Still from the future.
A potential fertility treatment involves taking skin cells and reverse engineering them into eggs and sperm.

One year after winter storms crippled Texas’s electricity grid, contributing to more than 200 deaths, a Cornell University-led analysis recommends contracting improvements to reduce decentralized energy markets’ vulnerability to rare events.
Such “energy-only” markets rely on investors to anticipate demand for all conditions and build appropriate resiliency into the system. They allow prices to soar during extreme events to incentivize preparedness.
But in Texas, where Winter Storm Uri caused catastrophic blackouts over five consecutive days of frigid temperatures, the crisis revealed the market’s failure to manage risk as designed, says Jacob Mays, assistant professor in the School of Civil and Environmental Engineering at Cornell. Winterization investment fell short, he said, because the payoff proved too distant and uncertain.


Feb 2 (Reuters) — State-owned China National Nuclear Corp (CNNC) has signed a contract in Argentina to build the $8 billion Atucha III nuclear power plant using China’s Hualong One technology, reviving a deal that had been stalled for years.
CNNC said on its WeChat account late on Tuesday that ithad signed an engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contract, which comes ahead of Argentine President Alberto Fernandez’s trip to China later this week.
Progress on the nuclear deal between the two nations had stalled since it was first negotiated by the administration of former President Cristina Fernandez, a left-wing populist who left office in 2015. She is now Argentina’s vice president.
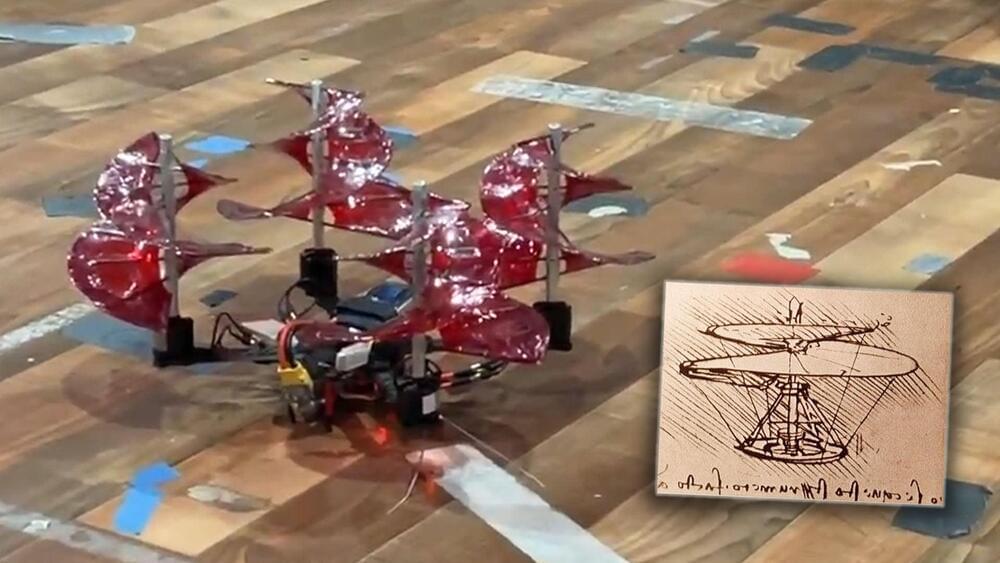

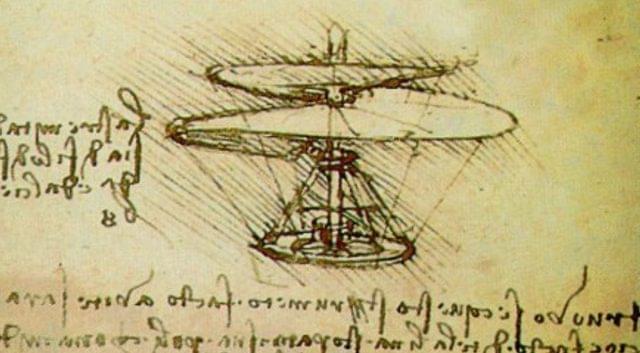
DaVinci penned the aerial screw design in the 1400s, way before air travel was a thing. Now, it’s being put to action with this student-built drone.
Drones aren’t anything new —multi-rotor aircraft are becoming a bigger part of people’s lives every day. From the latest batch of up-and-coming urban air mobility companies to hobby applications, electric aircraft with four or more motors are commonplace, and generally, they use conventional multi-bladed propellers to keep themselves aloft. That’s not what’s going on with this particular drone developed by engineering students at the University of Maryland, though.
Assembled for a student design competition hosted by the Vertical Flight Society, it’s a mixture of old and new. With rotors reminiscent of Leonardo DaVinci’s aerial screw illustrations from the late 1490s, it flies like any other drone would, all while looking extremely bizarre and having interesting flight characteristics.
Ben RayfieldWeather control tech exists, to some extent. EMP weapons exist. If there was a 477 mile long lightning, it was probably either due to the sun or is a weapon or a terraforming experiment.
Quinn SenaAuthor.
GIPHY
Genevieve Klien shared a link.
According to a series of etherscan transactions, an attacker has exploited Wormhole, a bridge between the Ethereum and Solana blockchains, for close to $323 million in ETH.
Wormhole is a bridging protocol that enables assets to move across various blockchain protocols. When a user sends assets from one chain to another, the bridge locks the assets and mints a wrapped version of the funds on the destination chain.

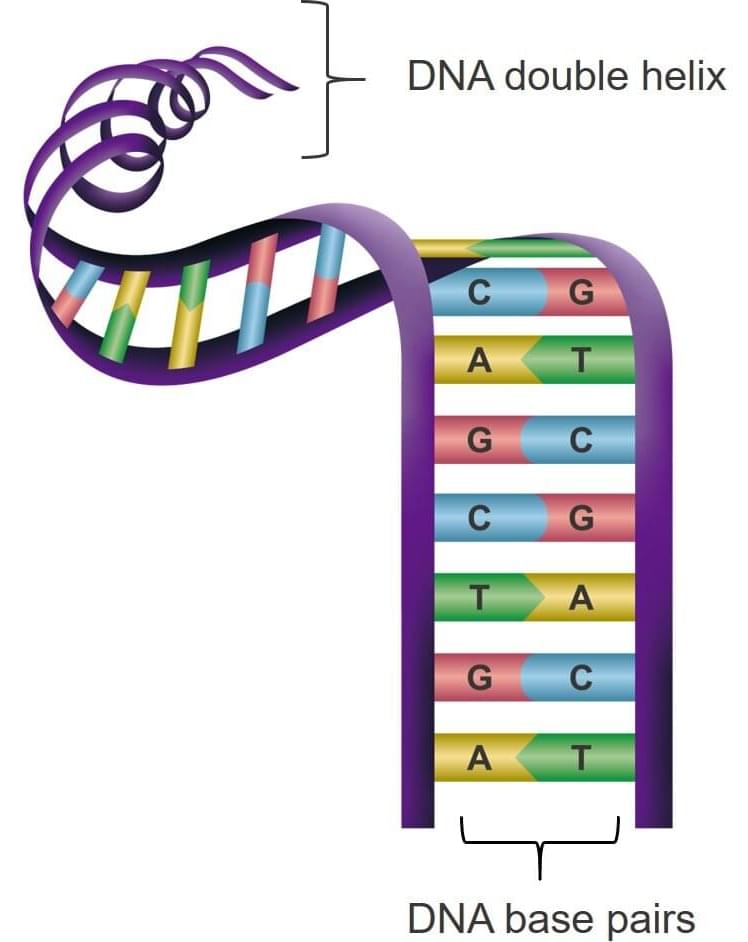
Researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have used microscopic strands of DNA to guide the assembly of gel blocks that are visible to the naked eye.
The hydrogel blocks, which measure up to 2mm in length and contain DNA on their surface, self-assembled in around 10–15 minutes when mixed in a solution, the scientists reported today in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“These hydrogel blocks are, we believe, the largest objects so far that have been programmed by DNA to form organized structures,” said Dr. Vyankat Sontakke, first author of the study and a postdoctoral researcher in the OIST Nucleic Acid Chemistry and Engineering Unit.

Stelco, which is a steelmaker producing flat-rolled, cold-rolled, and hot-rolled steel products, has announced that it is entering the electric vehicle battery recycling market through agreements with Primobius GmbH.
The company executed binding licensing and option agreements with Primobius to commercialize Primobius’ EV battery recycling and processing technologies in North America. Under the agreement, Stelco will be able to advance commercial lithium-ion battery feedstock sourcing agreements. It will also allow the company to begin the engineering and approval processes. The agreement enables Primobius the right to acquire between 25% and 50% equity in Stelco’s wholly-owned subsidiary.
The proposed Lake Erie Works refinery will enable Stelco to join the ranks of lithium-ion battery recycling leaders in North America. The integrated shredding and hydrometallurgical refinery will produce up to 18,400 net tons per year of nickel, manganese, and cobalt sulfates, and lithium hydroxide and carbonate. It’s expected to generate up to 40,000 net tons per year of scrap steel that Stelco will recycle into its steelmaking operations.