In this edition of Inverse Daily, read about an egg-shaped planet too close to its sun, how Twitch streamer Amouranth thinks the medium should change, and more.
Category: evolution – Page 129
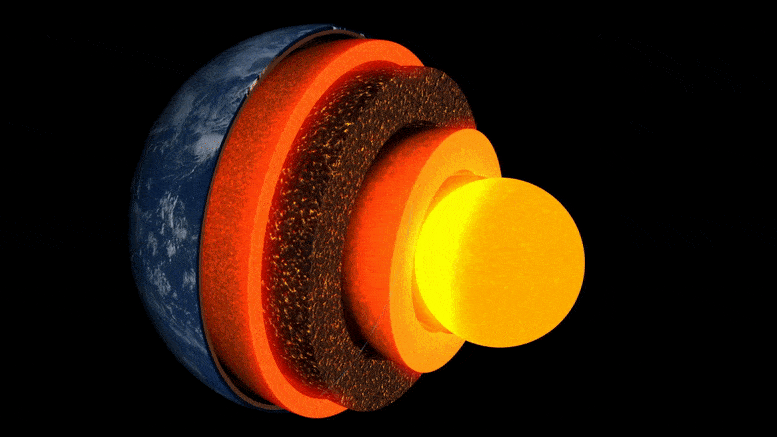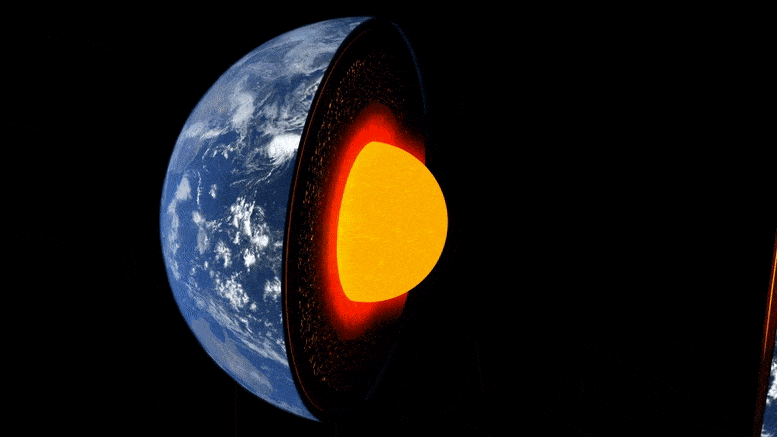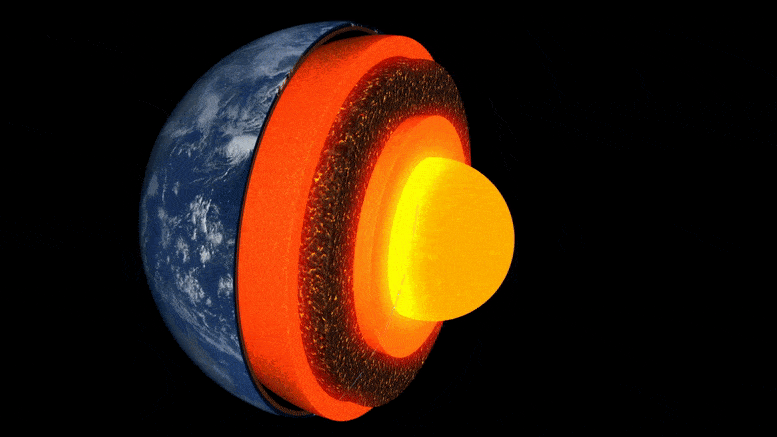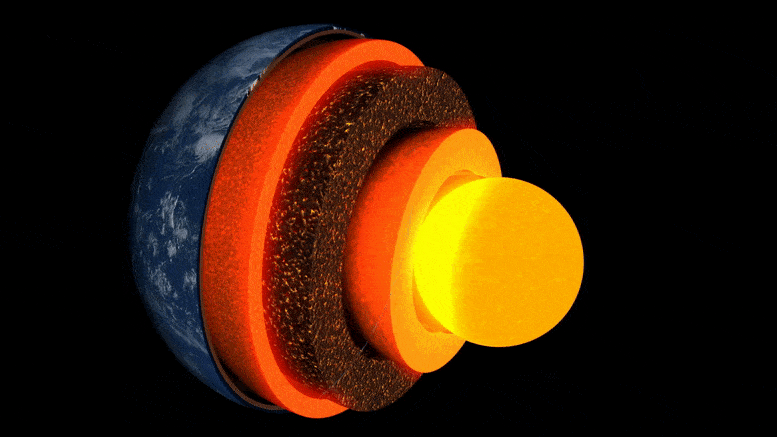
Earth’s Interior Is Cooling “Much Faster Than Expected”
Researchers at ETH Zurich have demonstrated in the lab how well a mineral common at the boundary between the Earth’s core and mantle conducts heat. This leads them to suspect that the Earth’s heat may dissipate sooner than previously thought.
The evolution of our Earth is the story of its cooling: 4.5 billion years ago, extreme temperatures prevailed on the surface of the young Earth, and it was covered by a deep ocean of magma. Over millions of years, the planet’s surface cooled to form a brittle crust. However, the enormous thermal energy emanating from the Earth’s interior set dynamic processes in motion, such as mantle convection, plate tectonics, and volcanism.
Still unanswered, though, are the questions of how fast the Earth cooled and how long it might take for this ongoing cooling to bring the aforementioned heat-driven processes to a halt.
Profound Discovery on Origins of Life on Earth — Evolution of Metal-Binding Proteins
Researchers explored the evolution of metal-binding proteins across billions of years.
Addressing one of the most profoundly unanswered questions in biology, a Rutgers-led team has discovered the structures of proteins that may be responsible for the origins of life in the primordial soup of ancient Earth.
The study appears in the journal Science Advances.
Mysterious Cosmic “Spider” Found To Be Source of Powerful Gamma-Rays
Investigated by the SOAR Telescope operated by NOIRLab, the binary system is the first to be found at the penultimate stage of its evolution. Using the 4.1-meter SOAR Telescope in Chile, astronomers have discovered the first example of a binary system where a star in the process of becoming a white.
MIT physicists and colleagues have discovered the “secret sauce” behind some of the exotic properties of a new quantum material that has transfixed physicists due to those properties, which include superconductivity. Although theorists had predicted the reason for the unusual properties of the material, known as a kagome metal, this is the first time that the phenomenon behind those properties has been observed in the laboratory.

Did aliens genetically engineer humans 780,000 years ago?
The first humans emerged on Earth about 4 million years ago, but new evidence from the study of human evolution has revealed compelling evidence that a small group of these hominins was genetically modified by ancient alien visitors to create the first Homo sapiens.
Researcher and author Daniella Fenton has thoroughly analyzed humanity’s earliest origins and its sudden acceleration in brain development nearly 800,000 years ago, and this research has led to a major revelation.
“Homo sapiens is the creation of ancient astronauts who came through a wormhole in the Pleiades star cluster more than 780,000 years ago.”
The Australian researcher, an expert in equine lineages and gene expression, discovered numerous genetic changes that mark humans as abnormal when compared to modern primate species, some so extreme that they are best explained by advanced genetic engineering.
Full Story:

Christians point to genetics breakthroughs to show Adam and Eve are not incompatible with evolution
Many Christians have rejected the scientific theory of evolution in part because they think it rules out the existence of a historical Adam and Eve. Yet some scientists and theologians argue that recent breakthroughs in genetics make a historical Adam and Eve compatible with evolution, and that this development may help bridge what many see as a conflict between faith and science.
“For over 160 years, the societal conflict over evolution has been deep and stubborn. But now, in a surprise twist, evolutionary science is making space for Adam and Eve,” S. Joshua Swamidass, an associate professor at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri, told Fox News Digital. “It turns out that the theological questions are about genealogical ancestry, not genetics. In this paradigm shift, we are finding a better way forward, a better story to tell.”
In his book “The Genealogical Adam and Eve: The Surprising Science of Universal Ancestry,” Swamidass argues that genetics and evolutionary theory do not conflict with the existence of Adam and Eve, universal ancestors of all humans whom Jesus died to save.
A 238-year-old invention could help us survive Venus’ hellish atmosphere
The study of Venus presents an opportunity to model the evolution of planetary environments, which can serve as a reference for what could happen in the future.
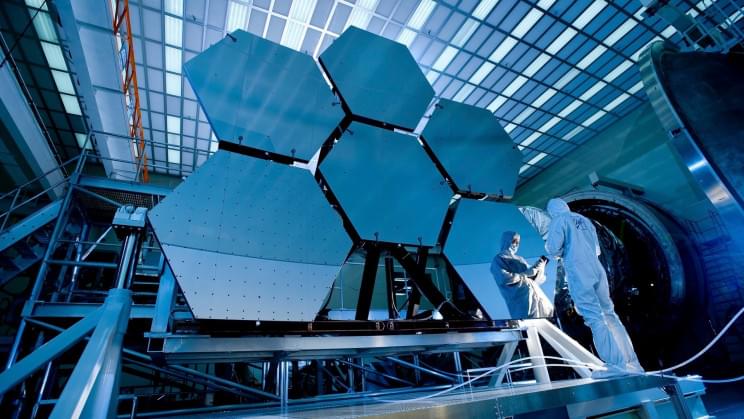

James Webb Space Telescope: The $10B Successor of the Hubble
It makes space travel look cheap.
Humans have been looking at the stars for millenia, but it was just over 30 years ago that the Hubble Space Telescope launched, and we started getting a really good look at what’s out there. Hubble was beset with more than a decade of setbacks before its launch in 1990. Then, just after taking its position orbiting Earth, astronomers realized that something wasn’t right. It took engineers another three years to fix a manufacturing error that had left one of the mirrors misshapen by one-millionth of a meter. Ultimately, that imperfection was enough to render the telescope’s mirrors effectively useless. The long wait was worth it, though. The Hubble enabled dozens of breakthroughs in astronomy. It also took beautiful pictures. A recent version of its famous “Hubble Deep Field” image includes galaxies that are 13 billion lightyears away, making them the farthest objects ever photographed.
NASA is scheduled to soon launch what it calls the “successor” to Hubble: the James Webb Space Telescope. Like the Hubble, the Webb telescope is also designed to take extraordinarily precise measurements of “Ultraviolet and visible light emitted by the very first luminous objects [and which] has been stretched or ‘redshifted’ by the universe’s continual expansion and arrives today as infrared light.” Webb will also study objects closer to home, such as planets and other bodies in our solar system with the aim of determining more about their origin and evolution. Webb will also observe exoplanets located in their stars’ habitable zones, to search for signatures of habitability, and to learn about their chemical compositions.