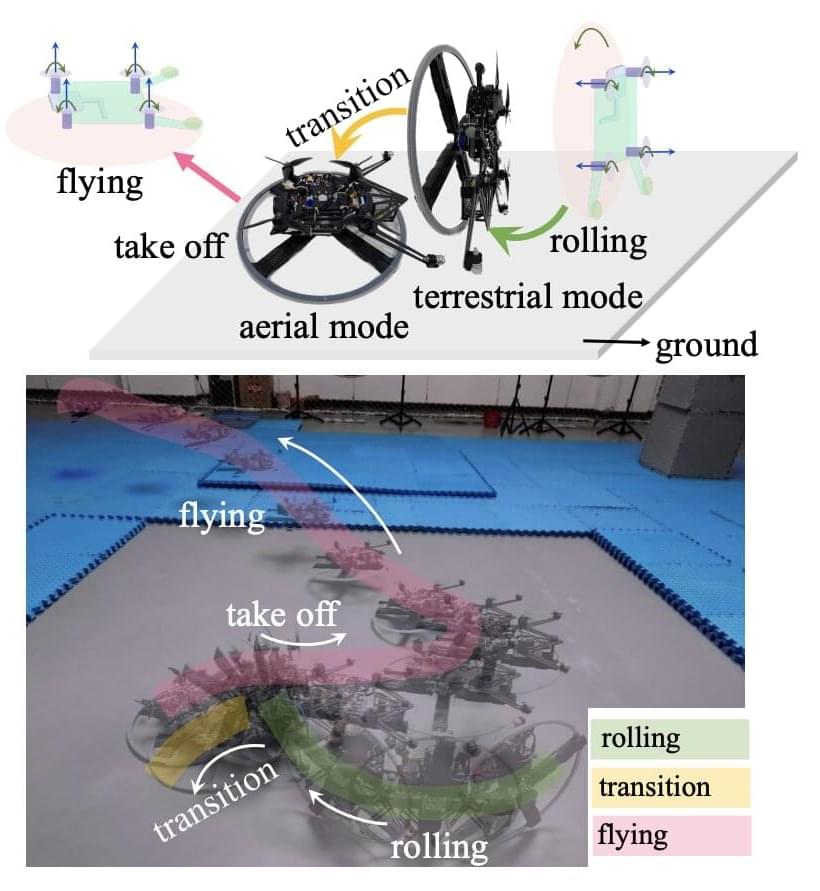
As per the company, traditional rovers may not be able to traverse everywhere and perform tasks like their drone-like hopper.
For decades, Earth’s natural satellite has been one of the most popular destinations for space exploration. The upcoming Artemis missions, along with the excitement on establishing a human settlement on the Moon, have collectively boosted the lunar economy market substantially in recent years.
Several startups have been preparing to offer their technological solutions to gain a better understanding of the valuable resources available and provide services to future astronauts.