Solid state laser :3.
Advances in high-energy solid-state lasers and encouraging results from field trials show expanded capabilities of recent U.S military laser prototypes.
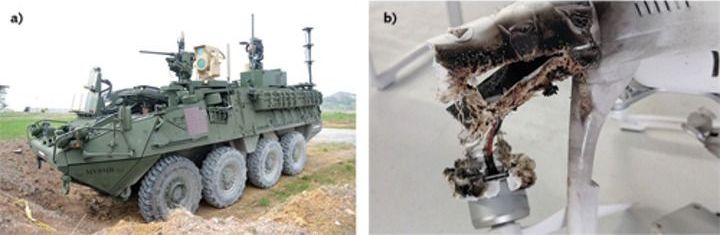
Solid state laser :3.
Advances in high-energy solid-state lasers and encouraging results from field trials show expanded capabilities of recent U.S military laser prototypes.

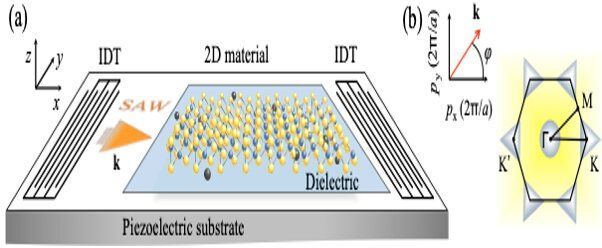
Researchers at the Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems (PCS), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea), and colleagues have reported a novel phenomenon, called Valley Acoustoelectric Effect, which takes place in 2-D materials, similar to graphene. This research is published in Physical Review Letters and brings new insights to the study of valleytronics.
In acoustoelectronics, surface acoustic waves (SAWs) are employed to generate electric currents. In this study, the team of theoretical physicists modelled the propagation of SAWs in emerging 2-D materials, such as single-layer molybdenum disulfide (MoS2). SAWs drag MoS2 electrons (and holes), creating an electric current with conventional and unconventional components. The latter consists of two contributions: a warping-based current and a Hall current. The first is direction-dependent, is related to the so-called valleys—electrons’ local energy minima—and resembles one of the mechanisms that explains photovoltaic effects of 2-D materials exposed to light. The second is due to a specific effect (Berry phase) that affects the velocity of these electrons travelling as a group and resulting in intriguing phenomena, such as anomalous and quantum Hall effects.
The team analyzed the properties of the acoustoelectric current, suggesting a way to run and measure the conventional, warping, and Hall currents independently. This allows the simultaneous use of both optical and acoustic techniques to control the propagation of charge carriers in novel 2-D materials, creating new logical devices.


It’s easy to take time’s arrow for granted — but the gears of physics actually work just as smoothly in reverse. Maybe that time machine is possible after all?
An experiment earlier this year shows just how much wiggle room we can expect when it comes to distinguishing the past from the future, at least on a quantum scale. It might not allow us to relive the 1960s, but it could help us better understand why not.
Researchers from Russia and the US teamed up to find a way to break, or at least bend, one of physics’ most fundamental laws on energy.

(21 Oct 2017) LEADIN:
Forget plugging in to charge up your new electric car, engineers are now working towards a future where you never need to plug in ever again.
That’s some time off, but a new generation of batteries is being designed to power the latest electric cars, from high energy cells to power sports models to those that power over long distances.
STORYLINE:
Electric cars are no longer concepts kept in top secret bunkers at a car manufacturers research unit.
Nor are they a seen as four wheeled status symbols of the wealthy elite.
