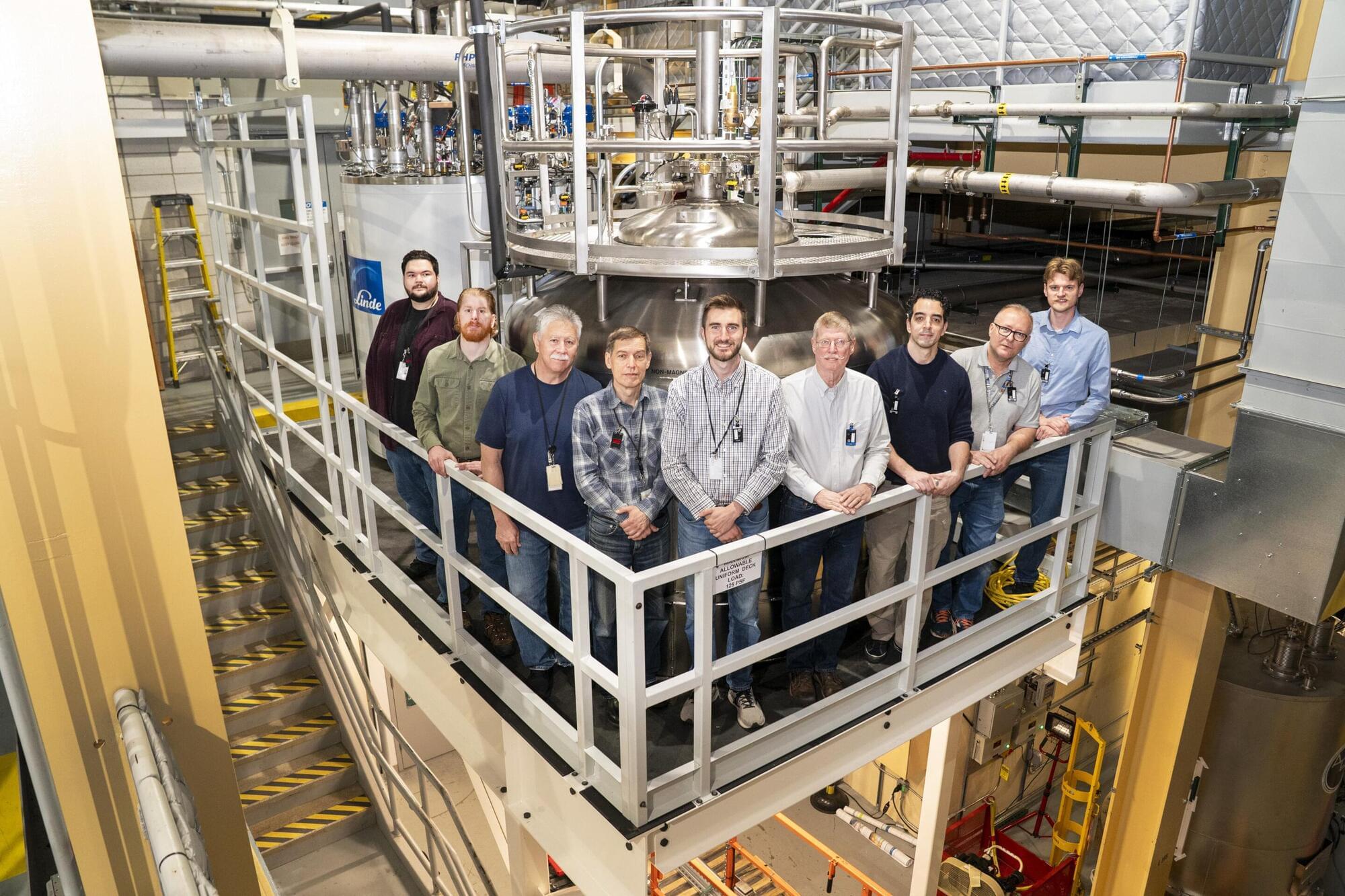
Running a synchrotron light source is a massive team effort that brings hundreds of highly skilled and specialized professionals together. The radiofrequency (RF) group at the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science user facility at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory, plays an integral role in synchrotron operations. The work they do, often behind the scenes, ensures that the electron beam that enables cutting-edge science at NSLS-II remains bright, powerful, and stable.
The electrons that circle through NSLS-II’s nearly half-mile-long storage ring lose energy as they produce X-rays, which scientists use to perform a variety of experiments at the facility. To keep the beam moving steadily, the electrons pass through hollow RF cavities. These cavities, tuned to a precise frequency, restore the electrons’ energy each time they pass through.
When cooled to cryogenic temperatures, the material that the cavities are comprised of, niobium, takes on superconducting properties that nearly eliminate electrical resistance and drastically improve energy efficiency and beam stability. The design also allows unwanted high-frequency oscillations to be safely damped, ensuring a stable, high-intensity X-ray beam.