The international study surveys 23,000 higher education students about using and perceiving popular AI tools.


Tags; #science #neuroscience #happiness #happiness #neurodegenerativediseases #disease #health #mentalhealth #sleep #neuroscientist #disease #education #success.
******************
About me:
I am Shambhu Yadav, Ph.D., a research scientist at Harvard Medical School (Boston, MA, USA). I also work (for fun) as a Science Journalist, editor, and presenter on a YouTube channel. Science Communication is my passion.
***********************************************************
Disclaimer 1: The video content is for educational and informational purposes only, not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your physician or qualified healthcare provider regarding any medical condition. Do not disregard or delay seeking professional medical advice based on information from this video. Any reliance on the information provided is at your own risk.
Disclaimer 2: The Diary Of A Scientist (DOAS) channel does not promote or encourage any unusual activities, and all content provided by this channel is meant for EDUCATIONAL purposes only.
*Credits and thanks**
The video was recorded using iPhone and edited using Adobe Premiere Pro: a timeline-based and non-linear video editing software.
Music source: Epidemic sound.

More than 800 researchers, policy makers and government officials from around the world gathered in Paris this week to attend the official launch of the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology (IYQ). Held at the headquarters of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO), the two-day event included contributions from four Nobel prize-winning physicists – Alain Aspect, Serge Haroche, Anne l’Huillier and William Phillips.
Opening remarks came from Cephas Adjej Mensah, a research director in the Ghanaian government, which last year submitted the draft resolution to the United Nations for 2025 to be proclaimed as the IYQ. “Let us commit to making quantum science accessible to all,” Mensah declared, reminding delegates that the IYQ is intended to be a global initiative, spreading the benefits of quantum equitably around the world. “We can unleash the power of quantum science and technology to make an equitable and prosperous future for all.”
The keynote address was given by l’Huillier, a quantum physicist at Lund University in Sweden, who shared the 2023 Nobel Prize for Physics with Pierre Agostini and Ferenc Krausz for their work on attosecond pulses. “Quantum mechanics has been extremely successful,” she said, explaining how it was invented 100 years ago by Werner Heisenberg on the island of Helgoland. “It has led to new science and new technology – and it’s just the beginning.”
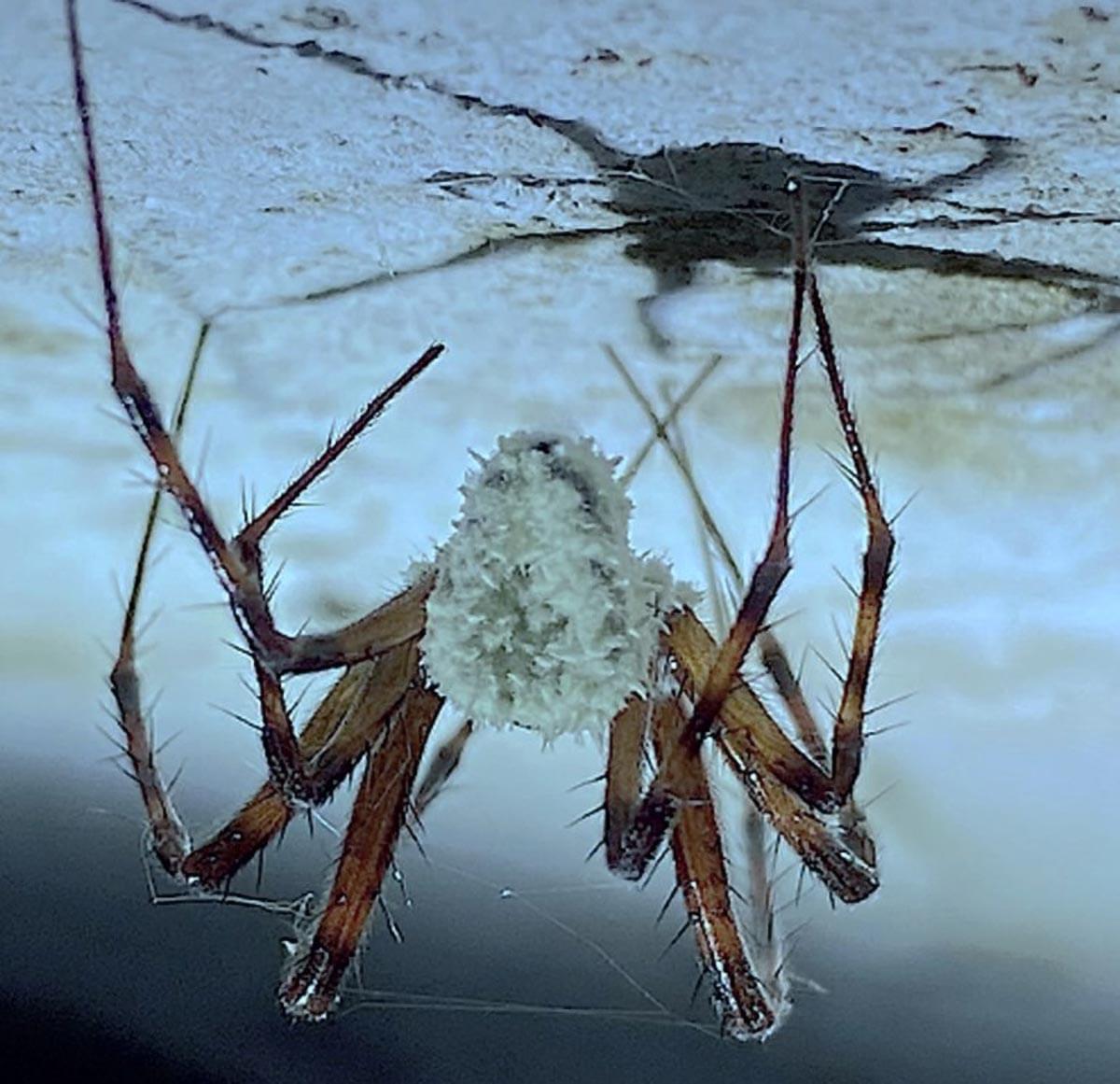


Scientists identified a new fungus, Gibellula attenboroughii, infecting cave spiders in Ireland. The fungus manipulates spider behavior, resembling “zombie-ant fungi.”
Dr. Harry Evans, Emeritus Fellow at CAB International, led a team of scientists—including experts from the Natural History Museum of Denmark and the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew—in a study to identify a fungus discovered on a spider during the filming of the BBC Winterwatch series in Northern Ireland.
Through morphological and molecular analysis, the researchers confirmed the fungus as a previously unknown species.
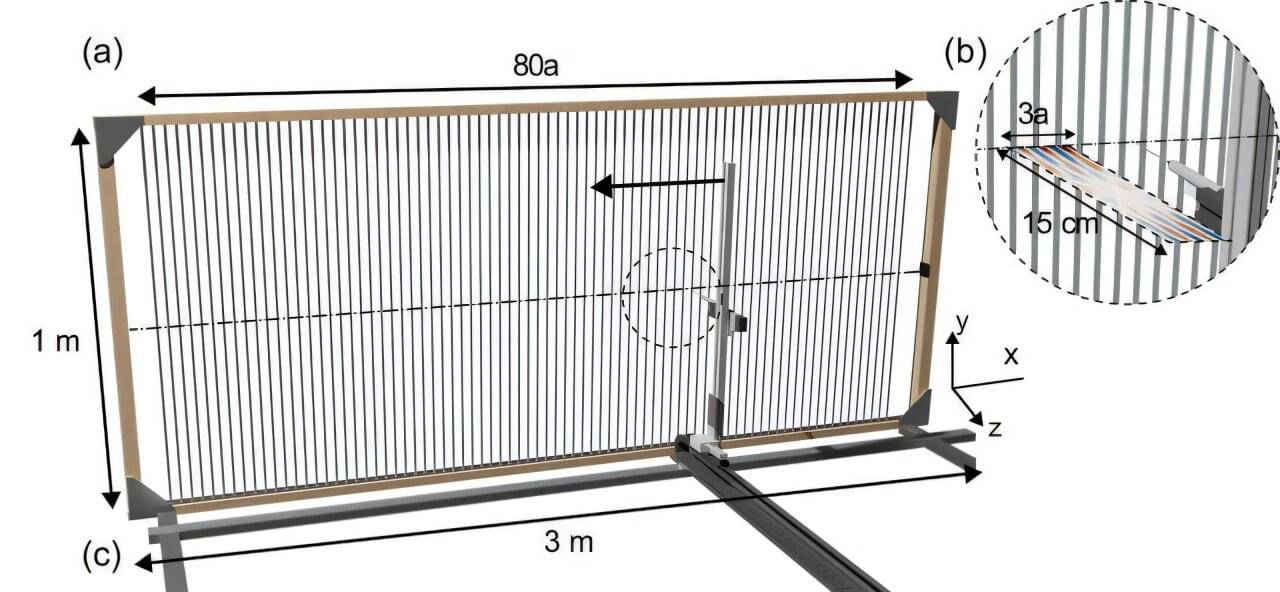
So-called Rayleigh–Bloch waves can release an enormous amount of energy that can damage technical systems under certain circumstances. They only exist below a precisely defined cut-off frequency; above this, they disappear abruptly. Strangely enough, however, there are isolated high frequencies at which they can also be detected.
Mathematicians from the Universities of Augsburg and Adelaide have recently proposed an explanation for this puzzling phenomenon. Together with researchers from the University of Exeter, they have now been able to prove experimentally that their theory is indeed correct. The study has just been published in the journal Communications Physics.
Suppose you had a gigantic barbecue grill that could easily accommodate several hundreds of sausages. Then, you could not only use it to invite your children’s entire school to a barbecue. The numerous stainless steel struts aligned parallel to each other are also ideal for generating Rayleigh–Bloch waves.
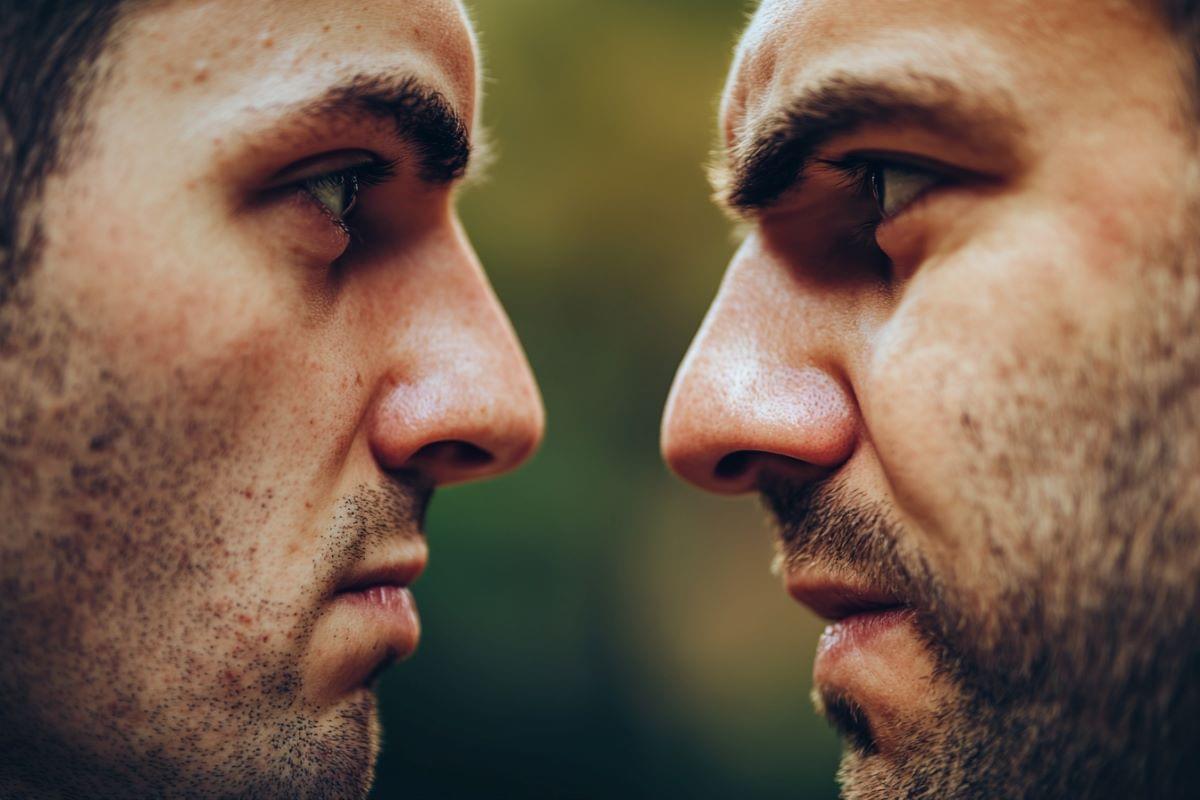

Summry: New research reveals that dopamine plays a crucial role in teaching young male mice to fight, with the chemical’s influence diminishing as they gain experience. In novice fighters, boosting dopamine increased aggression, while blocking it stopped them from fighting.
However, experienced fighters showed no changes in behavior regardless of dopamine manipulation, highlighting the role of experience in shaping aggression. The study identifies the lateral septum as a key brain region for “aggression learning” in males, but no similar effect was observed in females.
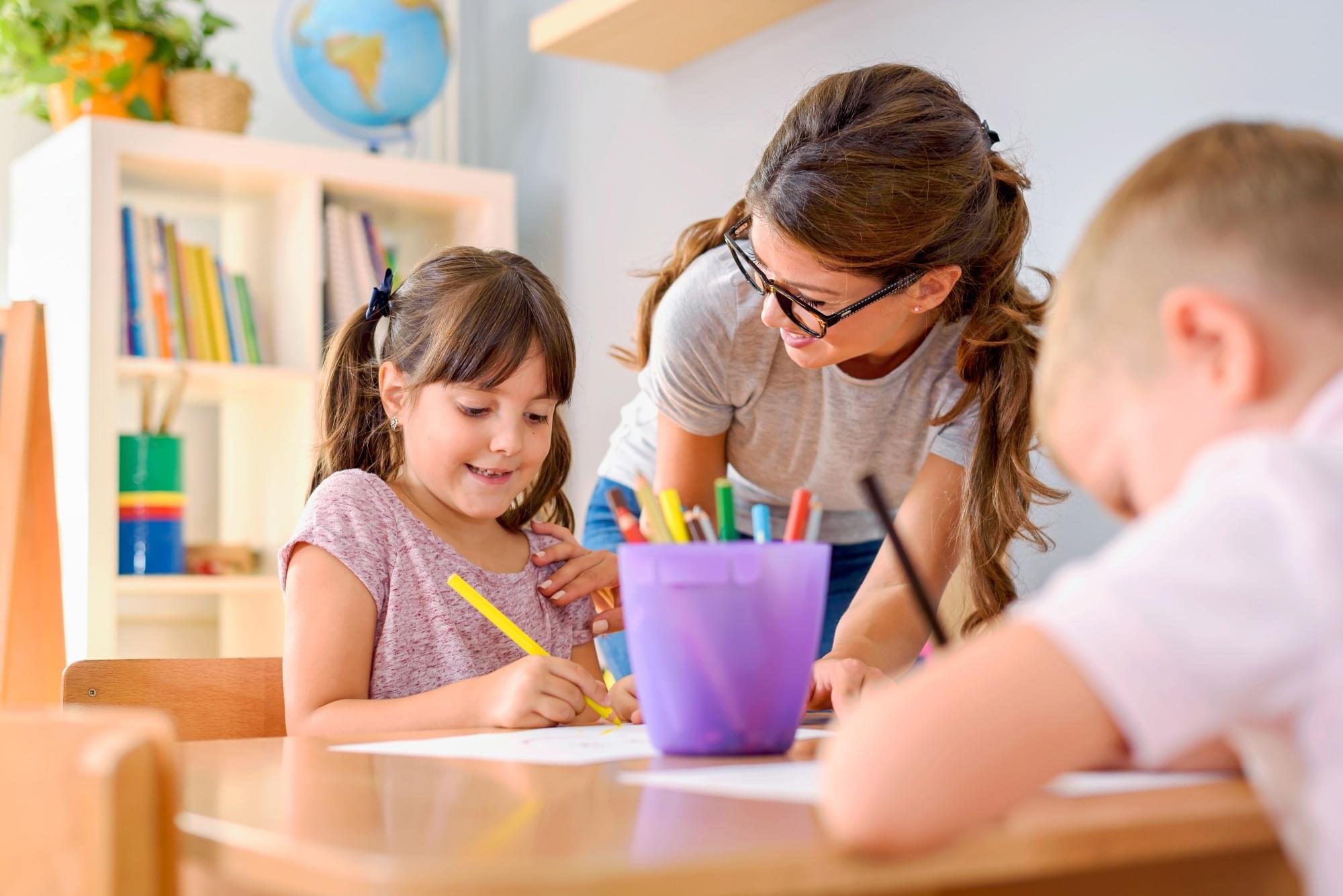

Teaching healthy lifestyle behaviors to very young children is foundational to their future habits. Previous evidence suggests that philosophical thinking (PT) can help children develop moral values, cognitive skills, and decision-making abilities.
A recent study published in BMC Public Health explores the role of PT in assisting preschoolers to adopt healthy lifestyle behaviors. Some of these habits include being physically active, eating healthy, washing hands properly, having respect for one’s body, being aware of one’s needs, feelings, abilities, and responsibilities, getting sufficient sleep, and sharing one’s thoughts with others.
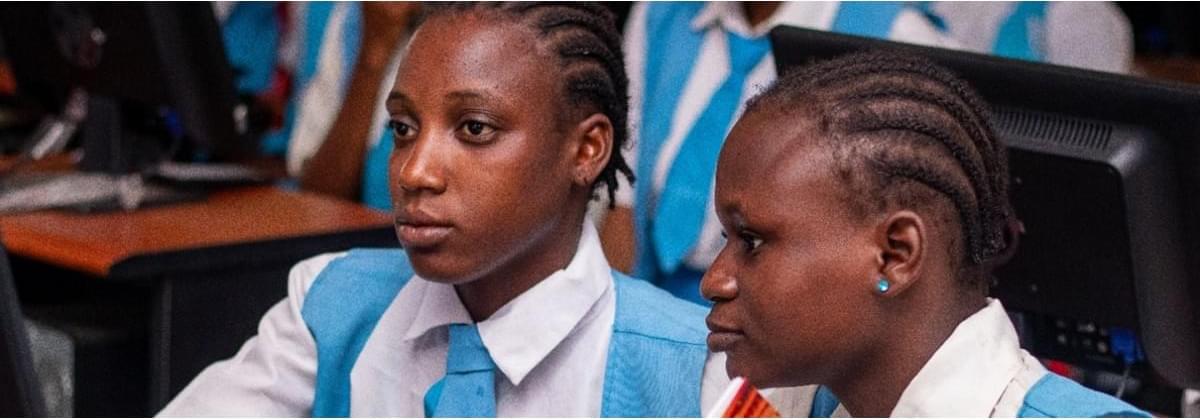

Students participate in an AI after-school program in Edo, Nigeria. Copyright: SmartEdge/World Bank
“AI helps us to learn, it can serve as a tutor, it can be anything you want it to be, depending on the prompt you write,” says Omorogbe Uyiosa, known as “Uyi” by his friends, a student from the Edo Boys High School, in Benin City, Nigeria. His school was one of the beneficiaries of a pilot that used generative artificial intelligence (AI) to support learning through an after-school program.
A few months ago, we wrote a blog with some of the lessons from the implementation of this innovative program, including a video with voices from beneficiaries, such as Uyi. Back then, we promised that, if you stayed tuned, we would get back with the results of the pilot, which included an impact evaluation. So here we are with three primary findings from the pilot!
Biopunk androids replicants.
What happens when humans begin combining biology with technology, harnessing the power to recode life itself.
What does the future of biotechnology and genetic engineering look like? How will humans program biology to create organ farm technology and bio-robots. And what happens when companies begin investing in advanced bio-printing, artificial wombs, and cybernetic prosthetic limbs.
Other topic include: bioengineered food and farming, bio-printing in space, new age living bioarchitecture (eco concrete inspired by coral reefs), bioengineered bioluminescence, cyberpunks and biopunks who experiment underground — creating new age food and pets, the future of bionics, corporations owning bionic limbs, the multi-trillion dollar industry of bio-robots, and bioengineered humans with super powers (Neo-Humans).
As well as the future of biomedical engineering, biochemistry, and biodiversity.