Design for system that provides solar- or wind-generated power on demand should be cheaper than other leading options.



This pugnacious antipathy toward scientists, research funding and universities threatens to undercut the very advantages that have made the U.S. such a dominant technological power over the last century. Just as Hasan Ibn al-Haytham’s achievements draw a sharp contrast with the Middle East’s current lagging position in science, sepia-colored nostalgia for Isaac Newton will ring bitterly hollow if the West turns away from Newton’s legacy. A civilization is only as great as its last failure.
It’s absurd to claim otherwise — especially now, as America turns away from Newton’s legacy.
Wearable devices that harvest energy from movement are not a new idea, but a material created at Rice University may make them more practical.
The Rice lab of chemist James Tour has adapted laser-induced graphene (LIG) into small, metal-free devices that generate electricity. Like rubbing a balloon on hair, putting LIG composites in contact with other surfaces produces static electricity that can be used to power devices.
For that, thank the triboelectric effect, by which materials gather a charge through contact. When they are put together and then pulled apart, surface charges build up that can be channeled toward power generation.
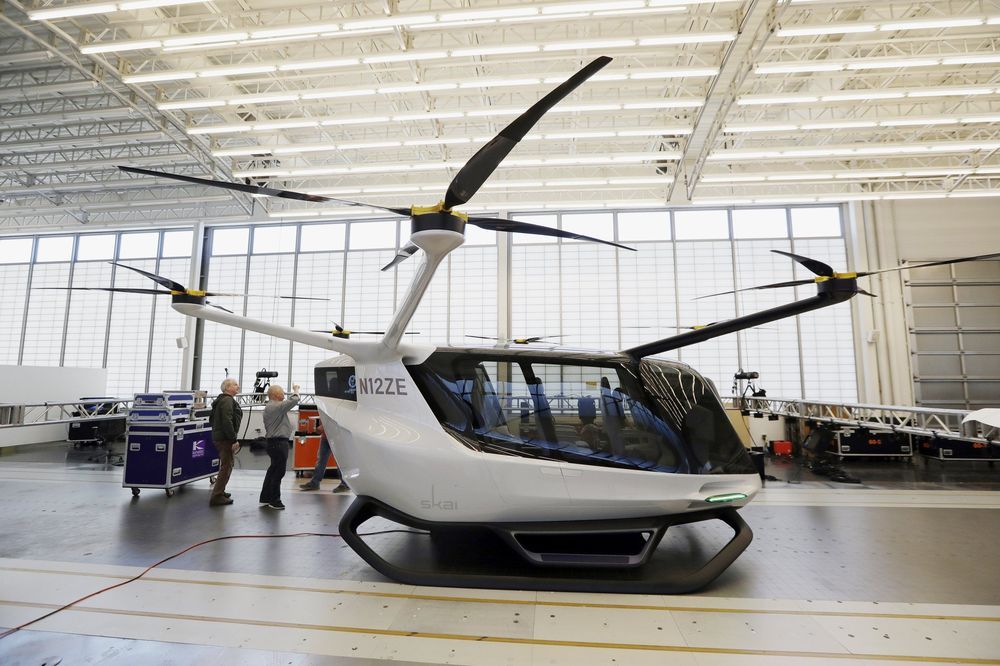

LOS ANGELES (AP) — A transportation company is betting its sleek new hydrogen-powered electric flying vehicles will someday serve as taxis, cargo carriers and ambulances of the sky, but experts say they will have to clear a number of regulatory hurdles before being approved for takeoff years in the future.
With six rotors on the roof and seats inside for five people, a passenger model of the Skai (pronounced “sky”) unveiled Wednesday near Los Angeles resembles an oversized drone crossed with a luxury SUV.
Like a drone, the vehicle from Alaka’i Technologies takes off and lands vertically. It’s one of many similar electric flying crafts in production, including prototypes from Boeing and Airbus that made successful test flights this year, according to Vertical Flight Society, an industry group.

The science exhibition, which goes by the name “Vigyan Samagam”, will highlight India’s contributions to some of the world’s biggest science projects. It is a jointly-funded effort by the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
While in India, the CERN exhibit will be bilingual — in English and Hindi for the public to make the most of.
What if the wood your house was made of could save your electricity bill? In the race to save energy, using a passive cooling method that requires no electricity and is built right into your house could save even chilly areas of the US some cash. Now, researchers at the University of Maryland and the University of Colorado have harnessed nature’s nanotechnology to help solve the problem of finding a passive way for buildings to dump heat that is sustainable and strong.

Despite this, electric garbage trucks are still few and far between. BYD’s main competitor is Motiv Power Systems, which has sold small fleets of class 8 side-loading garbage trucks to Los Angeles and Sacramento, California. Wrightspeed, which was also making hybrid-electric garbage trucks—featured in this article from 2015—appears to have gone dormant, despite a contract to supply the New Zealand cities of Auckland and Wellington. And recently, Volvo announced a battery electric garbage truck, the FE Electric, although it appears to be limited to the European market.
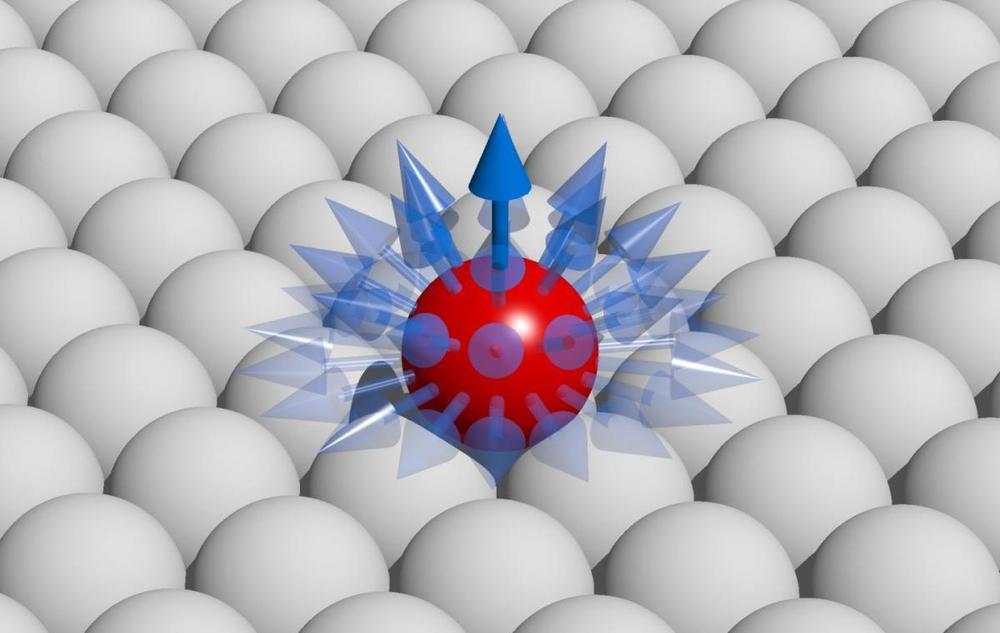
The European research institution Jülich just released new information on “zero-point energy” and its effect on the stability of nanomagnets. If scientists can determine how to magnetically store data, information can be stored in extremely small spaces.
Quantum mechanics becomes important when we’re talking about small spaces, such as nanometers. Magnetic moments are difficult to stabilize, or point in designated directions. A specific direction corresponds to effectively storing data.
In order to save data, the magnetic moments of atoms in constant motion must be counteracted by energy barriers, which is dependent on the material used. Otherwise, the magnetic moments change and any information saved is then lost.
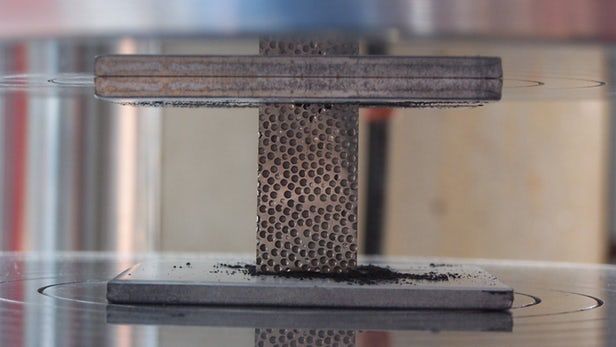
Radiation generally comes under the heading of “things you want to stay away from,” so it’s no surprise that radiation shielding is a high priority in many industries. However, current shielding is bulky and heavy, so a North Carolina State University team is developing a new lightweight shielding based on foam metals that can block X-rays, gamma rays, and neutron radiation, as well as withstanding high-energy impact collisions.

So-called supercapacitors, AKA ultracapacitors, are amazing devices. While they don’t store as much total energy as a comparable battery, they can discharge this energy extremely quickly. They can also charge rapidly, as demonstrated by Mike Rigsby’s “Little Flash.” As described in his project write-up, the mini rover “runs for twenty minutes, charges in ten seconds.”