Sable co-created the story with artist Kristian Donaldson (Unthinkable, The Guild) and Mey Rude, a transgender woman who served as a consulting editor on the project. Sable took some time to talk to SYFY WIRE about biohacking, transhumanism, and how science fiction often predicts the future.
The Dark, by screenwriter and playwright Mark Sable (Unthinkable, Godkillers), is a graphic novel about a world plunged into chaos when a biotech virus pulls everything offline. The plot twists around government conspiracies, techno warfare, biohacking, and the unlikely pair out to stop it before another world war breaks loose. To make it all the scarier, Sable bases his fiction on fact. As a futurist who has consulted with think tanks and The Art of Future Warfare Project, he is well versed in techno warfare scenarios.
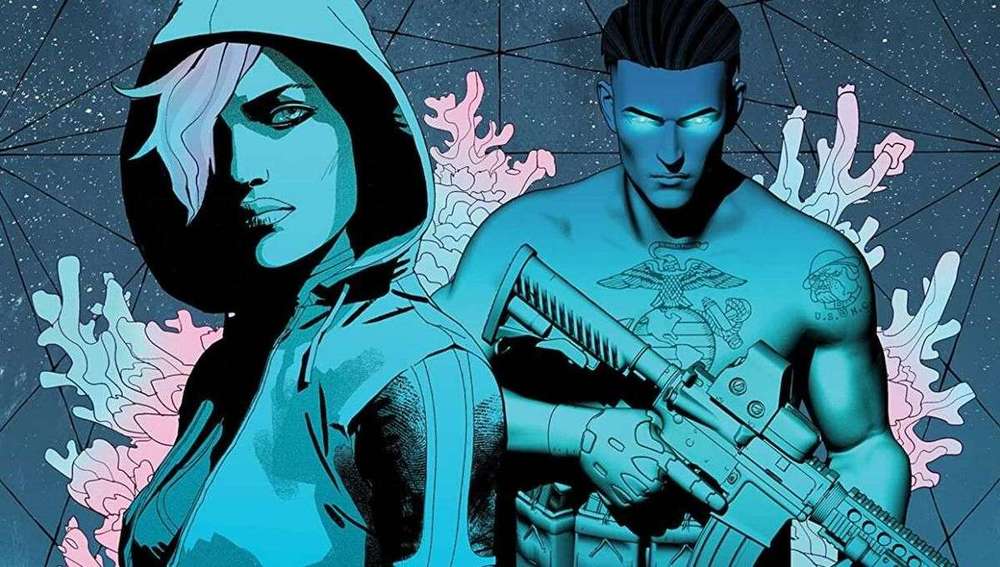
The Dark begins in 2035 and follows Master Sergeant Robert Carter, a N.E.O. (Networked Exoskeleton Operator) Marine whose power armor links him to the world’s technology, and whose implants mentally connect him to his unit. He feels what they feel, which proves torturous when his unit is attacked. The Dark takes on a double meaning as the experience leaves him both physically and technologically blind as the world’s tech crashes.
His world changes when he is sent after Camille — a skilled biohacker and analyst for NSA’s Bumble Hive — who is on a mission to expose the government’s use of bio-hacked surveillance. But she’s also attempting to recode herself in the process. You see, Camille is a trans woman and has discovered a way to change her gender at the molecular level. Camille’s quest to expose the truth and Carter’s pursuit of that very truth throw them together in a race against time to save the world.