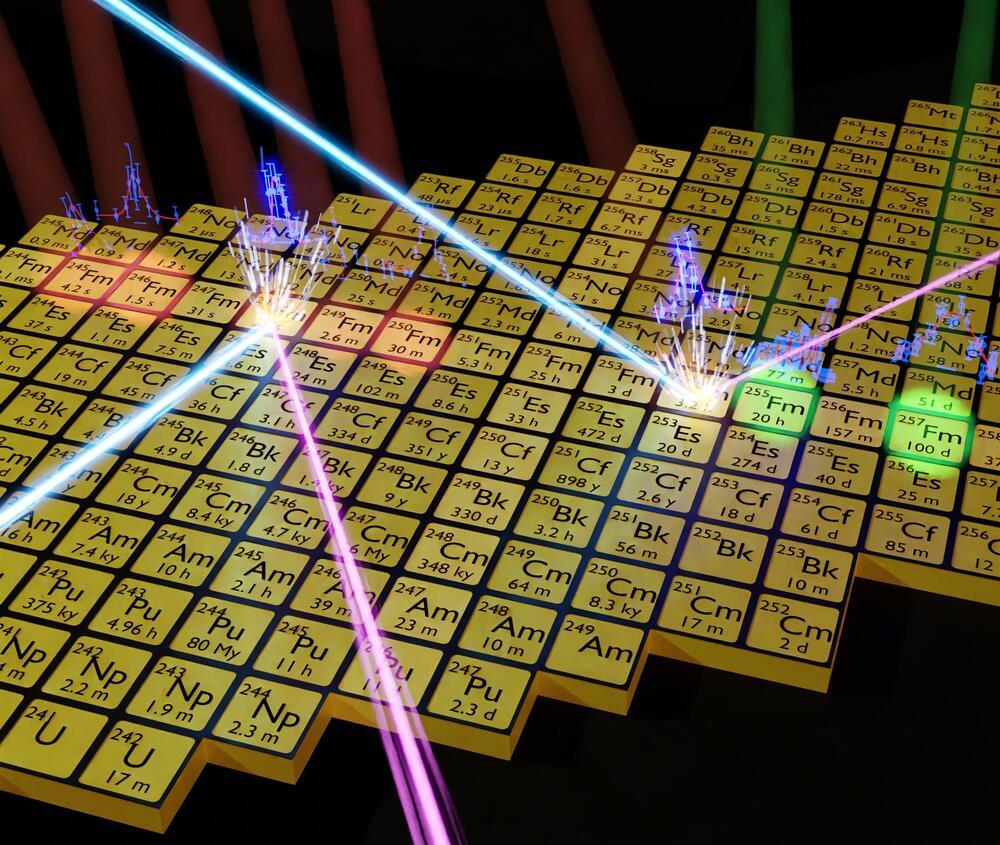
Fermium studies indicate nuclear shell effects diminish as nuclear mass increases, emphasizing macroscopic influences in superheavy elements.
Where does the periodic table of chemical elements end and which processes lead to the existence of heavy elements? An international research team has conducted experiments at the GSI/FAIR accelerator facility and at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz to investigate these questions.
Their research, published in the journal Nature, provides new insights into the structure of atomic nuclei of fermium (element 100) with different numbers of neutrons. Using forefront laser spectroscopy techniques, the team traced the evolution of the nuclear charge radius and found a steady increase as neutrons were added to the nuclei. This indicates that localized nuclear shell effects have a reduced influence on the nuclear charge radius in these heavy nuclei.