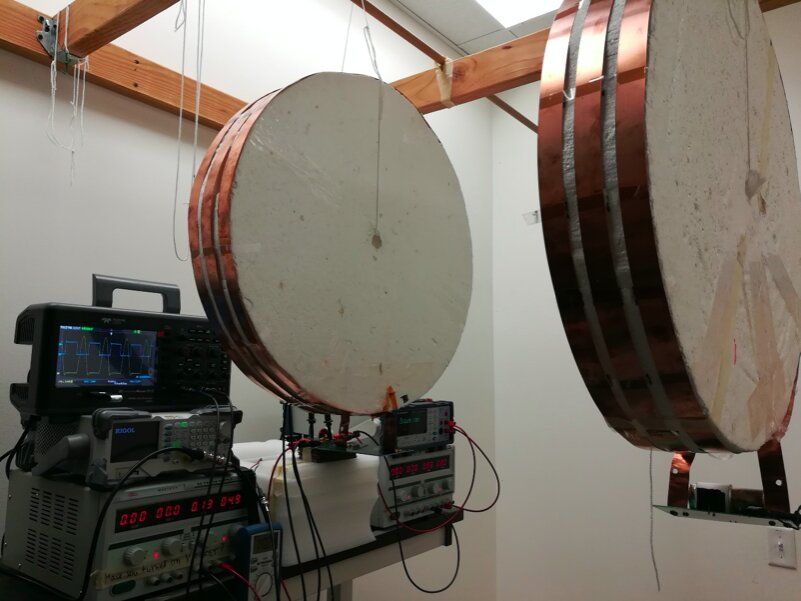
Current methods for charging electronic devices via wireless technology only work if the overall system parameters are set up to match a specific transfer distance. As a result, these methods are limited to stationary power transfer applications, which means that a device that is receiving power needs to maintain a specific distance from the source supplying it in order for the power transfer to be successful.
Researchers at Stanford University have recently developed a new technique that could enable more efficient wireless power transfer regardless of the distance between a device and its power source. Their paper, published in Nature Electronics, could help to overcome some of the current limitations of existing tools for the wireless charging of elecronic devices.
“The main purpose of our study was to overcome the barrier to dynamic wireless charging,” Sid Assawaworrarit, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “Our idea is based on parity-time symmetry (PT symmetry), which concerns systems with balanced gain and loss.”