Johannes Kalliauer, a postdoc at the MIT Concrete Sustainability Hub, studies how structures like DNA and bridges relate with Newtonian mechanics.



This new invention is highly scalable since its raw materials are commercially available and easy to access.
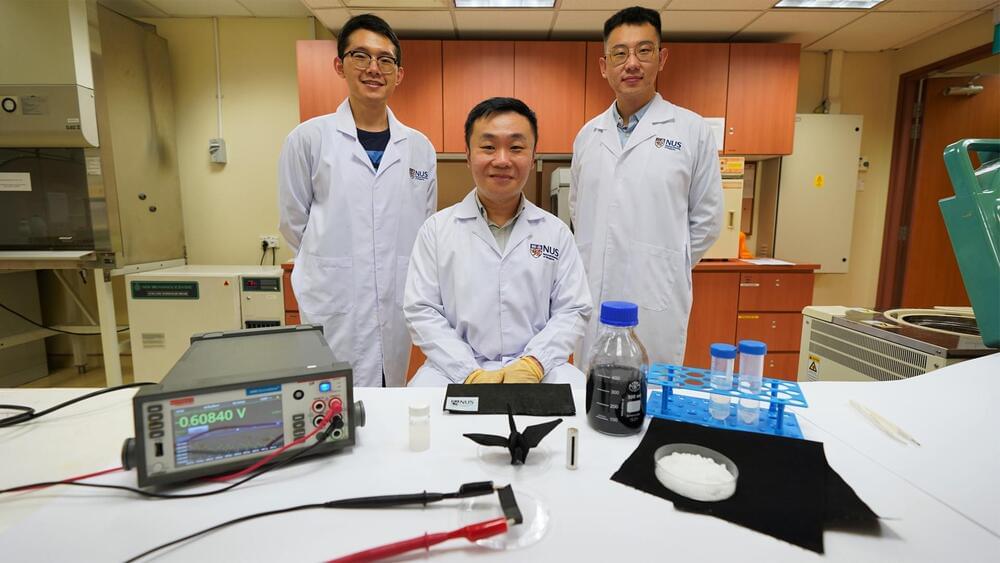
A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore’s (NUS) College of Design and Engineering (CDE) has developed a self-charging electricity generation (MEG) device that generates electricity from air moisture, according to a press release by the institution.
Imagine being able to generate electricity by harnessing moisture in the air around you with just everyday items like sea salt and a piece of fabric, or even powering everyday electronics with a non-toxic battery that is as thin as paper. A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore’s (NUS) College of Design and Engineering (CDE) has developed a new moisture-driven electricity generation (MEG) device made of a thin layer of fabric — about 0.3 millimetres (mm) in thickness — sea salt, carbon ink, and a special water-absorbing gel.
The concept of MEG devices is built upon the ability of different materials to generate electricity from the interaction with moisture in the air. This area has been receiving growing interest due to its potential for a wide range of real-world applications, including self-powered devices such as wearable electronics like health monitors, electronic skin sensors, and information storage devices.
Key challenges of current MEG technologies include water saturation of the device when exposed to ambient humidity and unsatisfactory electrical performance. Thus, the electricity generated by conventional MEG devices is insufficient to power electrical devices and is also not sustainable.
Imagine being able to generate electricity by harnessing moisture in the air around you with just everyday items like sea salt and a piece of fabric, or even powering everyday electronics with a non-toxic battery that is as thin as paper. A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore’s (NUS) College of Design and Engineering (CDE) has developed a new moisture-driven electricity generation (MEG) device made of a thin layer of fabric—about 0.3 millimeters (mm) in thickness—sea salt, carbon ink, and a special water-absorbing gel.
The concept of MEG devices is built upon the ability of different materials to generate electricity from the interaction with moisture in the air. This area has been receiving growing interest due to its potential for a wide range of real-world applications, including self-powered devices such as wearable electronics like health monitors, electronic skin sensors, and information storage devices.
Key challenges of current MEG technologies include water saturation of the device when exposed to ambient humidity and unsatisfactory electrical performance. Thus, the electricity generated by conventional MEG devices is insufficient to power electrical devices and is also not sustainable.
Iron could massively boost ocean algae populations.
Scientists suggest we could fertilize the world’s oceans with iron to fight climate change. Iron would lead to phytoplankton blooms, which would help to pull carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere.
One “very conservative” estimate suggests a gigaton of carbon dioxide could be removed per year with this method.
Scientists have hatched a plan to flood the world’s oceans with phytoplankton in a bid to avoid the worst effects of climate change.
Scientists are seriously considering blocking out the Sun. To be more precise, they want to reflect a fraction of the sunlight that reaches Earth back out into the Solar System via a method called solar geoengineering.
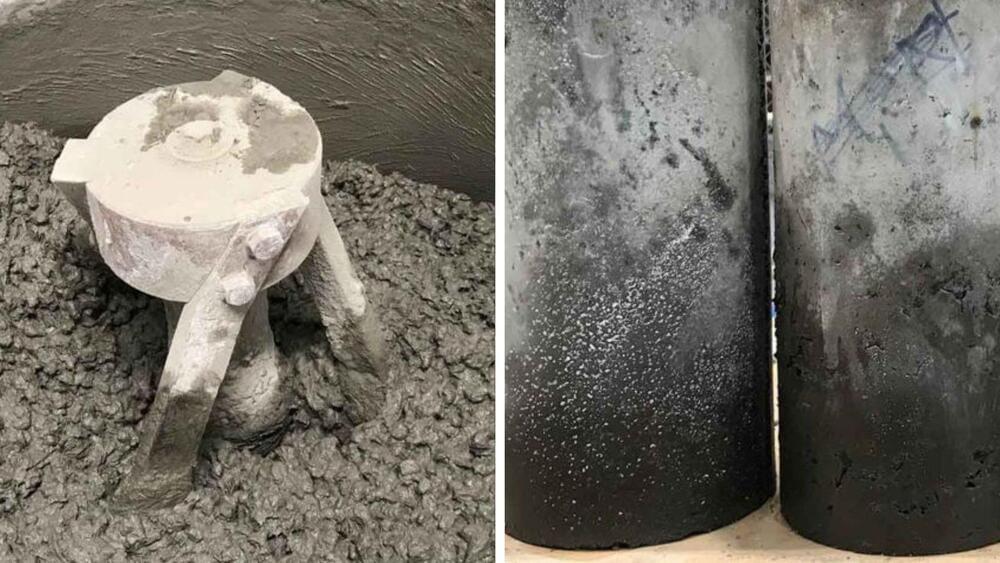

The new concrete made of tyres will be eco-friendly and cheaper. Engineers from RMIT succeeded in producing concrete from materials such as gravel, tyre, rubber, and crushed rock. It is believed that this innovation will be cheaper and eco-friendly. The team is now looking into reinforcing the concrete to see how it can work in structural elements. A group of researchers from the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT), has succeeded in replacing the classic method of making concrete, which is made of gravel and crushed rock, with rubber from discarded tyres that are suitable for building codes.
According to the press release that has been published by the university, new greener and lighter concrete also promises to reduce manufacturing and transportation costs significantly. Small amounts of rubber particles from tyres are already used to replace these concrete aggregates. However, the previous process of replacing all concrete with aggregates had not been successful.
The study published in the Resources, Conservation & Recycling journal showed the tyres’ manufacturing process.
Lead author and Ph.D. researcher from RMIT University’s School of Engineering, Mohammad Momeen Ul Islam, stated that this work was revolutionary because it showed what could be done with recycled rubber pieces.
Full Story:
Australia’s RMIT engineering team made greener and lighter concrete.

View insights.
Since 2016, engineering firm NuScale has been working toward getting approval for a first-of-its-kind nuclear reactor, and late last week, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) gave it the green light. The company’s pint-sized nuclear reactor has numerous safety benefits over larger reactors, and the small size makes it possible to build them at a centralized facility before shipping them to their final destination.
Nuclear power seems to flip between savior and boogeyman every few years. As climate change escalates due to the use of fossil fuels, nuclear is seen as a way to reduce carbon emissions while maintaining high electricity generation. However, all it takes is one accident like Fukushima or a reminder that Chernobyl is still incredibly dangerous decades later to make people second-guess the construction of new fission generators.
NuScale, which has been anticipating approval of this design since the last technology review in 2020, says its small modular reactor (SMR) addresses these concerns. It’s based on a “Multi-Application Small Light Water Reactor” developed at Oregon State University in the early 2000s. It has a compact uranium nuclear core along with helical coil steam generators inside the same steel reactor vessel. So, it generates power through the same mechanism as a traditional reactor (no fancy uranium or thorium salts here), but each SMR only produces about 50 MWe (megawatts electrical) compared with 1,000 or more in existing reactor designs.
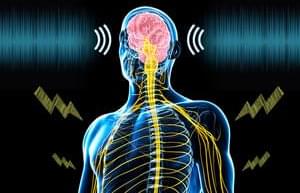
A University of Minnesota Twin Cities-led team has found that electrical stimulation of the body combined with sound activates the brain’s somatosensory or “tactile” cortex, increasing the potential for using the technique to treat chronic pain and other sensory disorders. The researchers tested the non-invasive technique on animals and are planning clinical trials on humans in the near future.
The paper is published in the Journal of Neural Engineering, a highly regarded, peer-reviewed scientific journal for the interdisciplinary field of neural engineering.
During the experiments, the researchers played broadband sound while electrically stimulating different parts of the body in guinea pigs. They found that the combination of the two activated neurons in the brain’s somatosensory cortex, which is responsible for touch and pain sensations throughout the body.
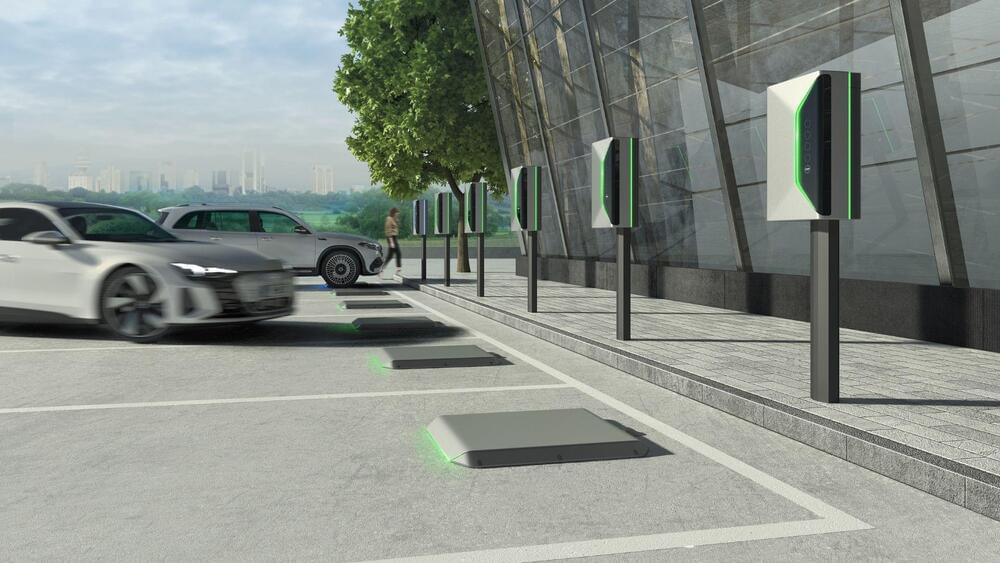

The companies aim to achieve standardization in inductive charging systems.
Siemens and MAHLE have announced that the two companies signed a letter of intent.
They are teaming up to develop infrastructure and automotive engineering and to provide wireless charging to electric vehicles.
The aim is to close gaps to ensure full interoperability between vehicles and the charging infrastructure.
Siemens.
Two companies have announced that they have signed a letter of intent to collaborate in the field of inductive charging of electric vehicles.

Sustained space exploration will require infrastructure that doesn’t currently exist: buildings, housing, rocket landing pads.
So, where do you turn for construction materials when they are too big to fit in your carry-on and there’s no Home Depot in outer space?
“If we’re going to live and work on another planet like Mars or the moon, we need to make concrete. But we can’t take bags of concrete with us—we need to use local resources,” said Norman Wagner, Unidel Robert L. Pigford Chair of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the University of Delaware.

For the first time ever, electricity is delivered through heated supercritical carbon dioxide.
The method has so far succeeded in adding 10 kilowatts to the grid.
Researchers were inspired by elevators to create the system.
They are now trying to get it to function at higher temperatures.
For the first time ever, Sandia National Laboratories have used heated supercritical carbon dioxide instead of steam to generate electricity, according to a press release by the organization. The breakthrough happened at the Sandia-Kirtland Air Force Base electrical grid.
A non-toxic stable material
The organization described supercritical carbon dioxide as a non-toxic, stable material that is under so much pressure that it behaves like both a liquid and a gas. Because it stays within the system and is not released as a greenhouse gas, it can get much hotter than steam (1,290 degrees Fahrenheit or 700 Celsius). These temperatures allow it to be much more efficient at turning heat from power plants into energy.