In nature, organisms often support each other in order to gain an advantage. However, this kind of cooperation contradicts the theory of evolution proposed by Charles Darwin: Why would organisms invest valuable resources to help others? Instead, they should rather use them for themselves, in order to win the evolutionary competition with other species. A new study led by Prof. Dr. Christian Kost from the Department of Ecology at Osnabrueck University has now solved this puzzle. The results of the study were published in the scientific journal Current Biology. The research project was performed in collaboration with the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena.
Interactions between two or more organisms, in which all partners involved gain an advantage, are ubiquitous in nature and have played a key role in the evolution of life on Earth. For example, root bacteria fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, thus making it available to plants. In return, the plant supplies its root bacteria with nutritious sugars. However, it is nevertheless costly for both interaction partners to support each other. For example, the provision of sugar requires energy, which is then not available to the plant anymore. From this results the risk of cheating interaction partners that consume the sugar without providing nitrogen in return.
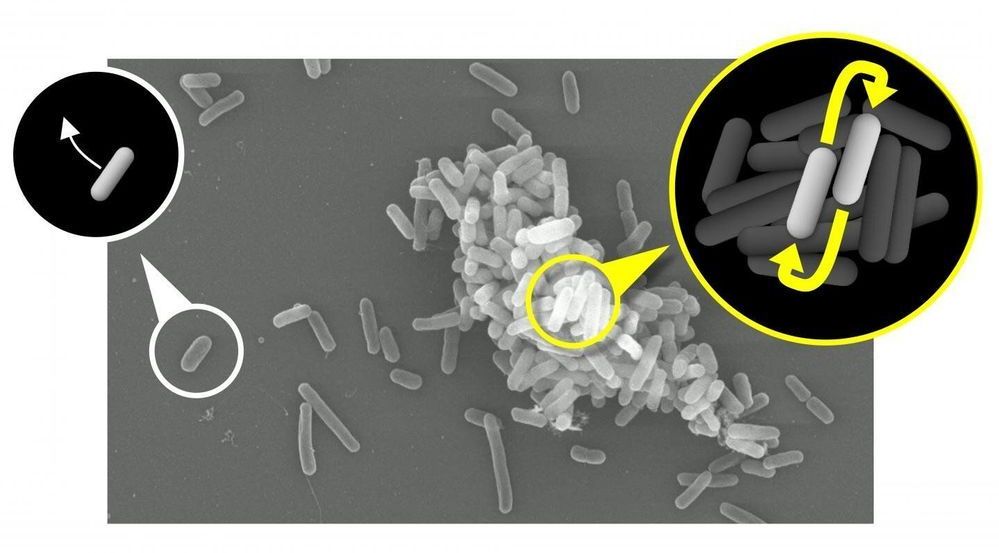
The research team led by Prof. Dr. Christian Kost used bacteria as a model system to study the evolution of mutual cooperation. At the beginning of the experiment, two bacterial strains could only grow when they provided each other with essential amino acids. Over the course of several generations, however, the initial exchange of metabolic byproducts developed into a real cooperation: both partners increased the production of the exchanged amino acids in order to benefit their respective partner. Even though the increased amino acid production enhanced growth when both partners were present, it was extremely costly when individual bacterial strains had to grow without their partner.