Circa 2018
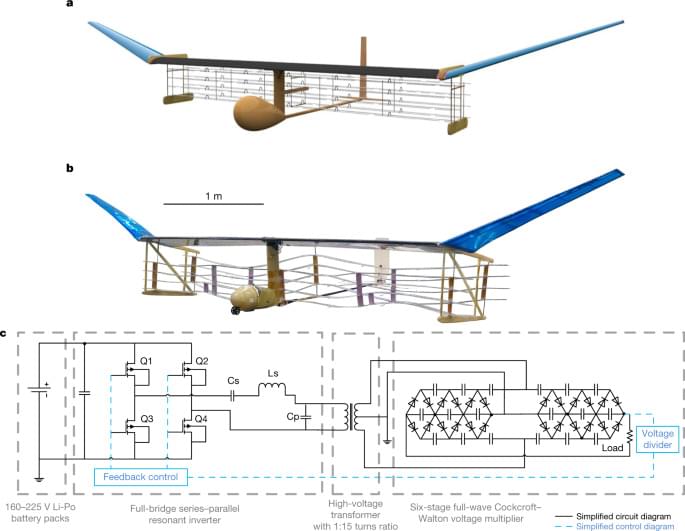
Since the first aeroplane flight more than 100 years ago, aeroplanes have been propelled using moving surfaces such as propellers and turbines. Most have been powered by fossil-fuel combustion. Electroaerodynamics, in which electrical forces accelerate ions in a fluid1,2, has been proposed as an alternative method of propelling aeroplanes—without moving parts, nearly silently and without combustion emissions3,4,5,6. However, no aeroplane with such a solid-state propulsion system has yet flown. Here we demonstrate that a solid-state propulsion system can sustain powered flight, by designing and flying an electroaerodynamically propelled heavier-than-air aeroplane. We flew a fixed-wing aeroplane with a five-metre wingspan ten times and showed that it achieved steady-level flight. All batteries and power systems, including a specifically developed ultralight high-voltage (40-kilovolt) power converter, were carried on-board. We show that conventionally accepted limitations in thrust-to-power ratio and thrust density4,6,7, which were previously thought to make electroaerodynamics unfeasible as a method of aeroplane propulsion, are surmountable. We provide a proof of concept for electroaerodynamic aeroplane propulsion, opening up possibilities for aircraft and aerodynamic devices that are quieter, mechanically simpler and do not emit combustion emissions.