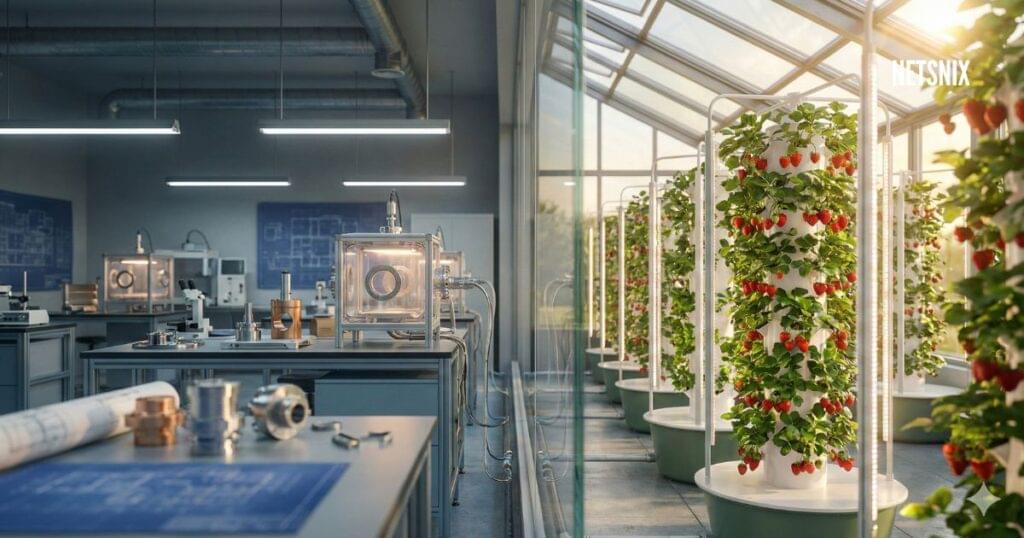
When James Dyson built his 5,127th prototype of a bagless vacuum cleaner, he had no idea that the same relentless engineering philosophy would one day transform him into Britain’s largest farmer. Today, Dyson strawberry farming represents one of the most ambitious applications of high-tech innovation to agriculture ever attempted in the United Kingdom.
The numbers tell an extraordinary story. After spending five years and creating over five thousand prototypes to perfect a single vacuum cleaner design, Dyson has now invested £140 million into a farming operation spanning 36,000 acres across five English counties. At the heart of this agricultural empire sits a 26-acre glasshouse in Lincolnshire, home to 1.25 million strawberry plants and technology that has increased yields by 250% compared to traditional farming methods.
This isn’t farming as your grandparents would recognize it. Inside Dyson’s facility, massive 5.5-meter “ferris wheel” structures rotate strawberry plants through optimal sunlight positions. Sixteen robotic arms delicately harvest ripe fruit using computer vision. UV-emitting robots patrol the aisles at night, destroying mould without chemicals. And all of it runs on renewable energy generated from an adjacent anaerobic digester.