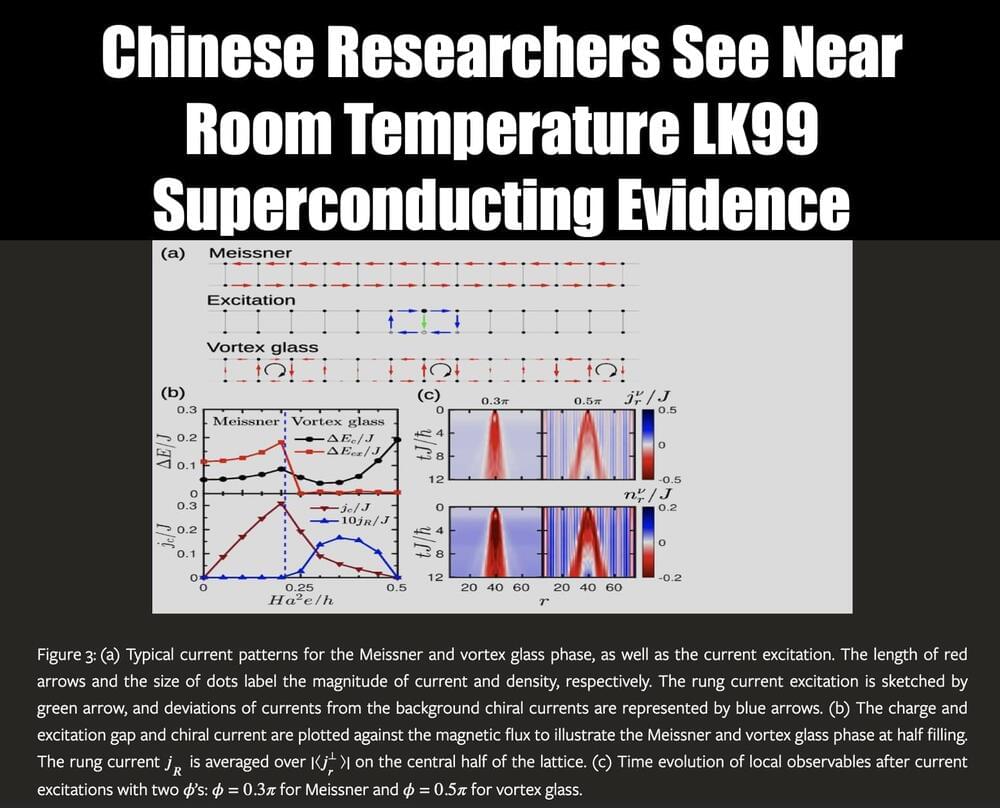
South China University of Technology and Central South University published a paper confirming the discovery of a near-room-temperature superconducting component in LK99-type materials through sample testing. This is significant experimental support for LK99 room temperature superconductivity.
They have found significant hysteresis and memory effect of LFMA in samples of CSLA. The effect is sufficiently robust in magnetic field sweep and rotation and will lose memory in a long duration. The temperature dependence of LFMA intensity exhibits a phase transition at 250 K. The phase diagram of superconducting Meissner and vortex glass is then calculated in the framework of lattice gauge model. In the near future, they will continue to improve the quality of samples to realize full levitation and magnetic flux pinning by increasing active components. The application of a microwave power repository will be considered as well.
Most superconductors have got the low-field microwave absorption (LFMA) due to the presence of superconducting gap and the relevant superconducting vortices as excited states. More importantly, the derivative LFMA of superconductors is positively dependent of the magnetic field as the vortices are more induced under higher field. As a comparison, although the soft magnetism is also active under low field, the precession of spin moments will be suppressed so that the derivative LFMA of magnetic materials is normally negative. The sign of LFMA can be always corrected by the signal of radicals in our measurements. In this case, the signals below 500 Gauss are all positive, implying the presence of superconductivity.