Dr. Dee J. Nelson and his wife Geo, produced a Kirlian photograph of Pyramid energy using a Tesla Coil in 1979.
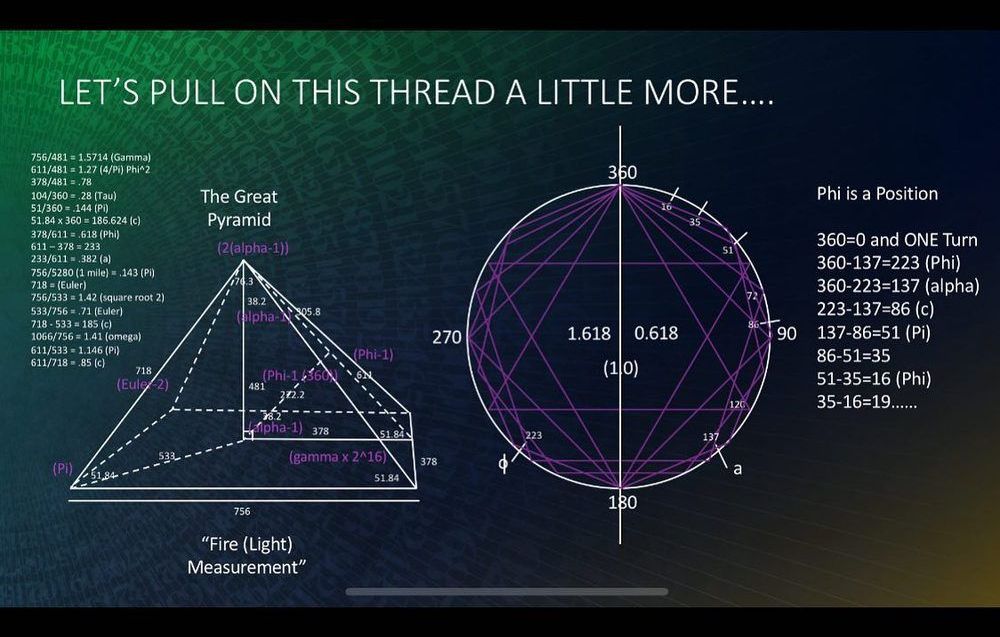
We have confirmed that the Great Pyramid encodes over 80 Mathematical and Physical constants (including but not limited to Pi, E, a, Phi, Y, Planck Length, Planck Time, and even math constants only discovered in the last century like Brun’s Constant and Tribonacci), our metric and imperial measurement systems (including Meter, Foot, Mile, Nautical Mile, and the ancient Sacred Egyptian Cubit), and even the Speed of Light in BOTH its Longitude and Latitude positions…and all with astounding accuracy.
Image and content from “The Etymology of Number” Course in Resonance Academy http://bit.ly/Resonance-Academy