A radical research program in deep design.

Researchers have created nearly freestanding nanostructured two-dimensional (2D) gold monolayers, an impressive feat of nanomaterial engineering that could open up new avenues in catalysis, electronics, and energy conversion.
The research has been published in Nature Communications.
Gold is an inert metal which typically forms a solid three-dimensional (3D) structure. However, in its 2D form, it can unlock extraordinary properties, such as unique electronic behaviors, enhanced surface reactivity, and immense potential for revolutionary applications in catalysis and advanced electronics.

Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly automating tasks like translation, text classification and customer service. But tapping into an LLM’s power typically requires users to send their requests to a centralized server—a process that’s expensive, energy-intensive and often slow.
Now, researchers have introduced a technique for compressing an LLM’s reams of data, which could increase privacy, save energy and lower costs. Their findings are published on the arXiv preprint server.
The new algorithm, developed by engineers at Princeton and Stanford Engineering, works by trimming redundancies and reducing the precision of an LLM’s layers of information. This type of leaner LLM could be stored and accessed locally on a device like a phone or laptop and could provide performance nearly as accurate and nuanced as an uncompressed version.
Researchers at the UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME) have realized a new design for a superconducting quantum processor, aiming at a potential architecture for the large-scale, durable devices the quantum revolution demands.
Unlike the typical quantum chip design that lays the information-processing qubits onto a 2D grid, the team from the Cleland Lab has designed a modular quantum processor comprising a reconfigurable router as a central hub. This enables any two qubits to connect and entangle, where in the older system, qubits can only talk to the qubits physically nearest to them.
“A quantum computer won’t necessarily compete with a classical computer in things like memory size or CPU size,” said UChicago PME Prof. Andrew Cleland.
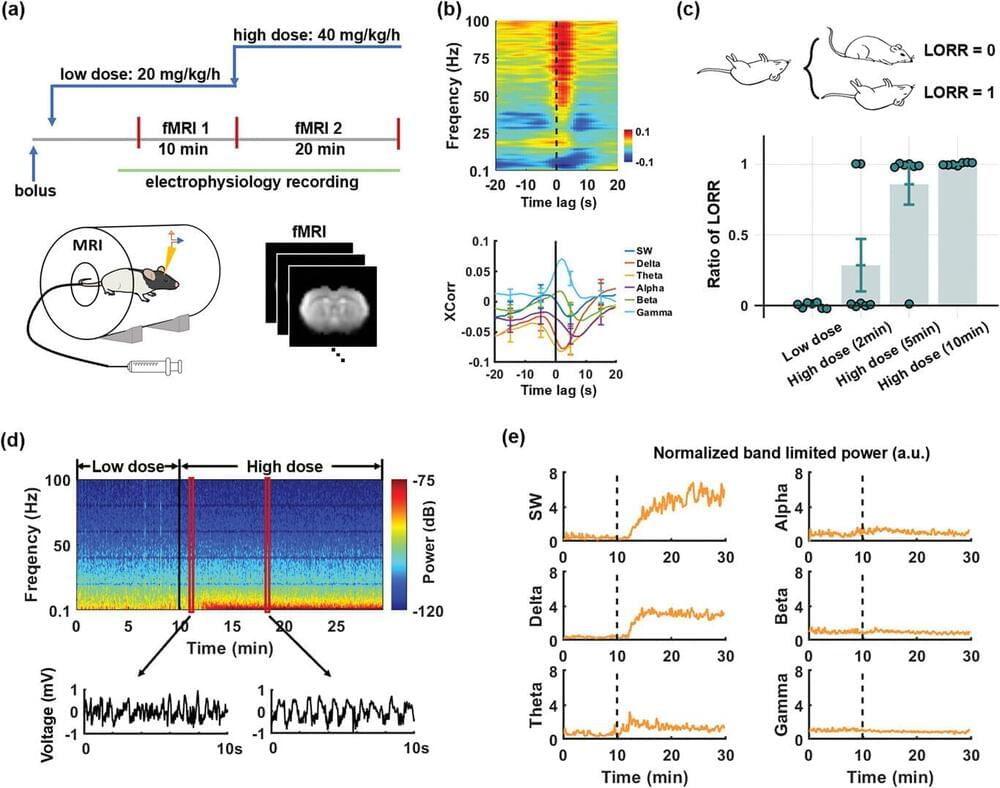
The shift from an awake state to unconsciousness is a phenomenon that has long captured the interest of scientists and philosophers alike, but how it happens has remained a mystery—until now. Through studies on rats, a team of researchers at Penn State has pinpointed the exact moment of loss of consciousness due to anesthesia, mapping what happens in different brain regions during that moment.
The study has implications for humans as well as for other types of loss of consciousness, such as sleep, the researchers said. They published their results in Advanced Science.
“People in the neuroscience field generally understand what happens to a patient who is going under anesthesia at a molecular level,” said corresponding author Nanyin Zhang, the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Chair in Brain Imaging and professor of biomedical engineering at Penn State.
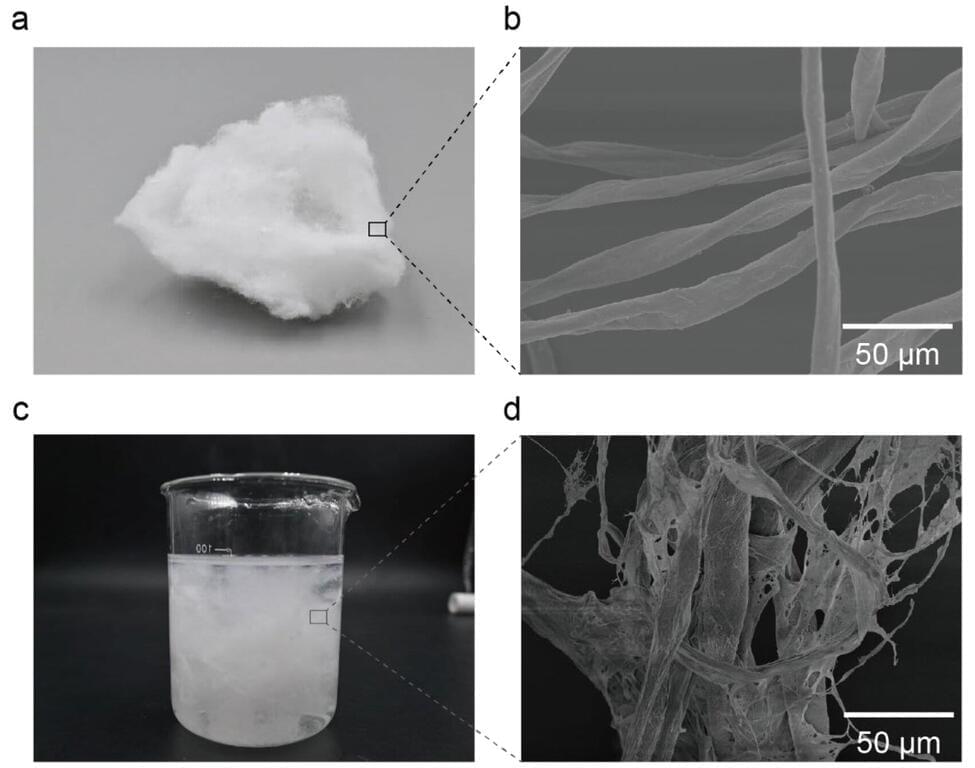
Wuhan University-led research is reporting the development of a revivable self-assembled supramolecular biomass fibrous framework (a novel foam filter) that efficiently removes microplastics from complex aquatic environments.
Plastic waste is a growing global concern due to significant levels of microplastic pollution circulating in soil and waterways and accumulating in the environment, food webs and human tissues. There are no conventional methods for removing microplastics, and developing strategies to handle diverse particle sizes and chemistries is an engineering challenge.
Researchers have been looking for affordable, sustainable materials capable of universal microplastic adsorption. Most existing approaches involve expensive or difficult-to-recover adsorbents, fail under certain environmental conditions, or only target a narrow range of microplastic types.

The new sound-based method moves objects regardless of surroundings or properties.
Researchers have successfully manipulated the movement of objects using sound. They directed floating objects around obstacles in an aquatic environment, unveiling new possibilities for noninvasive, targeted drug delivery and other biomedical applications.
Researchers from EPFL’s School of Engineering employed optics-inspired techniques to achieve this object manipulation.
“Optical tweezers work by creating a light ‘hotspot’ to trap particles, like a ball falling into a hole. But if there are other objects in the vicinity, this hole is difficult to create and move around,” said Romain Fleury, head of the Laboratory of Wave Engineering in EPFL’s School of Engineering.

PRESS RELEASE — Thirty years ago, the University of the Andes made the first internet connection in Colombia, and on Tuesday, December 3, the country’s first quantum computer will be unveiled. This acquisition marks a turning point in education and technological research, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and enhancing ongoing efforts by researchers at the University of the Andes and other institutions.
The University’s Faculties of Science and Engineering announced the arrival of the device, which will enable students and professors to explore fundamental aspects of quantum computing. This emerging technology seeks to solve problems and process information differently by leveraging the laws of quantum physics.
Professor Julián Rincón, a theoretical physicist, explains that this quantum computer employs a technique known as Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and operates at room temperature. This makes it particularly suitable for educational purposes, as it is easy to assemble and provides a straightforward way to test fundamental concepts. “This isn’t just a faster conventional computer; it’s a completely new way of processing information, based on the laws of quantum physics,” he clarifies.

Batteries made from waste and methane offer lower CO2 emissions than current technologies.
It’s also being claimed that the technology has the potential to improve fast-charging speed by up to 50%, making EV ownership even more convenient. Lithium-sulfur batteries are expected to cost less than half the price per kWh of current lithium-ion batteries, according to Stellantis.
The batteries will be produced using waste materials and methane, with significantly lower CO2 emissions than any existing battery technology. Zeta Energy battery technology is intended to be manufacturable within existing gigafactory technology and would leverage a short, entirely domestic supply chain in Europe or North America, according to a press release.
Ned Curic, Stellantis’s Chief Engineering and Technology Officer, stated that the collaboration with Zeta Energy is another step in helping advance the company’s electrification strategy as they work to deliver clean, safe, and affordable vehicles.