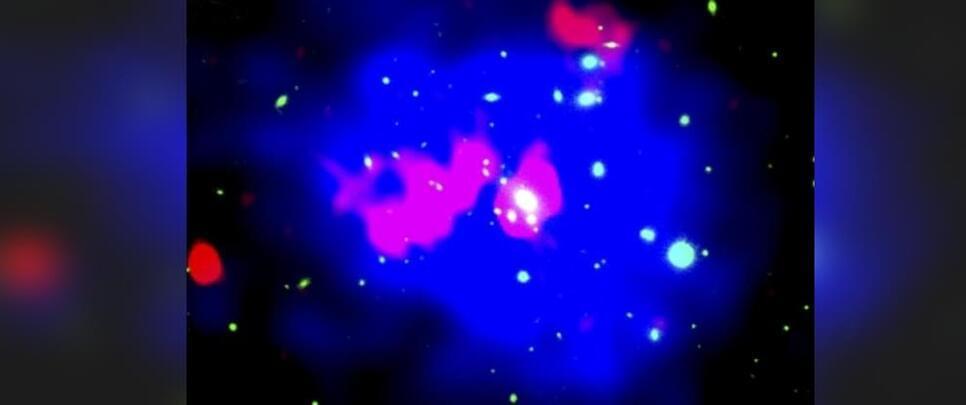

The oldest radio galaxy yet discovered is hidden in a cluster.
Astronomers claim to have found the oldest fossil radio galaxy yet discovered, hiding in a cluster. The brightest galaxy in the cluster erupted as a result of supermassive black hole activity, blowing massive bubbles of radio light into space, according to a report published by ScienceAlert.
“These newly discovered bubbles — known as radio lobes, or a radio galaxy — are the oldest of their kind we’ve ever seen,” claimed the astronomers’ team led by Surajit Paul and Savitribai Phule from Pune University in India.
A second team of astronomers led by Gopal Krishna of the University of Mumbai also discovered a pair of younger lobes that are linked to the same parent galaxy.
If we had been around and able to see into the heart of galaxy cluster Abell 980 around 260 million years ago, we may have seen something very spectacular indeed.
The brightest galaxy in the cluster erupted, the result of activity from its supermassive black hole, an event that would go on to blow massive bubbles emitting radio light out into space.
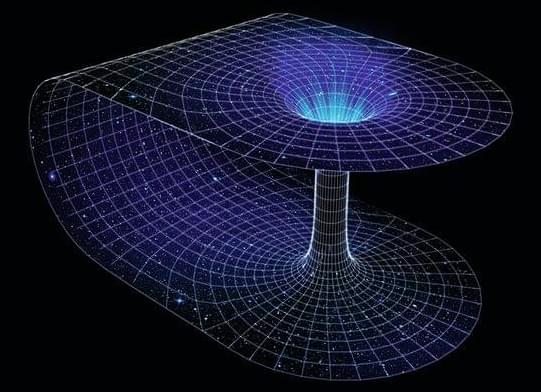
Are you curious?
Imagine two towns on two opposite sides of a mountain. People from these towns would probably have to travel all the way around the mountain to visit one another. But, if they wanted to get there faster, they could dig a tunnel straight through the mountain to create a shortcut. That’s the idea behind a wormhole.
A wormhole is like a tunnel between two distant points in our universe that cuts the travel time from one point to the other. Instead of traveling for many millions of years from one galaxy to another, under the right conditions, one could theoretically use a wormhole to cut the travel time down to hours or minutes.
You’ll often see wormholes in science fiction as a way to travel across the Galaxy.

Imagine two towns on two opposite sides of a mountain. People from these towns would probably have to travel all the way around the mountain to visit one another. But, if they wanted to get there faster, they could dig a tunnel straight through the mountain to create a shortcut. That’s the idea behind a wormhole.
A wormhole is like a tunnel between two distant points in our universe that cuts the travel time from one point to the other. Instead of traveling for many millions of years from one galaxy to another, under the right conditions, one could theoretically use a wormhole to cut the travel time down to hours or minutes.
Because wormholes represent shortcuts through space-time, they could even act like time machines. You might emerge from one end of a wormhole at a time earlier than when you entered its other end.
A sci fi documentary looking at a timelapse of future spacecraft. From the future of AI spaceships, Starship orbital refuelling, and space station worlds, to Mars colonization and in-space manufacturing.
Other topics include: SpaceX and the launch of their fleet of Starships — waiting in parking orbit around Earth, ready for the launch window to open to Mars. NASA and the mission of landing on the Martian Moon Phobos. Advances in spacecraft technology for protecting humans during multi-year interstellar journeys.
While the year 2100 and beyond, brings wormhole exploration, artificial intelligence based planets, and the possible need for a stellar engine — to protect the solar system.
Main narration by: Alexander Masters (www.alexander-masters.com)
Starship Artwork – used with permission and licensed from:
Erc X: https://twitter.com/ErcXspace.
Caspar Stanley: https://twitter.com/Caspar_Stanley.
Alex Svan: https://twitter.com/AlexSvanArt.
Additional footage sourced from: SpaceX, NASA, ESO, Ken Crawford, Nick Risinger, Northrop Grumman, SpinLaunch, Redwire Space.