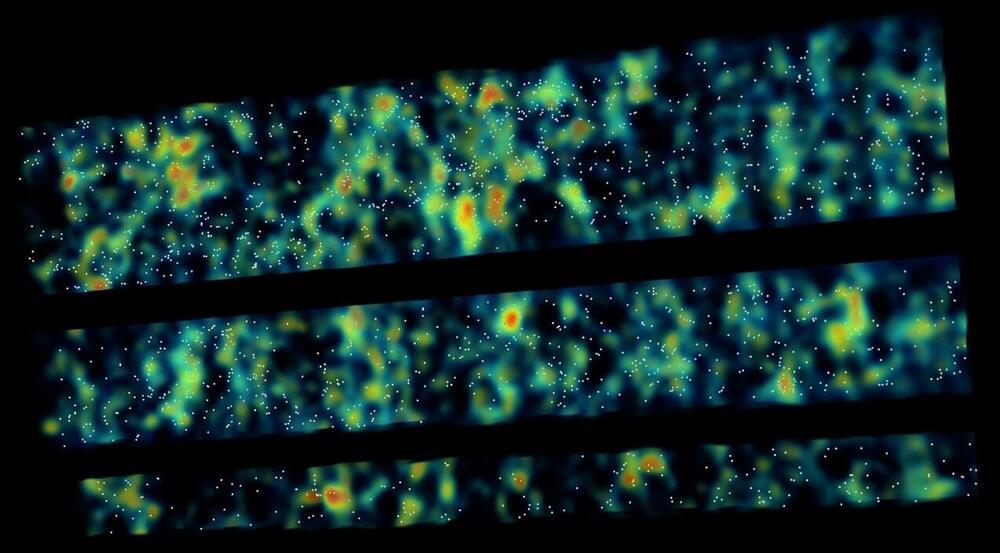
The ancestors of some of the largest galaxy clusters have been hiding in plain sight. New work led by Carnegie’s Andrew Newman demonstrates a new technique for identifying the precursors of the most extreme galactic environments. The team’s findings are published in Nature.
Like all of us, galaxies are shaped and molded by their surroundings. To obtain a complete picture of the various physical influences on a galaxy’s lifecycle, it’s crucial to trace the emergence of properties caused by environmental factors as they arise.
“We’ve known for a long time that the colors, masses, and shapes of galaxies depend on their cosmic environment, but there’s a lot we don’t know about when and how those differences appeared,” Newman said.