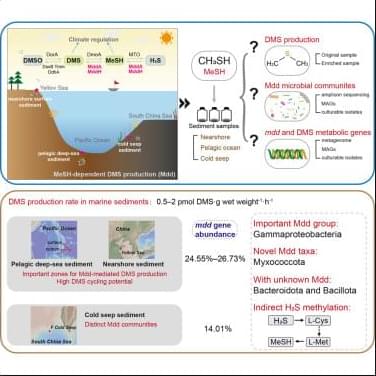
Knowing which genes are responsible for the transformations could help with developing antifungal treatments, and may have other pharmaceutical and industrial applications.




Camille Boutin, Laurent Kodjabachian et al. describe an inducible multiciliated cell line well suited for advanced microscopy and proteomic approaches. The study provides a detailed proteomic profiling of MCC during their differentiation.
Boutin et al., describe an inducible multiciliated cell line well suited for advanced microscopy and proteomic approaches. The study provides a detailed pr.

A new UCLA investigator-initiated study has found that adding immunotherapy to standard chemotherapy before surgery is safe and shows promise for some patients with borderline-resectable pancreatic cancer, a disease that has historically been difficult to treat.
The findings, published in Nature Communications, show that while the combination did not produce a clear survival advantage for most patients, a notable subset experienced unusually deep and durable responses. It also helped some patients live long enough to reach surgery, shrank tumors and produced encouraging survival outcomes.
The study also revealed immune changes that may limit how well immunotherapy works in pancreatic cancer, offering important clues for how future treatment strategies could be refined to further improve patient outcomes.

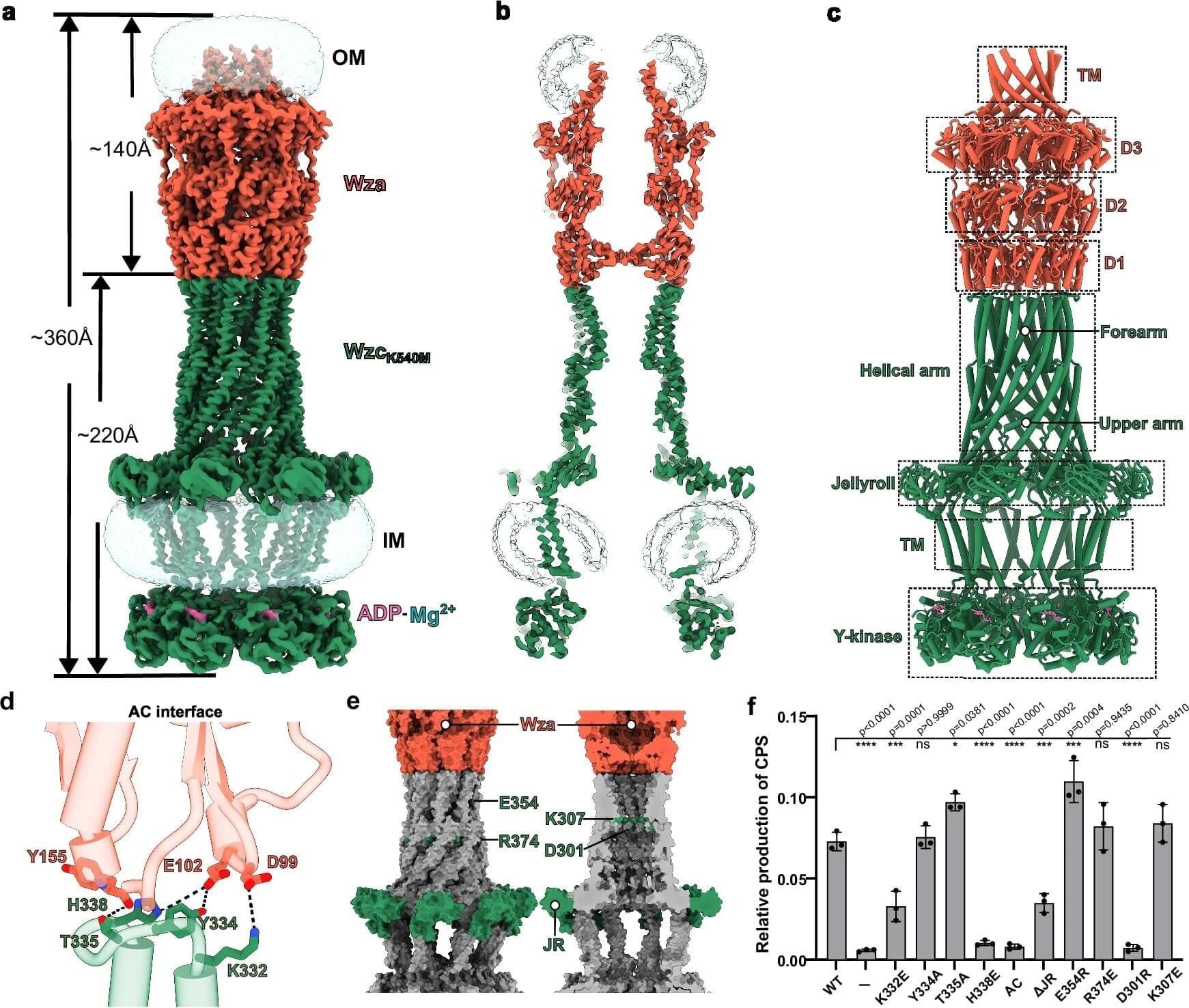
Most bacteria, including many bacterial pathogens, are surrounded by an outer protective layer of sugar molecules, known as a capsule. This primarily protects the bacteria from environmental influences, but also serves as a kind of cloak of invisibility, enabling them to evade the phagocytes of our immune system. Structural biologists at the Helmholtz Center for Infection Research (HZI) have now used cryo-electron microscopy to visualize the central Wza-Wzc protein complex, with which sugar molecules pass from the interior of the bacterial cell to the outside, in three dimensions at the atomic level for the first time.
Their investigations also show how the channel is formed and which molecular players are involved in the active transport of sugar molecules through the channel. The researchers hope that their study will help identify target structures for potential drugs that could inhibit or completely prevent the formation of the bacterial capsule in the future. This would also make such bacterial pathogens vulnerable to attack by the immune system.
The study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from the Center for Structural Systems Biology (CSSB) in Hamburg and has now been published in the journal Nature Communications.


