The team developed a structural battery by depositing carbon nanotubes on quartz-woven fabrics with efficient charge transport and retention.
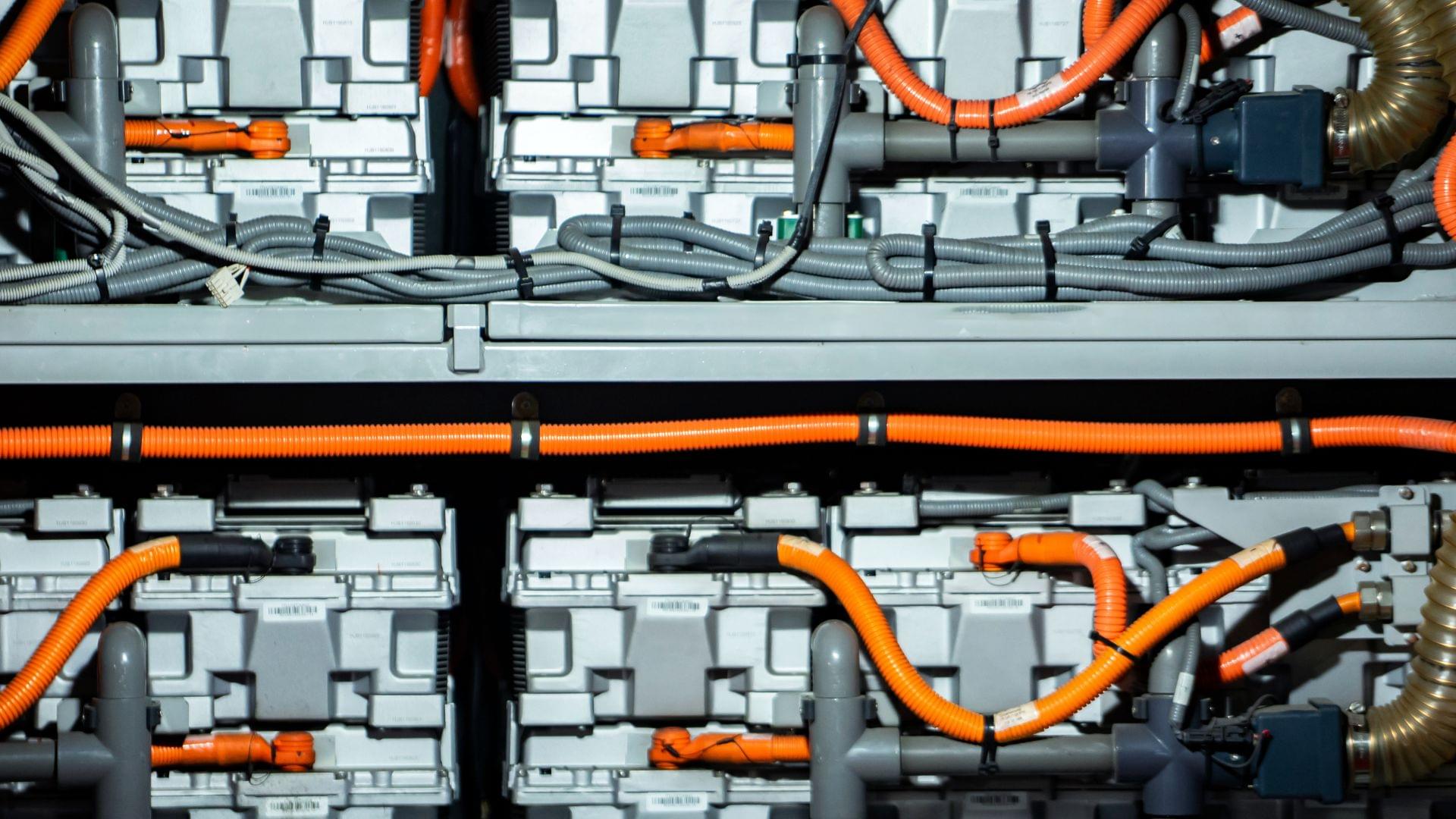



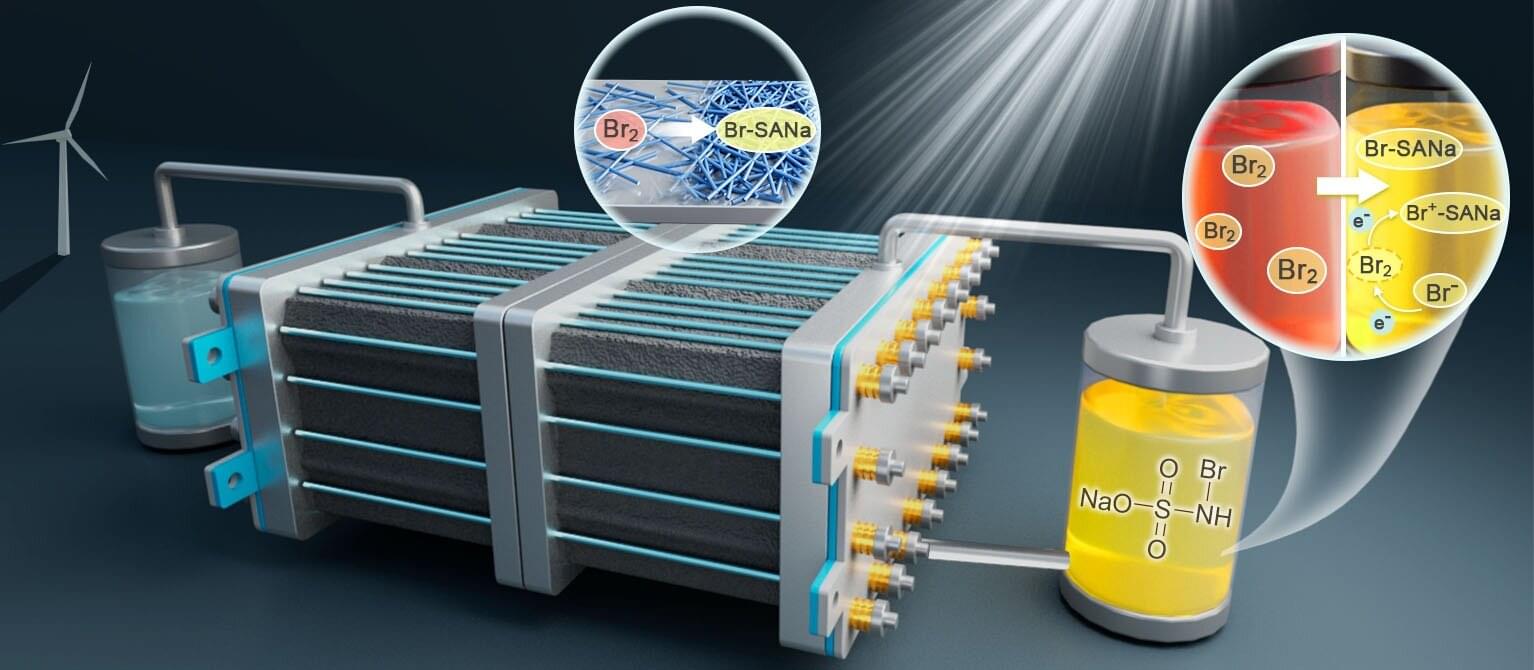
Grid storage batteries, for their part, collect excess power from various green energy sources, like wind farms. They can be charged and then discharged at times of higher demand and lower supply. Having plentiful, economical batteries is a key factor in pitching this kind of facility to nations and communities that are considering using renewables, or larger portions of renewables.
But setting up a mine to extract the massive deposit of lithium in Thacker Pass is not a simple task: it will require a wholly new process to separate the lithium from its natural clay deposit.
Lithium is all around us. The U.S. Geological Survey estimates there are 89 million tons of lithium in deposits on Earth, just two one-thousandths of 1 percent of Earth’s elemental abundance. Experts believe more than half of that lithium can be found in one triangular area of desert in western South America; but Thacker Pass in the United States, we now know, could contain as much as 40 million tons of lithium.
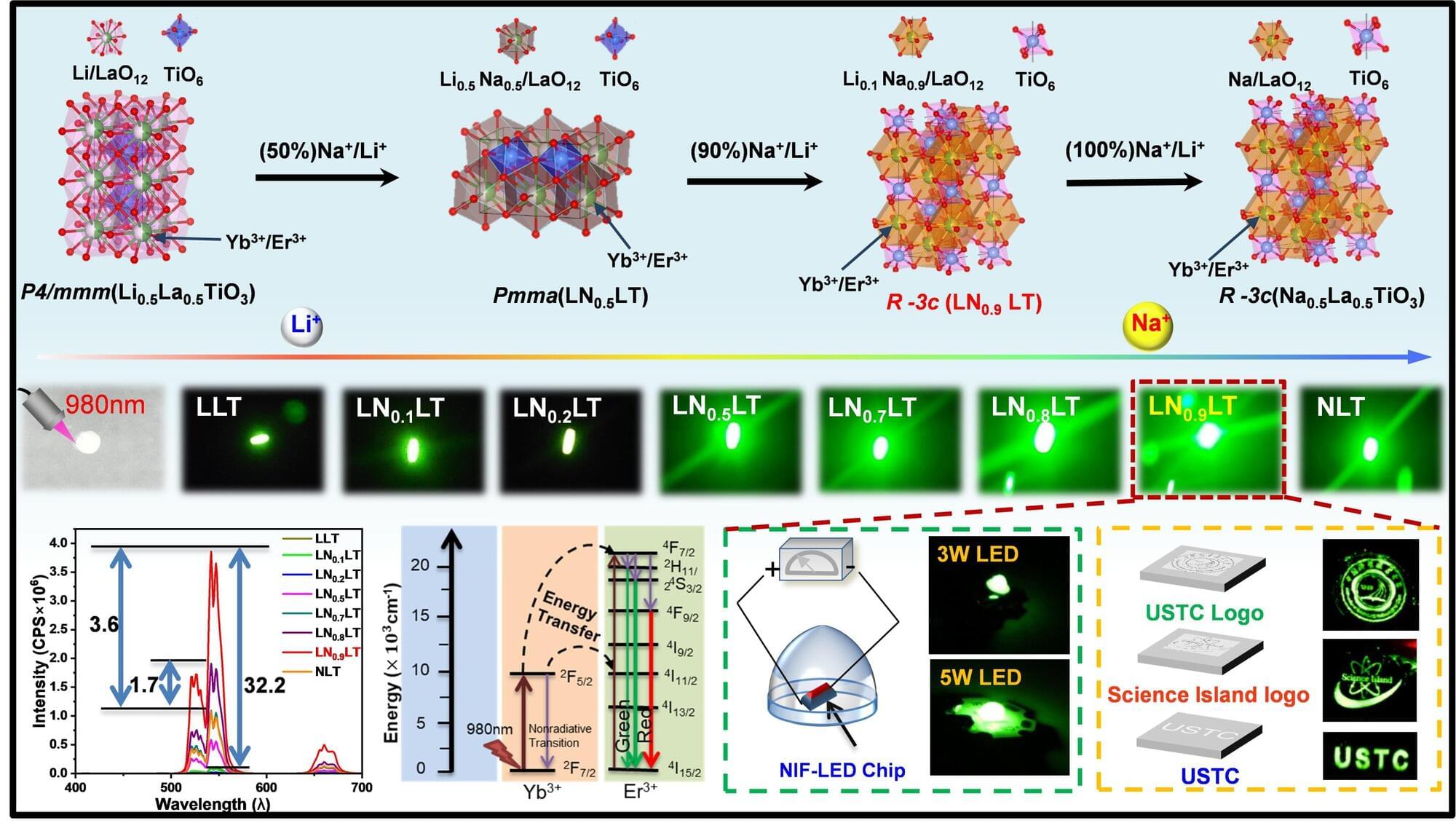
Researchers at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a new way to significantly enhance upconversion luminescence in oxide perovskites, a class of materials known for their thermal and chemical stability but limited optical efficiency.
Led by Professor Jiang Changlong, the team introduced a dual-cation substitution strategy in titanate perovskites by precisely adjusting the sodium-to-lithium ratio at the crystal’s A-site. This controlled substitution triggers a structural transition that improves energy transfer between rare-earth ions, resulting in a marked increase in luminescence intensity and quantum yield.
The findings are published in Journal of Alloys and Compounds.

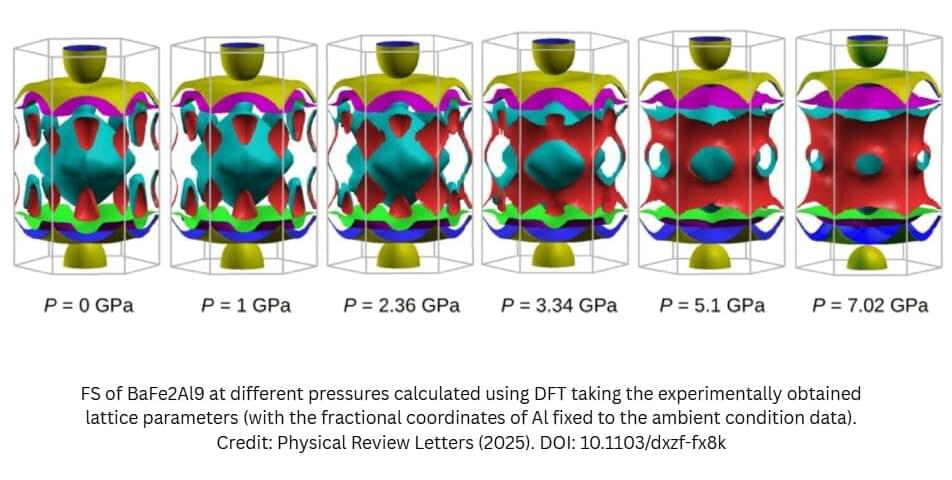
Scientists have discovered a way to efficiently transfer electrical current through specific materials at room temperature, a finding that could revolutionize superconductivity and reshape energy preservation and generation.
The paper is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
The much-sought-after breakthrough hinges on applying high pressure to certain materials, forcing their electrons closer together and unlocking extraordinary electronic behaviors.
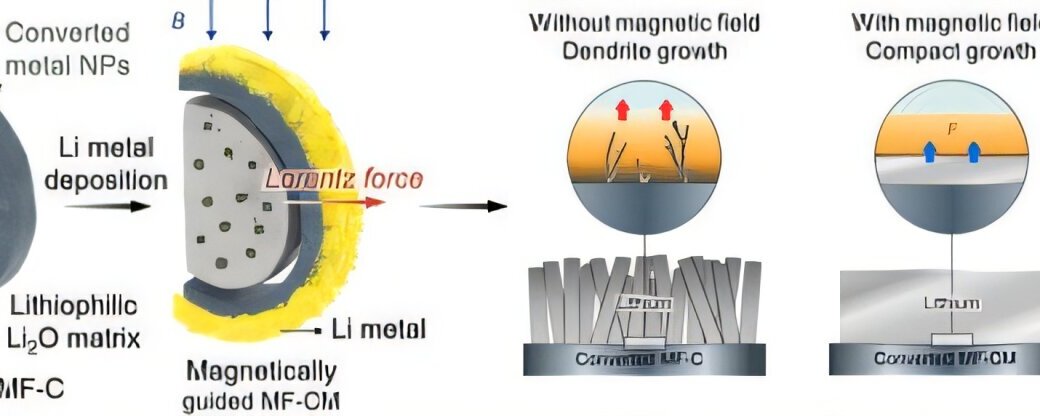
A new battery technology has been developed that delivers significantly higher energy storage—enough to alleviate EV range concerns—while lowering the risk of thermal runaway and explosion.
A research team at POSTECH has developed a next-generation hybrid anode that uses an external magnetic field to regulate lithium-ion transport, effectively suppressing dendrite growth in high-energy-density electrodes.
A POSTECH research team—led by Professor Won Bae Kim of the Department of Chemical Engineering and the Graduate School of Battery Engineering, together with Dr. Song Kyu Kang and integrated Ph.D. student Minho Kim—has introduced a “magneto-conversion” strategy that applies an external magnetic field to ferromagnetic manganese ferrite conversion-type anodes.

Physicists have so far failed to unify general relativity and quantum mechanics. As attempts to unite them into a quantum theory of gravity mount up, philosopher of physics Dean Rickles argues that the assumption of materialism is the problem. We need to look beyond the physical—beyond space, time and matter—to something primordial out of which minds can construct physical reality, and which explains both general relativity and quantum mechanics. Pioneers like John Wheeler and David Bohm have already begun to chart what such a realm of “pre-physics” might look like—it’s high time physics took their ideas more seriously.
A pair of recent physics Nobel prizes (2020 and 2022) were awarded for basic research in general relativity (Einstein’s theory of gravitation that explains gravity as the curvature of spacetime by matter and energy) and quantum mechanics (our best bet for a theory of matter and energy). The experimental successes of these theories keep piling up. There is clearly much truth in them. They both aim to describe the same world: this world. They should surely overlap, since the matter and energy described by quantum mechanics should curve spacetime as well as good old-fashioned non-quantum mechanical matter and energy. Why then can we not construct a theory in which they both appear? Why is it so difficult to build what would be a Quantum Theory of Gravity?

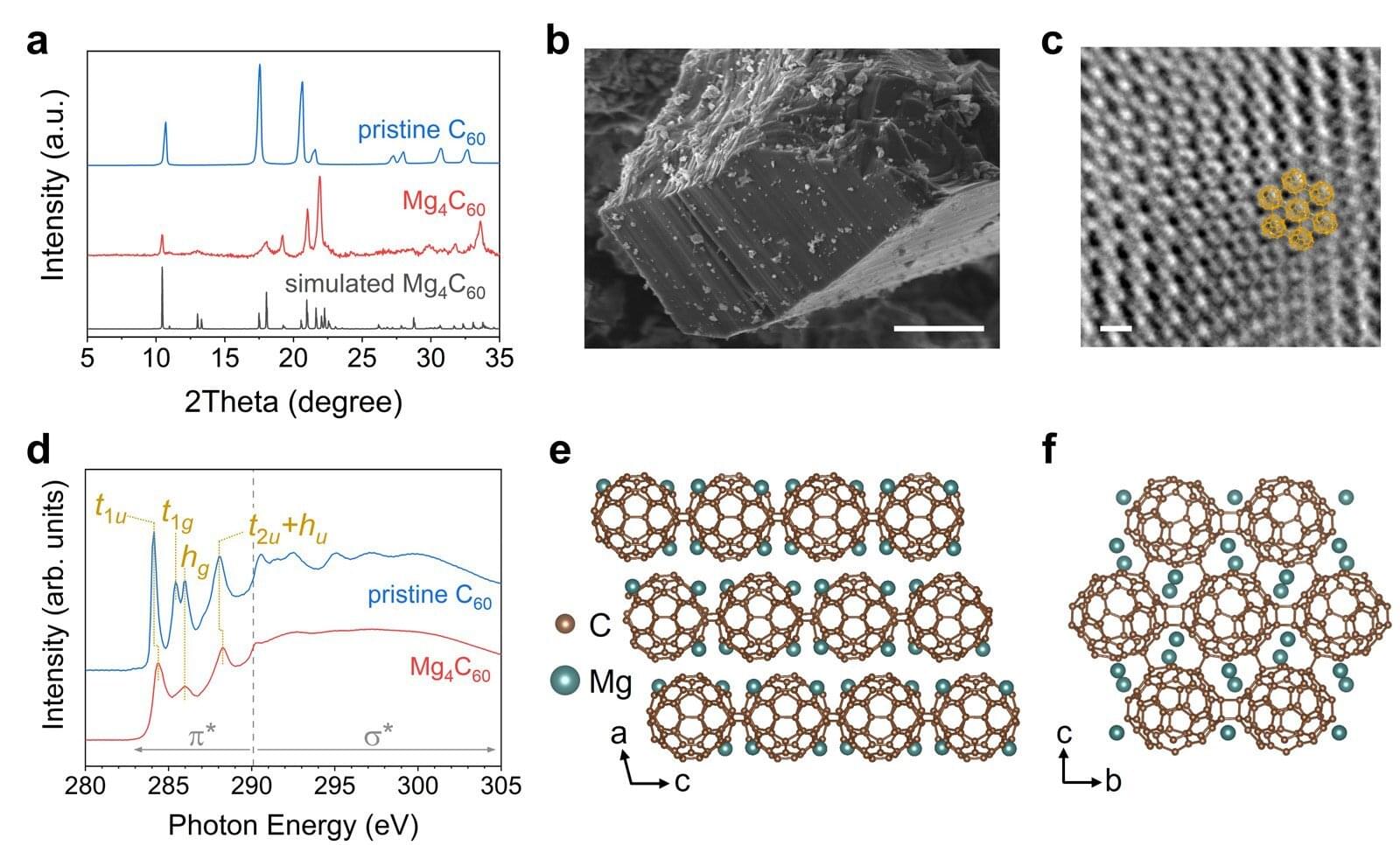
Research published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society demonstrates a new way to make carbon-based battery materials much safer, longer lasting, and more powerful by fundamentally redesigning how fullerene molecules are connected.
Today’s lithium-ion batteries rely mainly on graphite, which limits fast-charging speed and poses safety risks due to lithium plating. These research findings mean progress toward safer electric vehicles, longer-lasting consumer electronics, and more reliable renewable-energy storage.
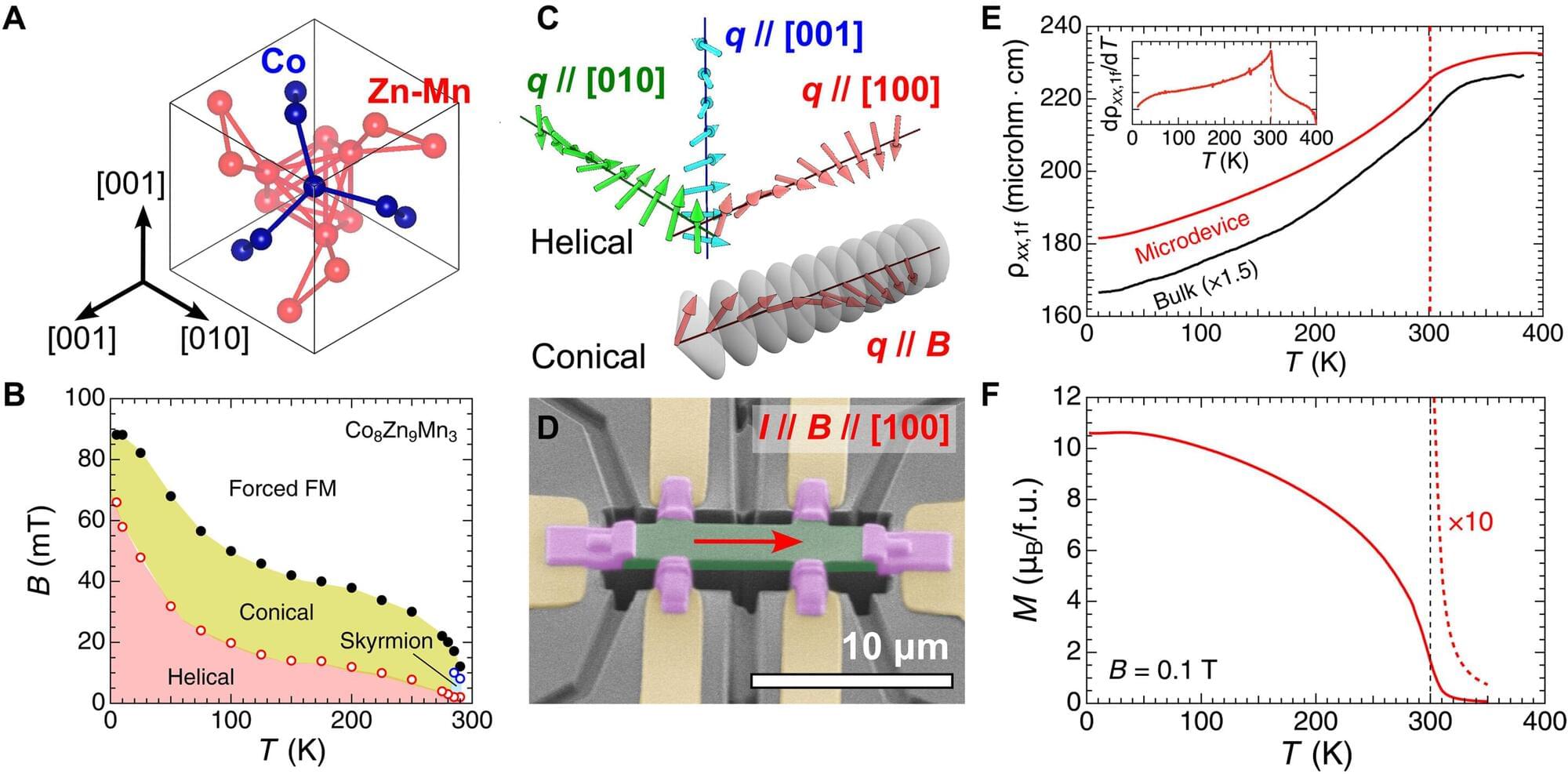
RIKEN physicists have discovered for the first time why the magnitude of the electron flow depends on direction in a special kind of magnet. This finding could help to realize future low-energy devices.
The work is published in the journal Science Advances.
In a normal magnet, all the spins of electrons point in the same direction. In a special class of magnets known as chiral magnets, the electron spins resemble a spiral staircase, having a helical organization.