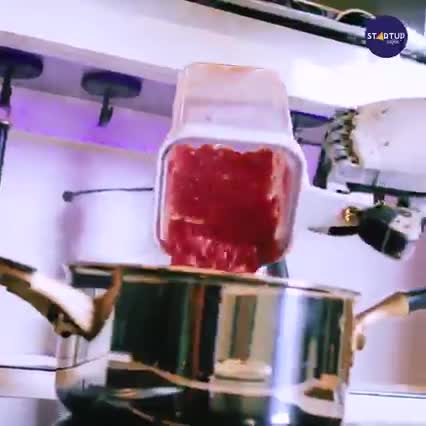
Three-dimensional “bio-printing” and real cow cells — an achievement that’s prompting the Israeli startup to eye other meat…The firm’s technology prints living cells that are incubated to grow, differentiate and interact to acquire the texture and qualities of a real steak. “It incorporates muscle and fat similar to its slaughtered counterpart,” Aleph Farms said, adding that the product boasts the same attributes “of a delicious tender, juicy ribeye steak you’d buy from the butcher.”