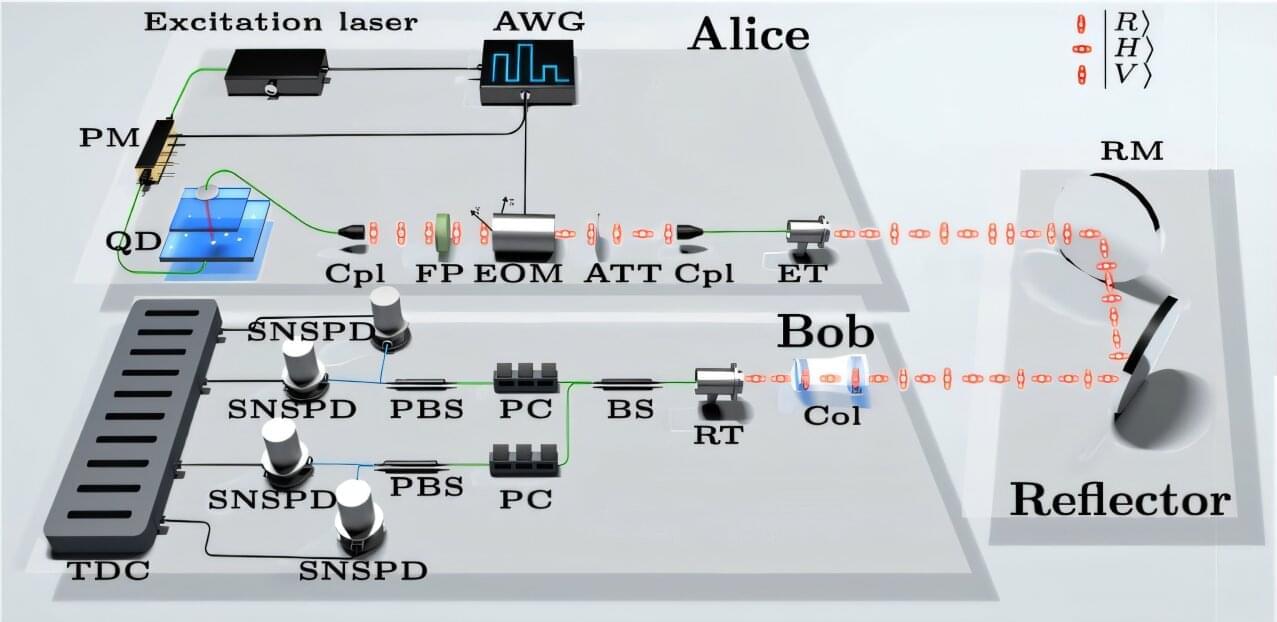
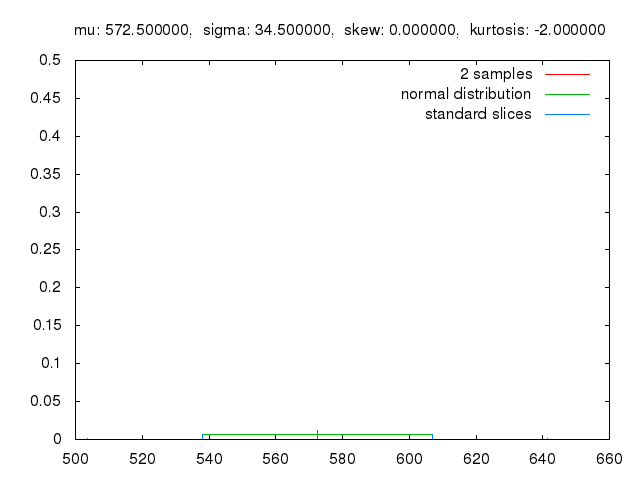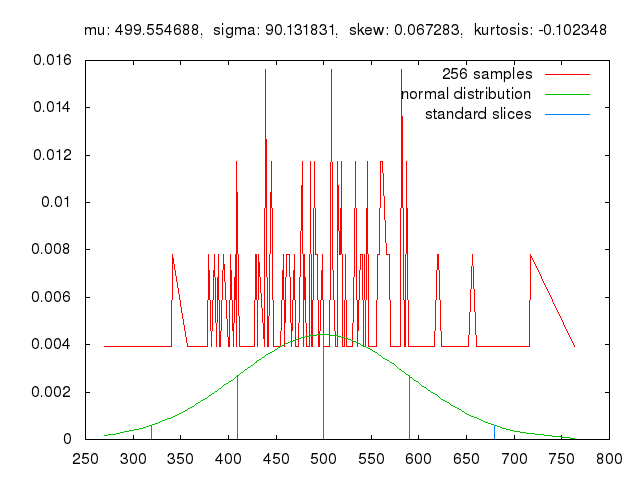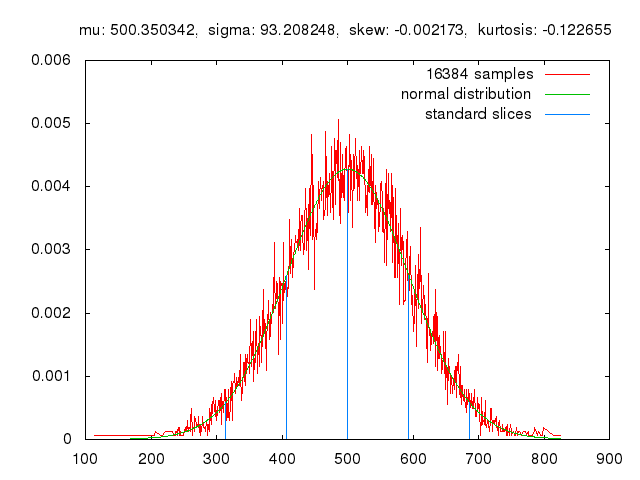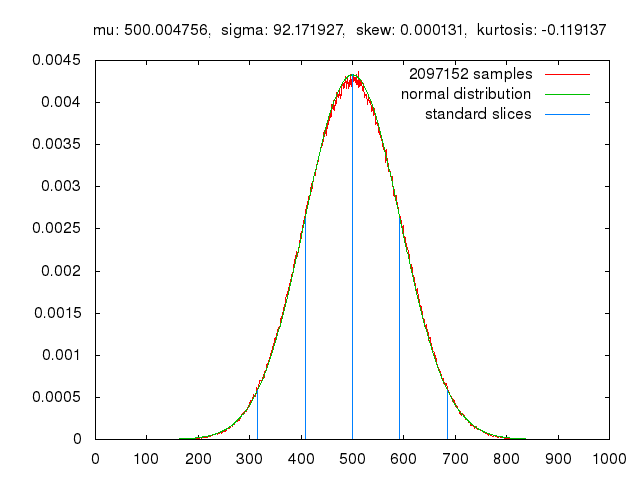Quantum key distribution (QKD), a cryptographic technique rooted in quantum physics principles, has shown significant potential for enhancing the security of communications. This technique enables the transmission of encryption keys using quantum states of photons or other particles, which cannot be copied or measured without altering them, making it significantly harder for malicious parties to intercept conversations between two parties while avoiding detection.
As true single-photon sources (SPS) are difficult to produce, most QKD systems developed to date rely on attenuated light sources that mimic single photons, such as low-intensity laser pulses. As these laser pulses can also contain no photons or more than one photon, only approximately 37% of pulses employed by the systems can be used to generate secure keys.
Researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) were recently able to overcome this limitation of previously proposed QKD systems, using a true SPS (i.e., a system that can emit only one photon on demand). Their newly proposed QKD system, outlined in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, was found to outperform techniques introduced in the past, achieving a substantially higher secure key rate (SKR).