Ever since physicist Ernest Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus in 1911, studying its structure and behavior has remained a challenging task. More than a century later, even with today’s high-tech tools for researching nuclear physics, mysteries of the universe abound.
Relying on leading-edge germanium detectors developed by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the scientific community pursues elusive nuclear processes to unlock persistent mysteries. Answers to questions they hope to resolve hold the potential to redefine the universe itself. Why does the universe contain more matter than antimatter? Can a particle be both a matter and antimatter version of itself? Is there a mismatch between what the Big Bang produced and what the Standard Model of particle physics suggests?
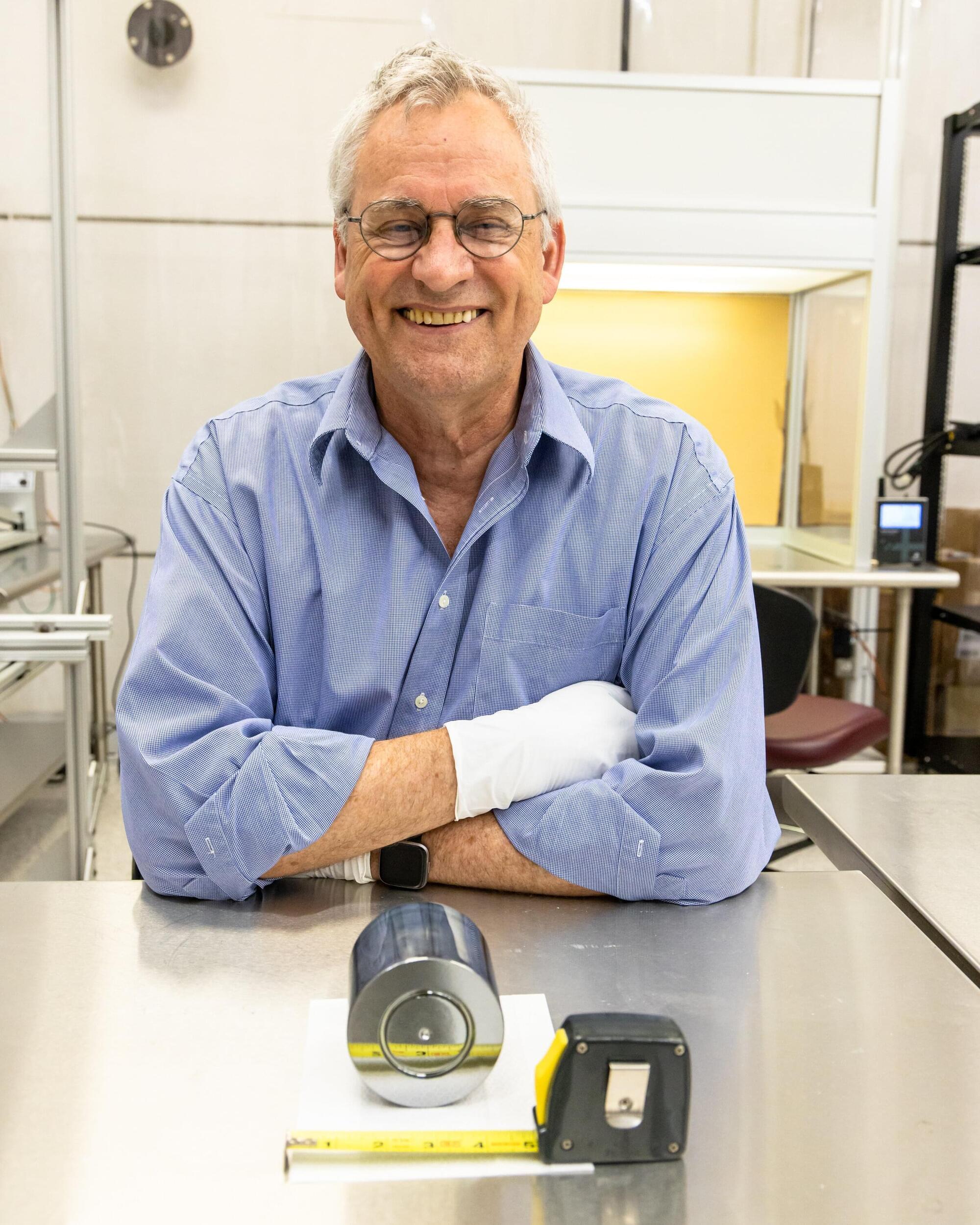
Long at the vanguard of international efforts to answer questions like these, ORNL’s contributions remain strong today. David Radford, head of the lab’s Fundamental Nuclear and Particle Physics section, is an internationally renowned expert in the field who has had an indelible impact on the development of germanium detectors. Vital experimentation tools at the forefront of fundamental physics research, germanium detectors are large, single crystals of germanium—a metallic element—used to detect radiation and enable incredibly precise energy measurements.