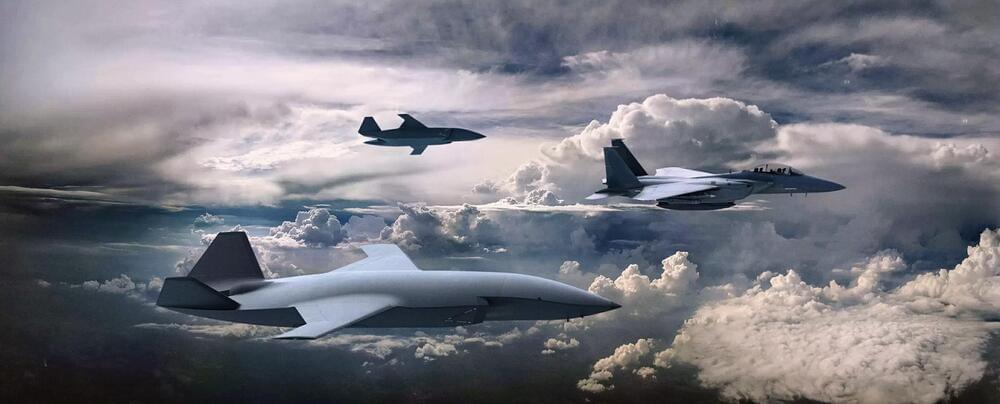
Chief of Staff Gen. David Allvin also did not explicitly say the Air Force would build its Next Generation Air Dominance fighter amid tight budgets.
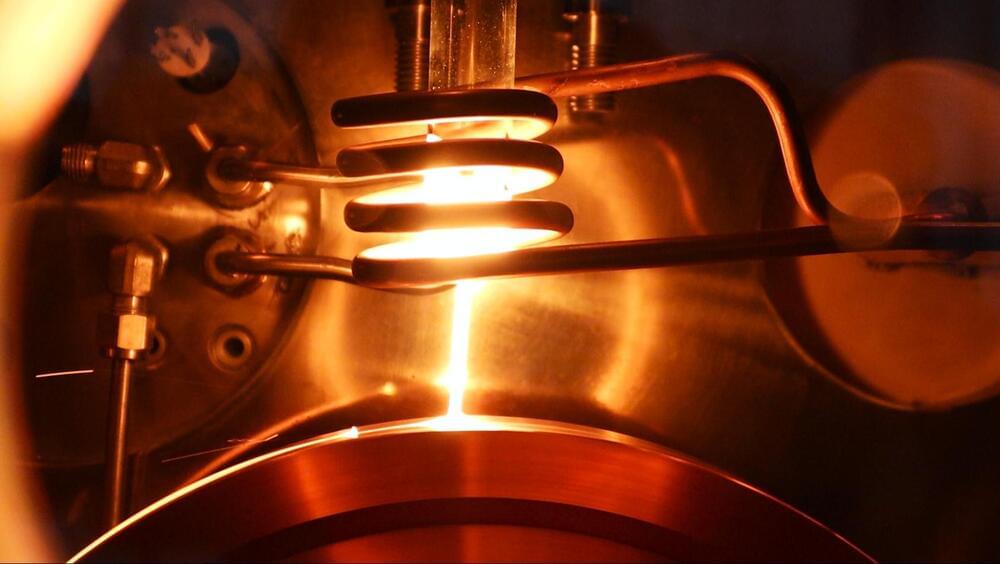



As some entities identify new (or at least overlooked) sources to meet the growing demand for rare earth materials, others are looking toward new tools. UK deep-tech company Materials Nexus announced on Tuesday that it has designed a new rare-earth-free permanent magnet with the help of its AI platform. It says the AI-driven discovery and development process was 200 times faster than the resource-intensive manual route, bringing new hope to an electrifying world with a growing appetite for powerful magnets.
With the world moving away from internal combustion engines and gradually embracing electric mobility, the demand for compact, high-power motors is rapidly rising. By far the most popular option in the automotive industry right now is the permanent magnet motor, which powers upward of 80% of modern electric vehicles.
Materials Nexus estimates that demand for permanent magnets will grow tenfold by 2030, in the EV industry alone. And it’s not just electric cars and trucks, either. Permanent magnet motors are in demand for many applications, including robotics, drones, wind turbines and HVAC equipment.

Drone wars, what haven’t we seen. If we look at active wars and mark those drones gen1, do we have in army hangars strategic gen 3 or 4 drones? what do they look like, how does that c&c works?
Top Admiral: “I want to turn the Taiwan Strait into an unmanned hellscape using a number of classified capabilities.”
Demonstration of RAF jackal drone firing missiles.
This footage shows a demonstration where a new RAF ‘Jackal’ drone fires missile at a target. The missile can be seen launching out the new drone as it flies above the ground.
The JACKAL drone capability has been designed and developed by experts from UK-based Flyby Technology, with Turkish partners FlyBVLOS Technology and Maxwell Innovations providing design engineering and prototyping expertise, to fill a recently discovered gap in modern combat operations.
As a Vertical Take Off and Landing (VTOL) platform, JACKAL is designed to satisfy a number of roles, including Battlefield Air Interdiction, Close Air Support, engaging helicopters in flight and killing tanks, to denying the use of runways and roads.
The trial — sponsored by the Rapid Capabilities Office (RCO) of the Royal Air Force – involved teams from Flyby and the technology giant Thales which also manufactures the LMM.
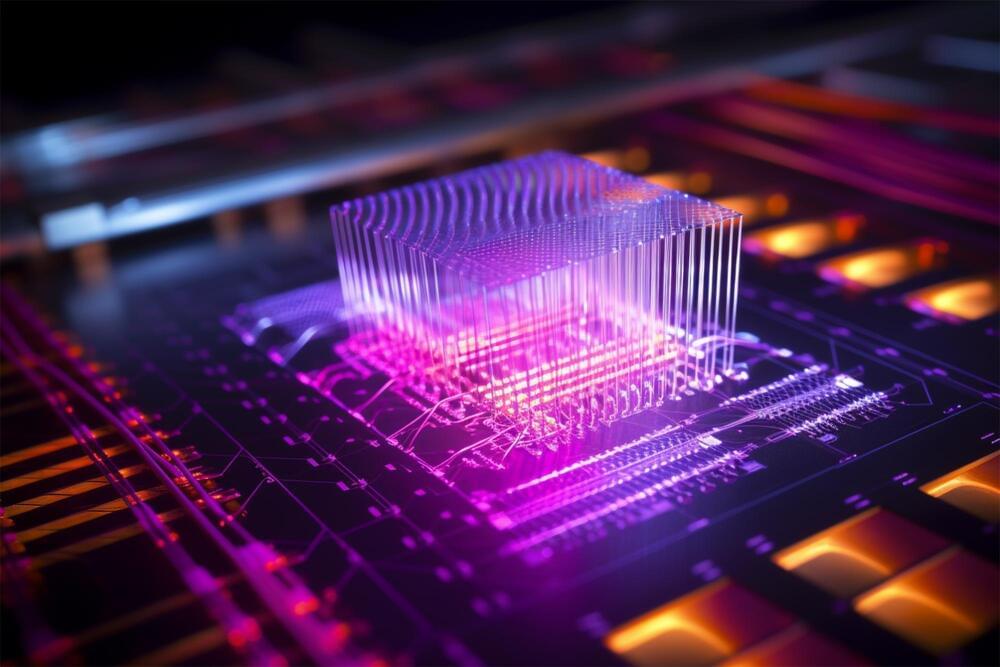
Researchers from the Photonics Research Laboratory (PRL)-iTEAM at the Universitat Politècnica de València, in collaboration with iPRONICS, have developed a groundbreaking photonic chip. This chip is the world’s first to be universal, programmable, and multifunctional, making it a significant advancement for the telecommunications industry, data centers, and AI computing infrastructures. It is poised to enhance a variety of applications including 5G communications, quantum computing, data centers, artificial intelligence, satellites, drones, and autonomous vehicles.
The development of this revolutionary chip is the main result of the European project UMWP-Chip, led by researcher José Capmany and funded by an ERC Advanced Grant from the European Research Council. The work has been published in the Nature Communications journal.
2023.
Drones combining the bodies of taxidermy pheasants and pigeons, with flapping wing mechanisms closely mimic living birds.
Researchers at New Mexico Tech have designed these lifelike drones to hover and glide but further development is required to implement a broader range of avian motions. These flapping-wing drones could help study flocks of birds or enable military spy mission.
–
Learn more ➤ https://www.newscientist.com/article/.…
“Batteries are the crux of many of the most important emerging technologies in both the civilian world and, important to our profession, on the battlefield,” said United States Military Academy Cadet Michael Williams. “More energy dense batteries allow, for instance, greater range on electric vehicles, longer battery lives for radios, and longer flight times for drones. Our work helps make manufacturing these batteries easier.”
Cadets Michael Williams, Avery Patel, and Nancy Astable have been working on a long-term project with their faculty mentors Dr. Enoch Nagelli, Dr. Simuck Yuk, and Army Col. John Burpo to develop new ways to maximize energy storage and generation for the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command’s Armaments Center. In collaboration with Cornell University, the team at USMA’s Department of Chemistry and Life Sciences is pursuing innovative approaches to increasing the quality and use of batteries and fuel cells.
The value of conducting scientific research to solve real-world problems is clear to the cadets.

Summary: Researchers developed a drone that flies autonomously using neuromorphic image processing, mimicking animal brains. This method significantly improves data processing speed and energy efficiency compared to traditional GPUs.
The study highlights the potential for tiny, agile drones for various applications. The neuromorphic approach allows the drone to process data up to 64 times faster while consuming three times less energy.
Championing an aerospace renaissance — elizabeth reynolds, managing director, US, starburst aerospace.
Elizabeth Reynolds is Managing Director, US of Starburst Aerospace (https://starburst.aero/), a global Aerospace and Defense (A\&D) startup accelerator and strategic advisory practice championing today’s aerospace renaissance, aligning early-stage technology innovators with government and commercial stakeholders and investors to modernize infrastructure in space, transportation, communications, and intelligence.
Elizabeth’s team works alongside hundreds of technology startups developing new aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, drones, sensors, autonomy, robotics, and much more.
Elizabeth brings 15 years of experience in deep tech entrepreneurship, growth, business operations, and strategy to the team. Prior to joining Starburst, she served as an executive for biotech, medtech, mobility, and interactive media companies, from founding through IPO. She is also an advisor to a number of startups and nonprofits supporting STEM education.
Starburst has offices in Los Angeles, Washington, D.C., Paris, Munich, Singapore, Seoul, Tel Aviv, and Madrid, has grown into a global team of 70 dedicated team members with a portfolio of 140+ startups, 20 accelerator programs, and 2 active venture funds which strive to provide enabling growth services for deep tech leaders disrupting the industry and working towards a safer, greener, and more connected world.
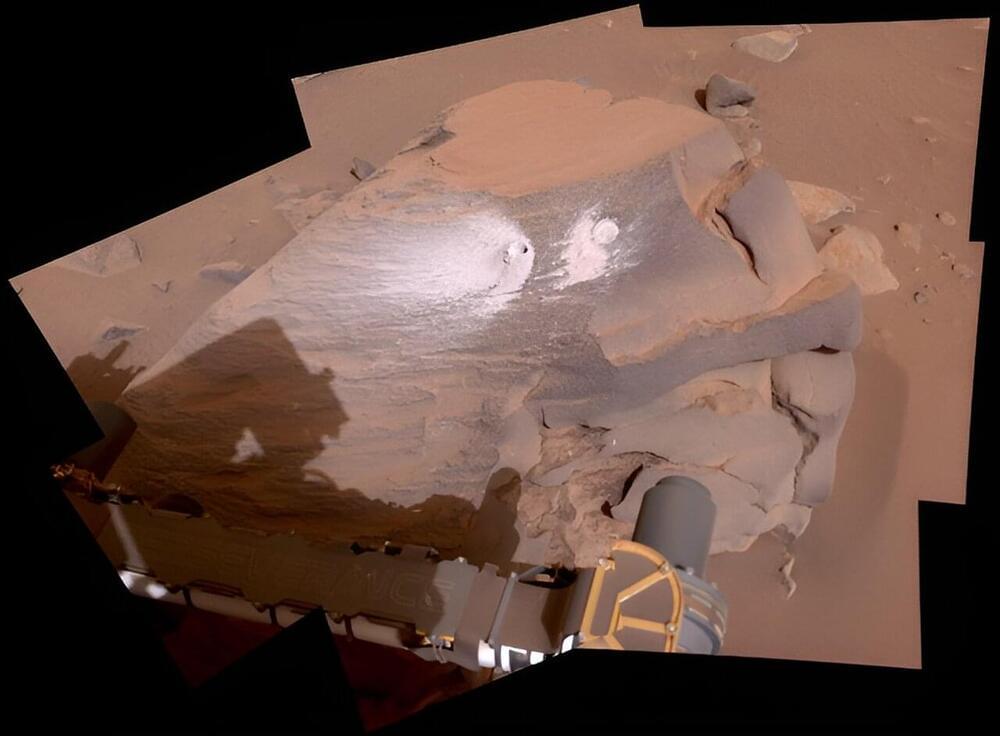

NASA recently asked the scientific community to help come up with innovative ideas for ways to carry out its Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission. This was in response to a report by an independent board that deemed that its US$11 billion (£8.7 billion) price tag was too expensive and its 2040 timeline too far in the future.
In brief, the ambitious plan was to collect rock samples cached inside containers by NASA’s Perseverance rover and deliver them to laboratories on Earth. Perseverance has been exploring Mars’ Jezero Crater, thought to have once hosted an ancient lake, since 2021. The mission would deliver the samples by sending a lander that carries a rocket (NASA’s Sample Retrieval Lander) down to the surface of Mars.
Perseverance would then deliver the cached rock samples to the lander, with small drone helicopters delivered on the lander as a back up. Perseverance’s samples would then be launched into Mars’ orbit using the lander’s rocket. A spacecraft already in Martian orbit, the Earth Return Orbiter, would then intercept these samples and deliver them to Earth.