Modern scientists aren’t content with predicting how life evolves. They want to shape it.



Author: Sharika Dhakappa The Big Bang is the most widely accepted theory of how the universe originated. Most physicists believe that the tremendously large universe we observe today began as a tiny, dense point. If the evolution of the universe till today were to be depicted as a movie, the Big Bang would be the beginning of it. We do not yet know what came before the Big Bang or whether that is even a meaningful question to ask. The cosmic movie would run for 13.8 billion years which is the current age of the universe as estimated by the WMAP satellite.

What is the weather like on water-rich exoplanets? This is something a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to shed light on as a team of researchers conducted laboratory experiments to simulate how hazy skies might form on such exoplanets throughout the cosmos. Haze changes the way light reacts to various gases within a planet’s atmosphere, which alters what astronomers detect, as well. This study comes as the number of potential water-rich exoplanets continues to grow and holds the potential to help scientists better understand the conditions necessary for the formation and evolution of water-rich exoplanets, including how life might form and evolve on them, whether on their surfaces or in their atmospheres.
Artist illustration of water-rich exoplanets comprised of hazy atmospheres, which was the focus of this study. (Credit: Roberto Molar Candanosa/Johns Hopkins University)
“The big picture is whether there is life outside the solar system, but trying to answer that kind of question requires really detailed modeling of all different types, specifically in planets with lots of water,” said Dr. Sarah Hörst, who is an associate professor of Earth and planetary sciences at Johns Hopkins University and a co-author on the study. “This has been a huge challenge because we just don’t have the lab work to do that, so we are trying to use these new lab techniques to get more out of the data that we’re taking in with all these big fancy telescopes.”

With a gravitational field so strong that not even light can escape its grip, black holes are probably the most interesting and bizarre objects in the universe.
Due to their extreme properties, a theoretical description of these celestial bodies is impossible within the framework of Newton’s classical theory of gravity. It requires the use of general relativity, the theory proposed by Einstein in 1915, which treats gravitational fields as deformations in the fabric of space-time.
Black holes are usually formed from the collapse of massive stars during their final stage of evolution. Therefore, when a black hole is born, its mass does not exceed a few dozen solar masses.
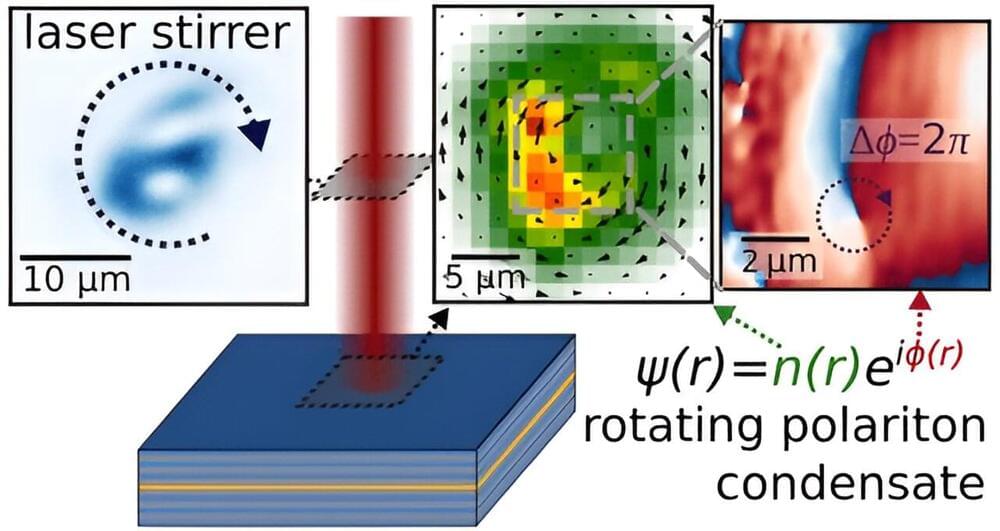
By using a special combination of laser beams as a very fast stirrer, RIKEN physicists have created multiple vortices in a quantum photonic system and tracked their evolution. This system could be used to explore exotic new physics related to the emergence of quantum states from vortex matter. The research is published in the journal Nano Letters.
In principle, if you were to swim in a pool filled with a superfluid, a single stroke would be all you need to swim an infinite number of laps. That’s because, unlike normal fluids like water, superfluids have no resistance to motion below a certain velocity.
Superfluids also behave weirdly when stirred. “If you stir a bucket of water, you typically get just one big vortex,” explains Michael Fraser of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science. “But when you rotate a superfluid, you initially create one vortex. And when you rotate it faster, you get progressively more and more vortices of precisely the same size.”

The Four Realms of Existence by Joseph LeDoux and Consciousness by John Parrington tell us a lot about human cognition, brain structure and evolution – but most of all they demonstrate how far this most tricky of quests still has to go.
Investigators from the laboratory of Ali Shilatifard, Ph.D., the Robert Francis Furchgott Professor and chair of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, have discovered a new repeat gene cluster sequence that is exclusively expressed in humans and non-human primates.
The discovery, detailed in a study published in Science Advances, is a breakthrough for human genome biology and has wide-ranging implications for future research in transcriptional regulation, human evolution, and the study of repetitive DNA sequences, according to the authors.
“This is an unbelievable discovery of the first elongation factor that is repeated within the human genome and is very primate-specific,” said Shilatifard, who is also director of the Simpson Querrey Institute for Epigenetics and a professor of Pediatrics.

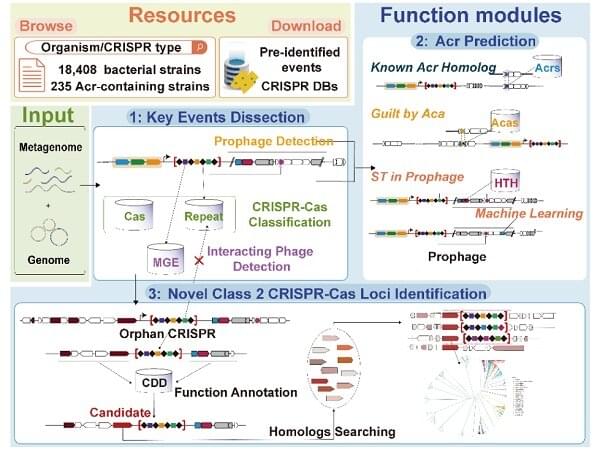
A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed an analysis service platform called CRISPRimmunity, which was an interactive web server for identifying important molecular events related to CRISPR and regulators of genome editing systems. The study is published in Nucleic Acids Research.
The new CRISPRimmunity platform was designed for integrated analysis and prediction of CRISPR-Cas and anti-CRISPR systems. It includes customized databases with annotations for known anti-CRISPR proteins, anti-CRISPR-associated proteins, class II CRISPR-Cas systems, CRISPR array types, HTH structural domains and mobile genetic elements. These resources allow the study of molecular events in the co-evolution of CRISPR-Cas and anti-CRISPR systems.
To improve prediction accuracy, the researchers used strategies such as homology analysis, association analysis and self-targeting in prophage regions to predict anti-CRISPR proteins. When tested on data from 99 experimentally validated Acrs and 676 non-Acrs, CRISPRimmunity achieved an accuracy of 0.997 for anti-CRISPR protein prediction.
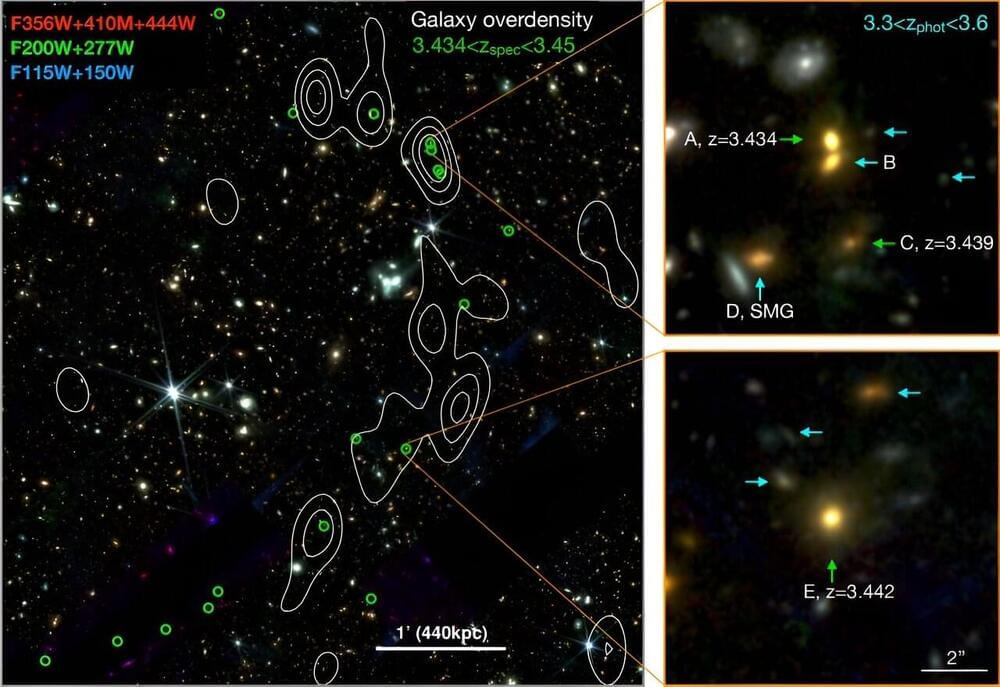
An international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a large-scale structure that consists of at least 20 massive galaxies. The structure, dubbed “Cosmic Vine,” has a size of about 13 million physical light years. The finding was detailed in a paper published Nov. 8 on the pre-print server arXiv.
Massive and dense structures of galaxies are perceived as progenitors of galaxy clusters—the most massive gravitationally-bound systems in the universe. Therefore, detecting new structures of this type and investigating them in detail is fundamental for our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution.
Now, a group of astronomers led by Shuowen Jin of the Technical University of Denmark, has detected a new object of this type—a large vine-like structure, hence its name Cosmic Vine. The structure was revealed at a redshift of 3.44, in the Extended Groth Strip (EGS) field observed with JWST. The observations were complemented by data from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).