The project will also become a new tourist attraction, ready to welcome tourists in early 2022.



Earth natural source of heat to warm the house.
These are typically powered by natural gas or electricity, which is usually generated by gas or another fossil fuel, causing a significant share of the nation’s carbon emissions.
Geothermal energy: While the temperature on Earth’s surface varies wildly with the weather, seasons, and location, that’s not the case below the surface. Dig about 10 feet down almost everywhere, and the temperature will be about 54 degrees Fahrenheit. Drill farther down, and it gets even warmer.
All 200 houses in Austin’s Whisper Valley development are equipped with geothermal heat pumps that take advantage of Earth’s consistent below-ground temperature to provide heat in the winter and cool air in the summer, eliminating the need for fossil fuel-powered systems.

Revolutionary tool will meet future pandemics with accelerated response.
A new tool speeds up development of vaccines and other pharmaceutical products by more than one million times while minimizing costs.
In search of pharmaceutical agents such as new vaccines, industry will routinely scan thousands of related candidate molecules. A novel technique allows this to take place on the nano scale, minimizing use of materials and energy. The work is published in the prestigious journal Nature Chemistry.
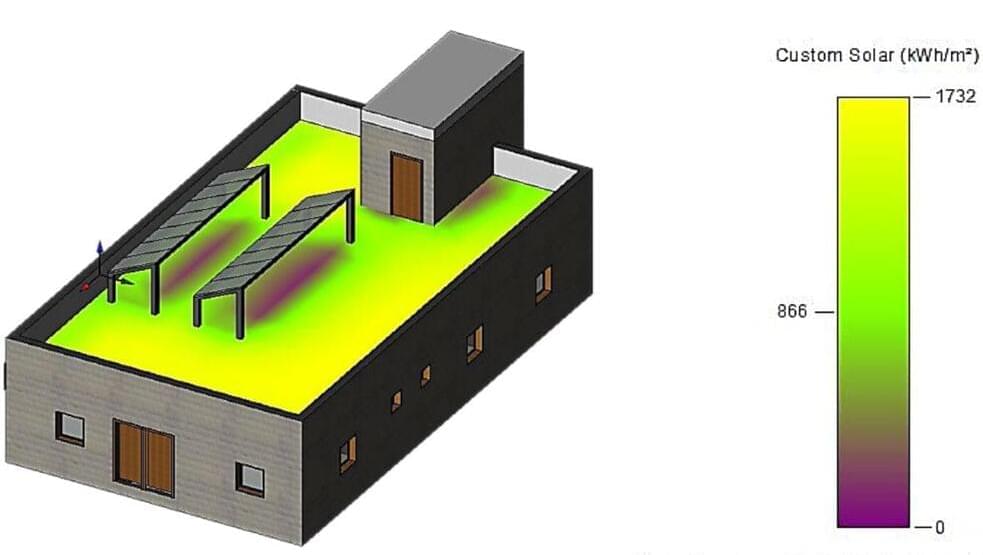
The research project took place during the heating period spanning November 2021 to April 2021 and the cooling period from May 2021 to October 2021. The PV system was designed to cover 4.9% of the roof surface area. The total installed power of the building was 480 kW.
Through their simulation, the scientists found that the shade effect of PV panels may reduce the building’s cooling demand by 10.87%, which means a lower power consumption of 136.6 kWh for the cooling months. “Conversely, PV panels increased the heating load in the winter by 3.8%, which means that the rise in heating loads in heating months was 175.3%,” they also explained. “A rooftop PV system provides a greater understanding of the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) energy demand variance in buildings which is critical in modern architecture.

Back in 1,859, long before the internet, a massive geoelectrical storm knocked out the telegraph systems in the world. Reports were given of telegraph operators being shocked, the paper catching fire, and the equipment being operated without the batteries being connected. This was caused by the massive surge of electrical power caused by the storm. These storms occur when a bubble of superheated gas from the sun hits the earth. These storms cause massive damage to our solar system. This occurrence causes a massive surge in electrical activity and damage. Scientists studying these events have concluded that they occur every 500 years. The event in 1,859, known as the Carrington Event, was the most recent. This could mean that in the year 2,359, another storm would wipe out the entire internet.
The Carrington Event was the largest recorded geoelectrical storm, but it wasn’t the first to happen. An even bigger storm happened in our solar system in A.D. 774, based on readings taken from ice core samples in the Antarctic. The solar flare that was launched from the sun during this event in the Antarctic caused the fastest and biggest rise in carbon-14. Carbon-14 is an isotope of Carbon, which is created from the sun and contains highly radioactive material. Though the Carrington Event was measured via observatories at the time, scientists were able to read the rings in the ice taken from the Antarctic event, which is now known as the Miyake event. Based on those readings, the Miyake event was even greater than the Carrington event. The readings of the ice showed a 14% increase in carbon-14. The Carrington event only saw an increase of less than 1% in carbon-14 readings.
Scientists have a rating system that measures the level of geoelectrical storms based on a scale of 1 to 5. The geoelectrical storms are then given a designation of G1 to G5 based on their intensity. The Carrington event was rated a G5. That would have meant the Miyake event was even more catastrophic in our solar system. A storm that was three times smaller than the Carrington event occurred in 1989. This event took place in Quebec, Canada, and caused the full collapse of the Hydro-Quebec electrical grid. The geoelectrical storm was so powerful that it also caused damage to a circuit breaker in New Jersey. This resulted in the grid’s circuit breakers going off, which caused five million people being without power for nine hours. Should an electrical storm like this occur in currently, the damage would be immeasurable.

With the web of undersea cables lacing the continents together now, it’s hard to imagine that it wasn’t until 1956 that the first transatlantic telephone cable was laid. Sure, there were telegraph cables under the Atlantic starting as early as the late 1800s, but getting your voice across the ocean on copper was a long time coming. So what was the discerning 1930s gentleman of business to do when only a voice call would do? He’d have used a radiotelephone, probably at an outrageous expense, which as this video on the receiving end of the New York to London radio connection shows, was probably entirely justified.
The video details the shortwave radiotelephone system that linked New York and London in the 1930s. It starts with a brief but thorough explanation of ionospheric refraction, and how that atmospheric phenomenon makes it possible to communicate over vast distances. It also offers a great explanation on the problems inherent with radio connections, like multipath interference and the dependency on the solar cycle for usable skip. To overcome these issues, the Cooling Radio Station was built, and its construction is the main thrust of the video.
Built on Cooling Marshes along the Thames well outside of London, the receive-only radio station was a gigantic undertaking. It consisted of a two-mile-long rhombic array antenna, pointed directly at the transmitting site in Lawrenceville, New Jersey. The pool-table-flat marshland made for a perfect place for the array; the fact that the ground was saturated with brackish tidal water had the added benefit of excellent electrical conduction, too. The amount of work it took to raise the antenna masts and booms is impressive — very little power equipment was used. And we loved the details about the hardline coaxial used to stitch the antennas together — it was made on-site from copper tube and insulating spacers.

The U.S. still imports lithium from other countries like Argentina, Chile, Russia, and China. Geothermal energy has long been the forgotten member of the clean energy family, overshadowed by relatively cheaper solar and wind power, despite its proven potential. But this may soon change – for an unexpected reason.
DWR’s Salton Sea Unit supports the California Natural Resources Agency’s Salton Sea Management Program (SSMP), created by then-Gov. Jerry Brown’s Salton Sea Task Force to address the urgent public and ecological health issues resulting from the drying and shrinking of the Salton Sea. The issues include air quality impacts from dust emissions and loss of important wildlife habitat.
While the SSMP is a long-range program, its immediate focus is on the development and implementation of the Phase I: 10-Year Plan. We support the SSMP and the Phase I Plan by providing planning, engineering, and environmental expertise for design and implementation of dust-suppression and habitat projects. The Phase I Plan includes projects that will be completed as early as the end of 2022. Proposition 1 provided $80 million in funding for SSMP implementation.

JWST recently snapped this infrared test image of a star, which also shows fainter background stars and galaxies — a testament to the telescope’s power.
In early February, NASA engineers began to remotely align the 18 hexagonal segments of the James Webb Space Telescope’s primary mirror, which had been folded away for launch. The goal of this meticulous, three-month-long process is to perfectly position the mirror segments relative to each other, creating a single, smooth, 6.5-meter-wide surface that can gather and focus light from the distant cosmos.
You may recall earlier snapshots that marked previous milestones. For example, the second of seven milestones was punctuated with a shot taken before the mirrors were fully aligned; it featured multiple images of a single star. Now, NASA has announced the fifth major alignment milestone is complete. Called fine phasing, this step helped to identify and correct small differences between individual mirror segments to bring the infrared universe into sharp, clear focus.