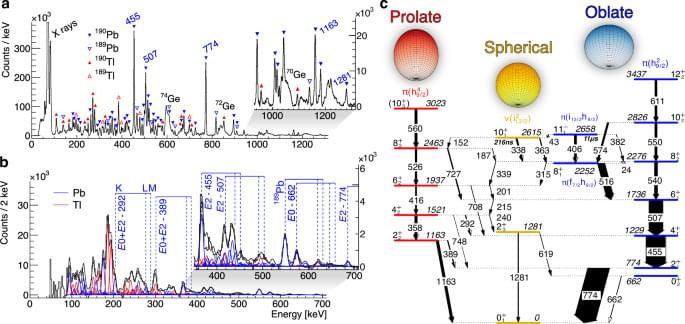
Since Morinaga proposed more than six decades ago that the excited \(0_2^+\) state in the 16 O nucleus was deformed1, a large body of experimental evidence has been collected to demonstrate that atomic nuclei can possess different shapes2. Apart from the lightest elements, shape coexistence has been suggested to be present in all nuclei3 and the competition of different configurations can result in several different shapes within the same nucleus4. Nevertheless, coexistence of three or more total energy minima near the ground state have been predicted to occur in only few regions in the chart of nuclei5, but direct experimental proof remained to be obtained. A notable example to date is the 186 Pb104 nucleus, where the three lowest-energy states are 0+ states, each assigned with a different shape – namely spherical, prolate and oblate6,7. The 186 Pb nucleus lies at the heart of the neutron-deficient Pb region, which has been a subject for numerous theoretical and experimental investigations3,8,9,10,11. Within the mean-field picture, the total energy curve along the quadrupole deformation shows spherical, prolate and oblate minima close in energy. These minima are related to the spherical Z = 82 shell gap, and prolate and oblate deformed gaps in the proton and neutron Nilsson orbitals, respectively. From a shell model perspective, the deformed minima (noted as \(\pi (h_9/24)\) for prolate and \(\pi (h_9/22)\) for oblate in the present work) are expected to have a complex spherical multiparticle-multihole configuration both for protons and neutrons10,11,12. Similar competition of different configurations is present in neighbouring isotopes around the N = 104 midshell13. In 188 Pb, in addition to low-lying deformed bands associated with predominantly prolate and oblate shapes14,15,16, three isomeric states assigned with different shapes17,18 have been proposed.
Intruding structures built on different configurations have also been observed in nuclei in the region around 186 Pb. In fact, the shape staggering of Hg isotopes observed in an isotopic shift experiment was a groundbreaking discovery in the 1970’s19 that triggered multiple investigations into shape coexistence. Laser spectroscopic measurements have examined the onset of ground-state deformation also in the even-mass Po and Pt isotopes20,21. Since the neutron-deficient Pb isotopes are spherical in their ground states22,23,24, the onset of deformation in the Pb isotopes can be assessed by investigating the \(2_1^+\) states. It is proposed that the heaviest Pb nucleus exhibiting collectivity associated with deformation is 194 Pb25, whereas in heavier Pb isotopes the underlying configurations of the lowest excited states arise from single-nucleon excitations in the seniority scheme leading to a spherical interpretation26.