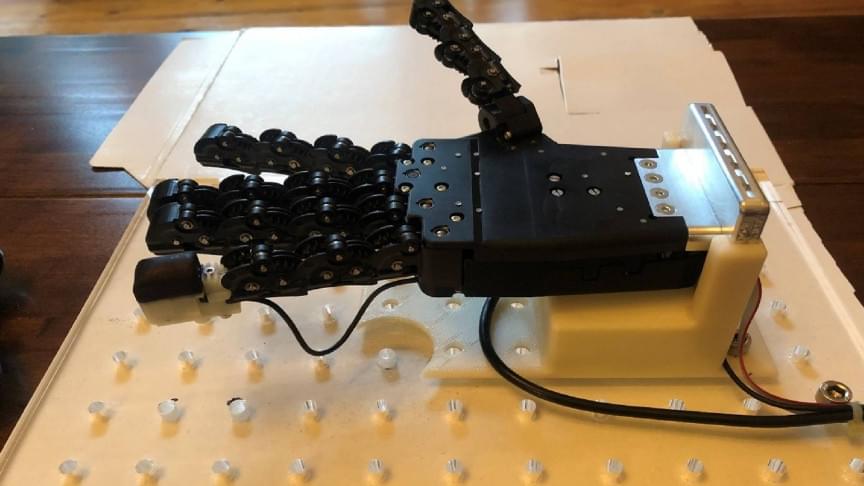
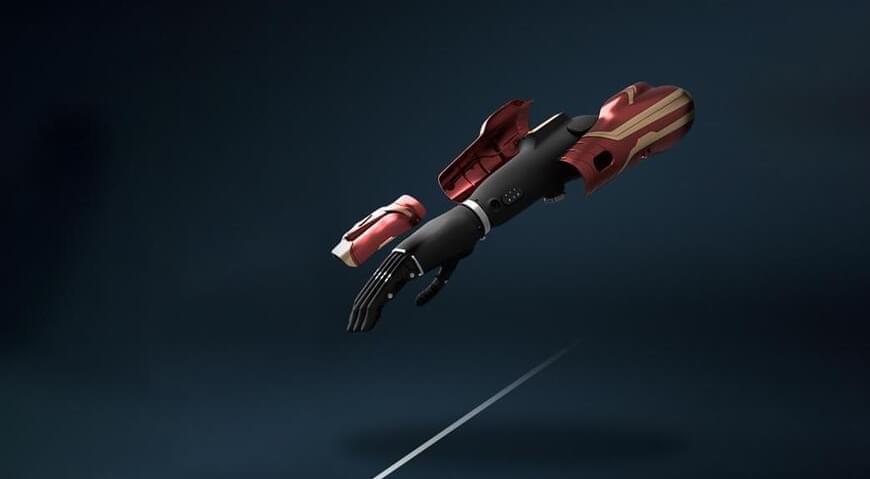
The Force was strong in him. One of Enzo Romero’s favorite activities is playing the guitar, which he effortlessly does with his bright blue hand. Initially, it used to hurt, as he used his handless right arm to press down on chords. But now, with fingers on the end, he can play music painlessly.
Star Wars: Episode V The Empire Strikes Back, marketed as simply The Empire Strikes Back, is a 1980 film directed by Irvin Kershner and written by Leigh Brackett and Lawrence Kasdan from a story by George Lucas. It is the second part of the Star Wars original trilogy.
The film concerns the continuing struggles of the Rebel Alliance against the Galactic Empire. During the film, Han Solo, Chewbacca, and Princess Leia Organa are being pursued across space by Darth Vader and his elite forces. Meanwhile, Luke Skywalker begins his major Jedi training with Yoda, after an instruction from Obi-Wan Kenobi’s spirit. In an emotional and near-fatal confrontation with Vader, Luke is presented with a horrific revelation and must face his destiny.
Though controversial upon release, the film has proved to be the most popular film in the series among fans and critics and is now widely regarded as one of the best sequel films of all time, as well as one of the greatest films of all time. It was re-released with changes in 1997 and on DVD in 2004. The film was re-released on Blu-ray format in September of 2011. A radio adaptation was broadcast on National Public Radio in the U.S.A. in 1983. The film was selected in 2010 to be preserved by the Library of Congress as part of its National Film Registry.