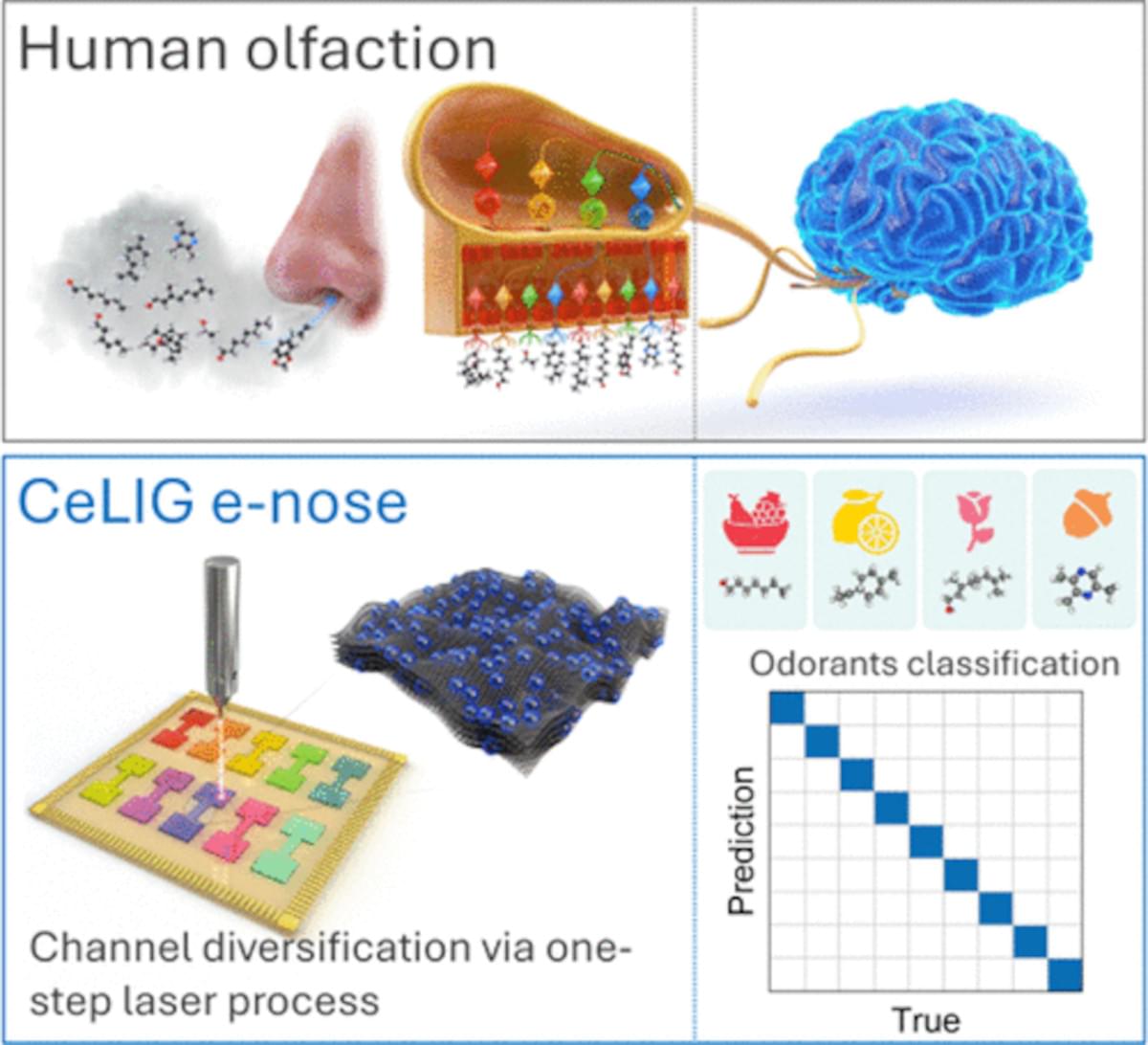
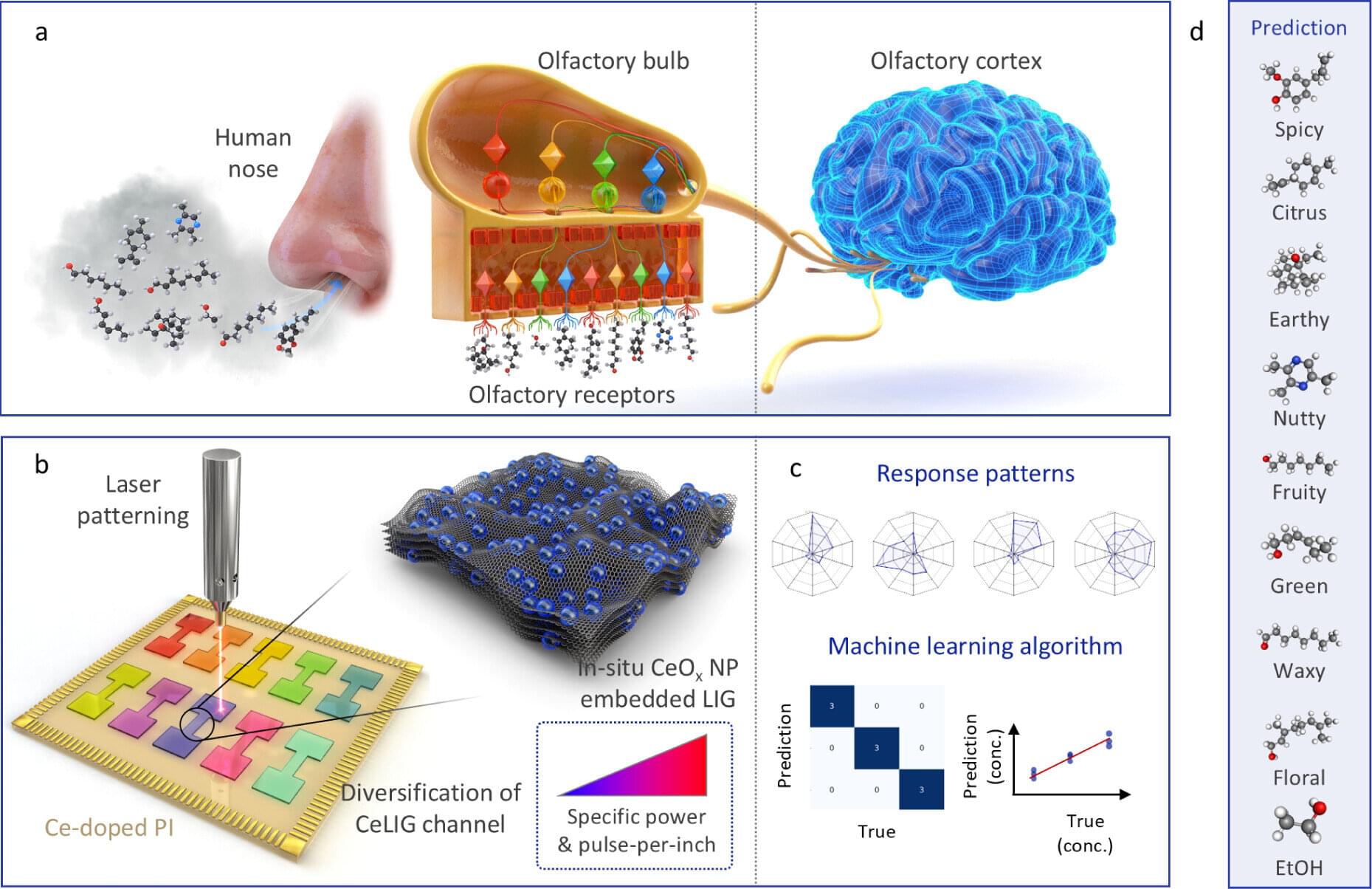
Researchers at Korea’s Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) have developed a porous laser-induced graphene (LIG) sensor array that functions as a “next-generation AI electronic nose” capable of distinguishing scents like the human olfactory system does and analyzing them using artificial intelligence.
This technology converts scent molecules into electrical signals and trains AI models on their unique patterns. It holds great promise for applications in personalized health care, the cosmetics industry, and environmental monitoring.
While conventional electronic noses (e-noses) have already been developed and used in areas such as food safety and gas detection in industrial settings, they struggle to distinguish subtle differences between similar smells or analyze complex scent compositions. For instance, distinguishing among floral perfumes with similar notes or detecting the faint odor of fruit approaching spoilage remains challenging for current systems. This gap has driven demand for next-generation e-nose technologies with greater precision, sensitivity, and adaptability.