Hot, dry rock deep underground could be used to heat water and produce electricity.




Since April 1980, the overall yearly growth in energy prices is at its highest level. Gasoline prices increased by 11.2 per cent last month and a startling 59.9 per cent over the previous year, accounting for half of the monthly rise.
As per Government data released on Wednesday (July 13), in June, the United States saw a new peak of 9.1 per cent inflation. This faster-than-expected increase in the consumer price index (CPI) was driven by significant increases in gasoline prices, reports AFP. The US Labor Department has reported that this 9.1 per cent CPI spike over the past 12 months to June was the fastest increase in 40 years, the last such increase was witnessed in November 1981.
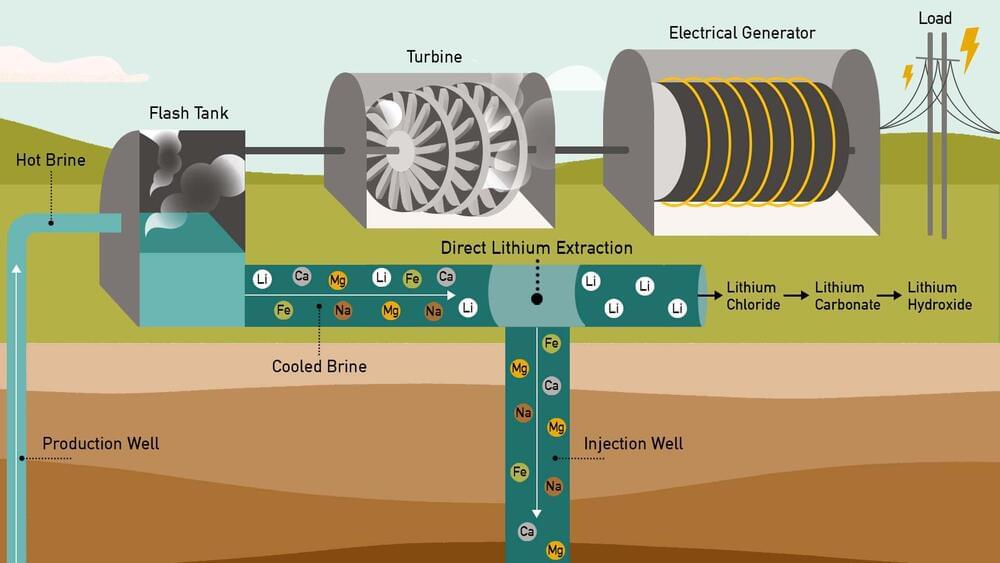
Berkeley Lab scientists assess the technology landscape for developing a domestic source of lithium.
If you had a jar of marbles of many different colors but wanted only the green ones, how could you efficiently pick them out? What if it wasn’t marbles but a jar of glitter, and there was sand, glue, and mud mixed in? That begins to describe the complexity of the brine pumped out from beneath California’s Salton Sea as part of geothermal energy production.
For geothermal fields around the world, produced geothermal brine has been simply injected back underground, but now it’s become clear that the brines produced at the Salton Sea geothermal field contain an immense amount of lithium, a critical resource need for low-carbon transportation and energy storage. Demand for lithium is skyrocketing, as it is an essential ingredient in lithium-ion batteries. Currently there is very little lithium production in the U.S. and most lithium is imported; however, that may change in the near future.
Researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have recently published a comprehensive review of past and current technologies for extracting minerals from geothermal brine. The review, published in the journal Energies, discusses and evaluates a broad array of technologies used for extraction of lithium from brines. The review finds that geothermal brines in the Salton Sea region of California are expected to be a major domestic source of lithium in the future but that significant technical challenges need to be overcome.
Motors are everywhere in our day-to-day lives—from cars to washing machines. A futuristic scientific field is working on tiny motors that could power a network of nanomachines and replace some of the power sources we use in devices today.
In new research published recently in ACS Nano, researchers from the Cockrell School of Engineering at The University of Texas at Austin created the first ever solid-state optical nanomotor. All previous versions of these light-driven motors reside in a solution of some sort, which held back their potential for most real-world applications.
“Life started in the water and eventually moved on land,” said Yuebing Zheng, an associate professor in the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering. “We’ve made these micro nanomotors that have always lived in solution work on land, in a solid state.”
If you live near a river and want clean energy to power your home, we have great news for you. Belgian company Turbulent has created a fish-friendly whirlpool turbine that can be installed in only one week.
The innovative turbine can provide energy 24 hours a day for dozens of homes by being installed in most rivers and canals. It also delivers low-cost power as the generator just uses flowing water to produce energy.
It can effectively power up to 60 homes. The system has a long operating life and requires little maintenance as a self-cleaning screen captures large debris. Best of all, it can be remotely monitored.
Visit our sponsor, Brilliant: https://brilliant.org/IsaacArthur/
Antimatter represents both the most powerful weapon and most powerful fuel for a future humanity, if we can ever learn to make it efficiently and store it safely.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
SFIA Merchandise available: https://www.signil.com/sfia/
Social Media:
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/antimatter-factories-and-uses.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/antimatter-fac…ation-only.
Credits:
Antimatter Factories & Uses.
Episode 239; May 21, 2020
Writers.
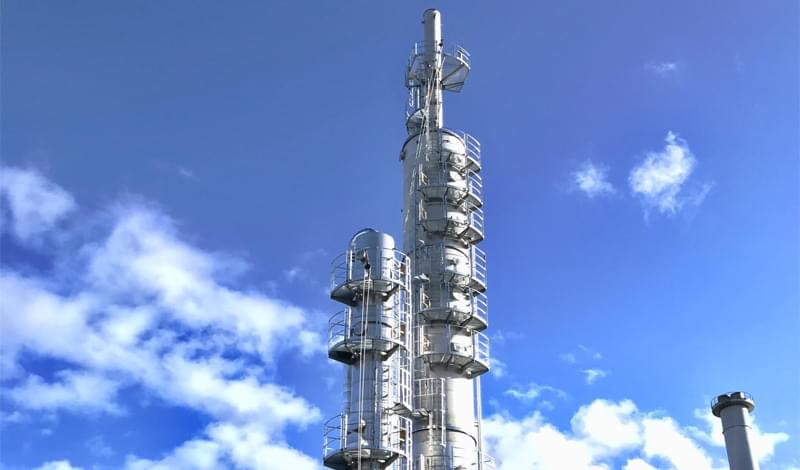

The plant seen here will capture 40,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) each year – 100 times more than the UK’s current largest facility and equivalent to taking 20,000 cars off the roads. The £20 million investment has been completed by Northwich-based Tata Chemicals Europe, one of Europe’s leading producers of sodium carbonate, salt and sodium bicarbonate.
The project will help to unlock the future of carbon capture and utilisation, as it proves the viability of the technology at a large scale, removing CO2 from gas power plant emissions for use in high-end manufacturing applications.
In a world-first, the captured emissions are being purified to food and pharmaceutical grade, then used as raw material for a form of sodium bicarbonate that will be known as Ecokarb. This unique and innovative manufacturing process is patented in the UK, with further patents pending in key territories around the world. Ecokarb will be exported to more than 60 countries.
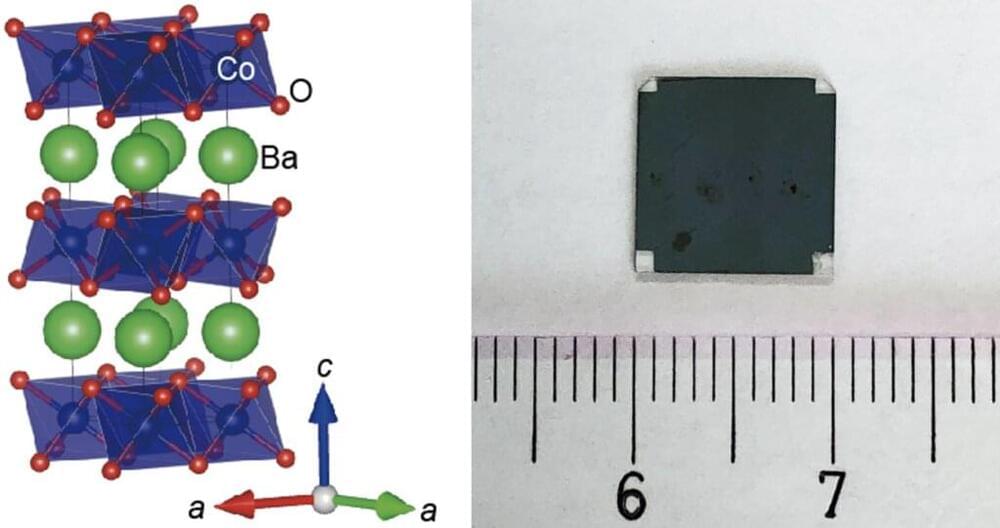
Waste heat is a promising source of energy conservation and reuse, by means of converting this heat into electricity—a process called thermoelectric conversion. Commercially available thermoelectric conversion devices are synthesized using rare metals. While these are quite efficient, they are expensive, and in the majority of cases, utilize toxic materials. Both these factors have led to these converters being of limited use. One of the alternatives is oxide-based thermoelectric materials, but the primary drawback these suffer from is a lack of evidence of their stability at high temperatures.
A team led by Professor Hiromichi Ohta at the Research Institute for Electronic Science at Hokkaido University has synthesized a barium cobalt oxide thermoelectric converter that is reproducibly stable and efficient at temperatures as high as 600°C. The team’s findings have been published in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Thermoelectric conversion is driven by the Seebeck effect: When there is a temperature difference across a conducting material, an electric current is generated. However, efficiency of thermoelectric conversion is dependent on a figure called the thermoelectric figure of merit ZT. Historically, oxide-based converters had a low ZT, but recent research has revealed many candidates that have high ZT, but their stability at high temperatures was not well documented.
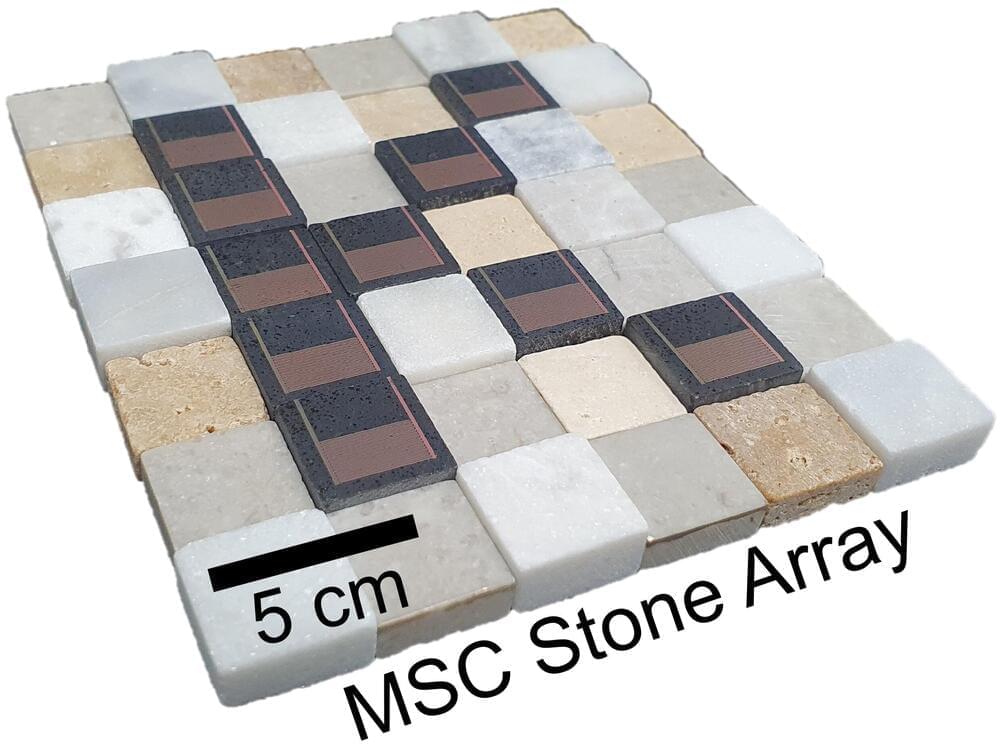

What if you could power the smart thermostats, speakers and lights in your home with a kitchen countertop? Stones, such as marble and granite, are natural, eco-friendly materials that many people building or renovating houses already use. Now, in a step toward integrating energy storage with these materials, researchers have fabricated microsupercapacitors onto the surface of stone tiles. The devices, reported in ACS Nano, are durable and easily scaled up for customizable 3D power supplies.
It would be convenient if the surfaces in rooms could charge smart home devices or other small electronics without being connected to the electrical grid. And although stone is a widely used material for floors, countertops and decorative backsplashes, it hasn’t been integrated with energy storage devices, such as batteries and capacitors.
But stones, even those that are polished and seem smooth, have microscopic bumps and divots, making it difficult to adhere electrical components to them. Researchers have recently figured out how to place microsupercapacitors, which have fast charging and discharging rates and excellent power supply storage, onto irregular surfaces with lasers. So, Bongchul Kang and colleagues wanted to adapt this approach to build microsupercapacitors on marble.