Researchers developed a fully automated cooperation task showing that rats engage in true reciprocity, not just mutual benefit.


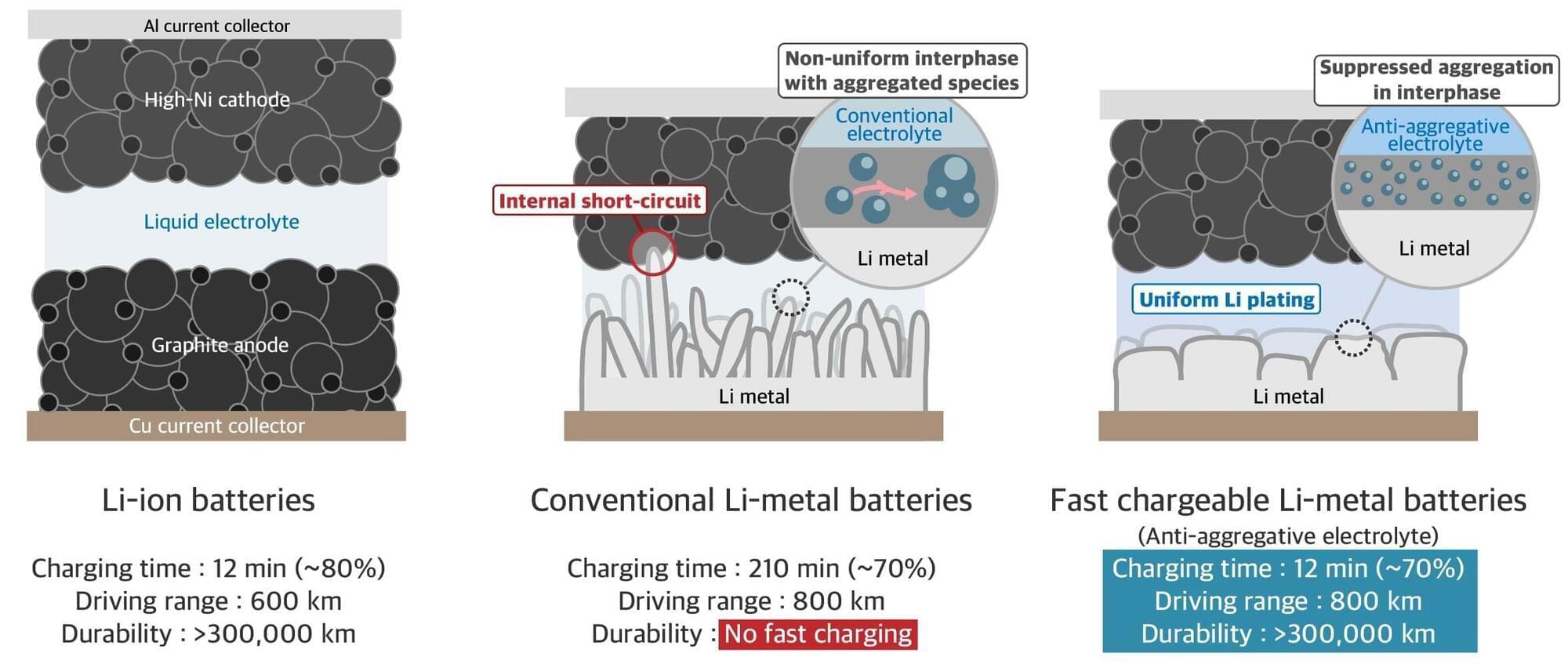
Korean researchers have ushered in a new era for electric vehicle (EV) battery technology by solving the long-standing dendrite problem in lithium-metal batteries. While conventional lithium-ion batteries are limited to a maximum range of 600 km, the new battery can achieve a range of 800 km on a single charge, a lifespan of over 300,000 km, and a super-fast charging time of just 12 minutes.
A research team from the Frontier Research Laboratory (FRL), a joint project between Professor Hee Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and LG Energy Solution, has developed a “cohesion-inhibiting new liquid electrolyte” original technology that can dramatically increase the performance of lithium-metal batteries. Their paper is published in Nature Energy.
Lithium-metal batteries replace the graphite anode, a key component of lithium-ion batteries, with lithium metal. However, lithium metal has a technical challenge known as dendrite, which makes it difficult to secure the battery’s lifespan and stability. Dendrites are tree-like lithium crystals that form on the anode surface during battery charging, negatively affecting battery performance and stability.

Engineers in Australia have created a new carbon-based material which allows supercapacitors to store as much energy as traditional lead-acid batteries and deliver charge much faster.
The new graphene materials are now being made in commercial quantities, says Dr Phillip Aitchison, chief technical officer of Monash University spinout Ionic Industries.
“We’re working with energy storage partners to bring this breakthrough to market-led applications – where both high energy and fast power delivery are essential.”
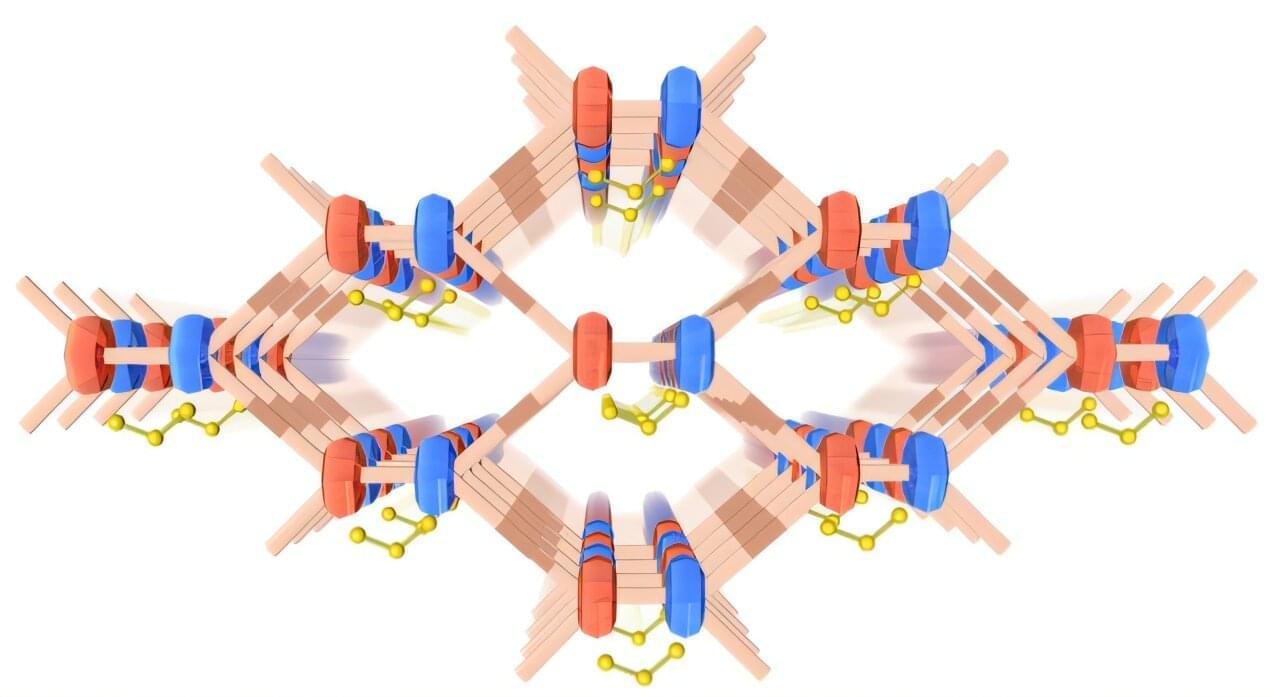
A team led by Prof. Yan Lu, HZB, and Prof. Arne Thomas, Technical University of Berlin, has developed a material that enhances the capacity and stability of lithium-sulfur batteries. The material is based on polymers that form a framework with open pores (known as radical-cationic covalent organic frameworks or COFs). Catalytically accelerated reactions take place in these pores, firmly trapping polysulfides, which would shorten the battery life.
Some of the experimental analyses were conducted at the BAMline at BESSY II. The research is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Crystalline framework structures made of organic polymers are a particularly interesting class of materials. They are characterized by their high porosity, comparable to a sponge, but with pores measuring only a few micrometers at most. These materials can exhibit special functionalities, which make them interesting for certain applications in electrochemical energy storage devices.


The movement of protons through electrically charged water is one of the most fundamental processes in chemistry. It is evident in everything from eyesight to energy storage to rocket fuel—and scientists have known about it for more than 200 years.
But no one has ever seen it happen. Or precisely measured it on a microscopic scale.
Now, the Mark Johnson lab at Yale has—for the first time—set benchmarks for how long it takes protons to move through six charged water molecules. The discovery, made possible with a highly customized mass spectrometer that has taken years to refine, could have far-reaching applications for researchers in years to come.
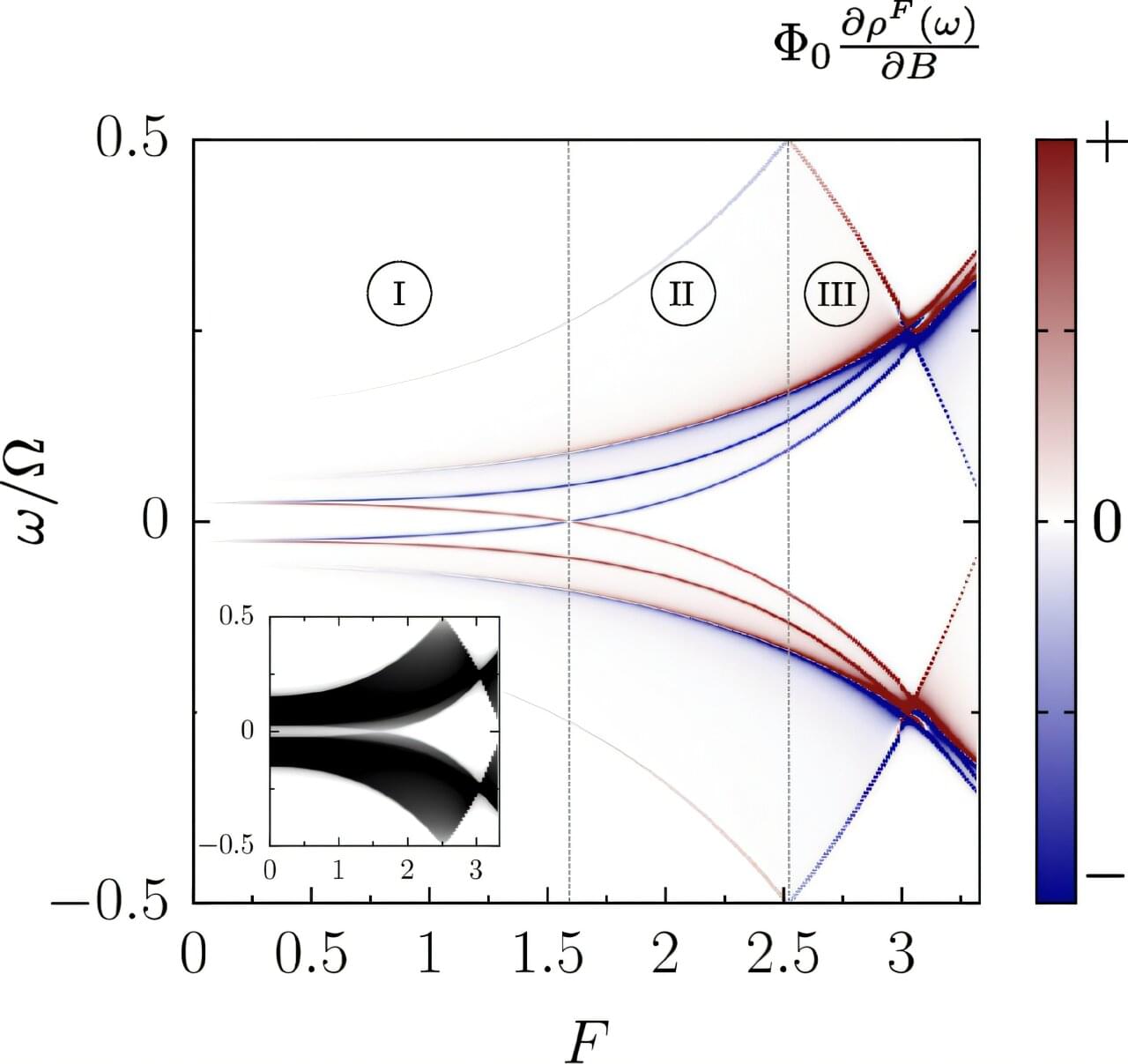
A new study addresses a foundational problem in the theory of driven quantum matter by extending the Středa formula to non-equilibrium regimes. It demonstrates that a superficially trivial “sum of zeros” encodes a universal, quantized magnetic response—one that is intrinsically topological and uniquely emergent under non-equilibrium driving conditions.
Imagine a strange material being rhythmically pushed—tapped again and again by invisible hands. These are periodically driven quantum systems, or Floquet systems, where energy is no longer conserved in the usual sense. Instead, physicists speak of quasienergy—a looping spectrum with no clear start or end.
When scientists measure how such a system responds to a magnetic field, every single contribution seems to vanish—like adding an infinite list of zeros. And yet, the total stubbornly comes out finite, quantized, and very real.
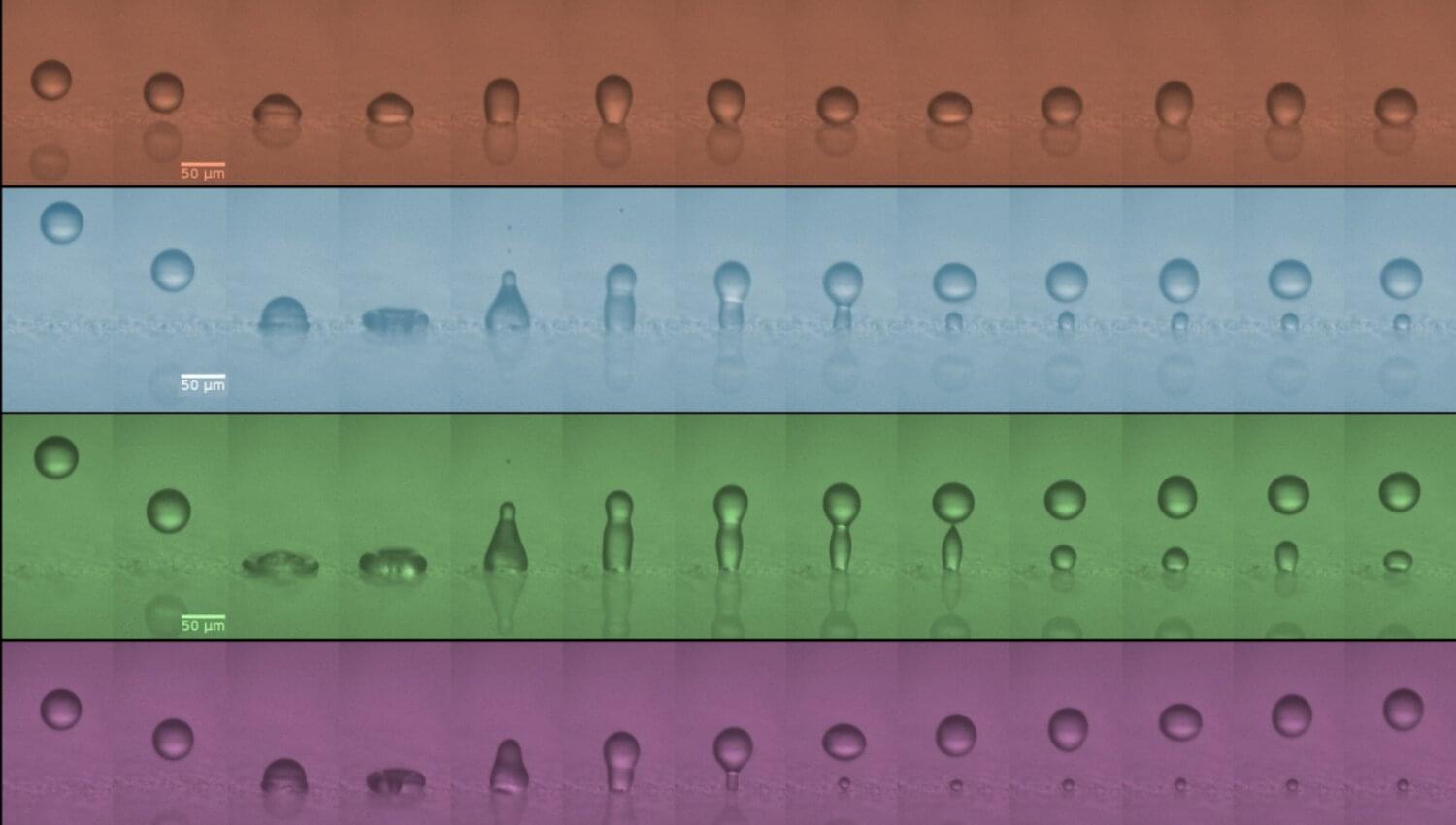

When a droplet of liquid the size of a grain of icing sugar hits a water-repelling surface, like plastics or certain plant leaves, it can meet one of two fates: stick or bounce. Until now, scientists thought bouncing depended only on how repellent the surface was and how the droplet lost its impact energy. Speed, they assumed, didn’t matter.
Now, new research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows that speed is actually the deciding factor—and that droplets only bounce within a “Goldilocks zone,” or just the right speed range.
“Bouncing only happens in a very narrow speed window,” said Jamie McLauchlan, first author of the study and Ph.D. student at the University of Bath.

Questions to inspire discussion.
Technical Specifications.
📏 Q: What are the physical characteristics of the Megapack 3? A: Megapack 3 features a 28-foot long enclosure that can be shipped globally, with 78% fewer connections in the thermal bay, and incorporates a larger battery module and larger cell leveraging the latest cell technology.
⚡ Q: What is the total usable energy capacity of Megapack 3? A: Tesla’s Megapack 3 is designed for 20 megawatt hours of usable AC energy, providing significant storage capacity for large-scale energy projects.
Installation and Efficiency.
🔧 Q: How does Megapack 3 improve installation efficiency? A: Megapack 3 eliminates above-ground cabling and features 78% fewer connections in the thermal bay, significantly streamlining the installation process and reducing potential points of failure.