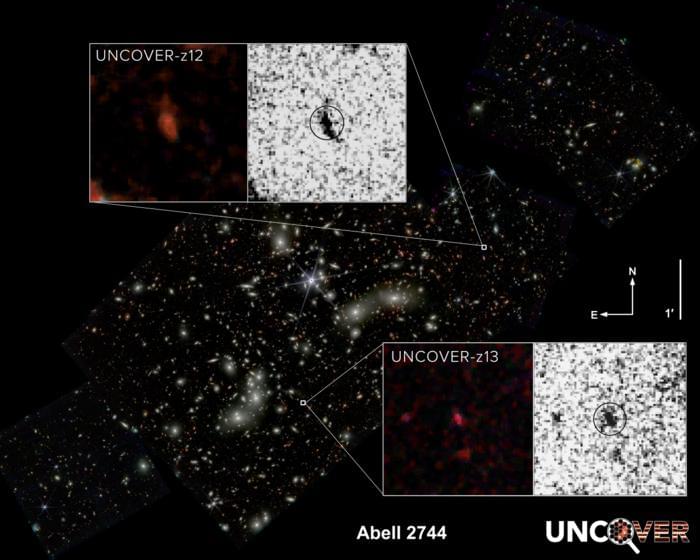
A recent study published in Astrophysical Journal Letters discusses how new data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has identified the second-and fourth-farthest and oldest galaxies in the universe, which are located approximately 33 billion light years from Earth and part of Abell 2744, also known as Pandora’s Cluster. The reason the galaxies are estimated to be 33 billion light years from Earth is due to the expansion of the universe, but astronomers hypothesize the two were first formed approximately 330 million years after the Big Bang, which is incredibly young in cosmic terms.
The two galaxies are named UNCOVER z-12 and UNCOVER z-13 since they were discovered by the JWST UNCOVER (Ultradeep NIRSpec and NIRCam ObserVations before the Epoch of Reionization) team. This study was conducted by an international team of more than two dozen researchers, who refer to the two galaxies as appearing like a peanut and fluffy ball, and this study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of the first galaxies after the Big Bang.
“Very little is known about the early universe, and the only way to learn about that time and to test our theories of early galaxy formation and growth is with these very distant galaxies,” said Dr. Bingjie Wang, who is a postdoctoral scholar in the Penn State Eberly College of Science and lead author of the study. “Prior to our analysis, we knew of only three galaxies confirmed at around this extreme distance. Studying these new galaxies and their properties has revealed the diversity of galaxies in the early universe and how much there is to be learned from them.”