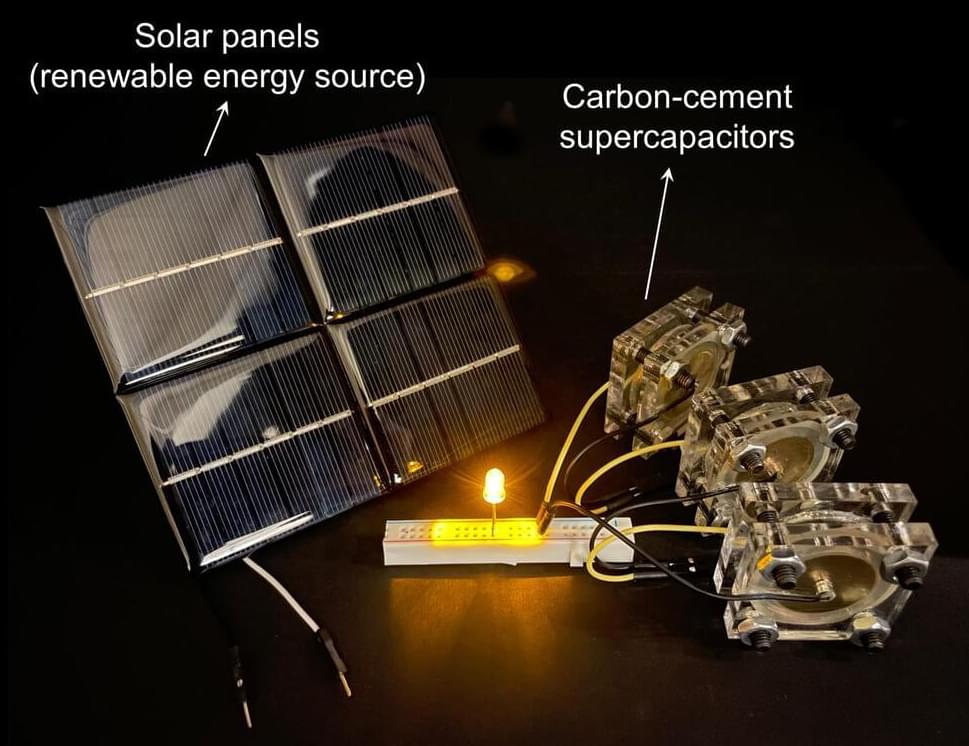
The two materials, the researchers found, can be combined with water to make a supercapacitor — an alternative to batteries — that could provide storage of electrical energy. As an example, the MIT researchers who developed the system say that their supercapacitor could eventually be incorporated into the concrete foundation of a house, where it could store a full day’s worth of energy while adding little (or no) to the cost of the foundation and still providing the needed structural strength. The researchers also envision a concrete roadway that could provide contactless recharging for electric cars as they travel over that road.
The simple but innovative technology is described this week in the journal PNAS, in a paper by MIT professors Franz-Josef Ulm, Admir Masic, and Yang-Shao Horn, and four others at MIT and at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering.
MIT engineers created a carbon-cement supercapacitor that can store large amounts of energy. Made of just cement, water, and carbon black, the device could form the basis for inexpensive systems that store intermittently renewable energy, such as solar or wind energy.