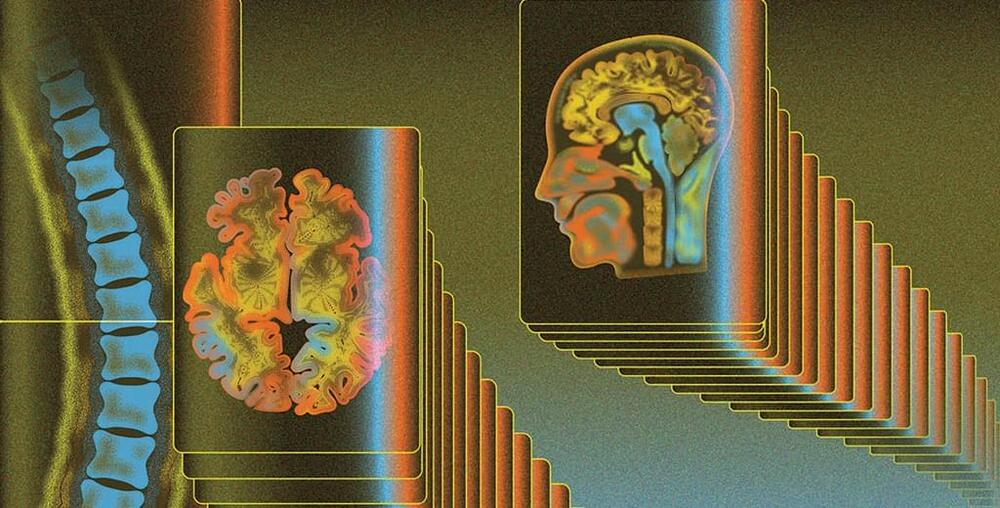
Intestinal stem cells play an important role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis and repairing damaged epithelial tissue. These cells function in a regenerative manner to generate new tissue throughout the growth phase and repair damaged tissue during the aging process.101 The interactions between the gut microbiome and intestinal stem cells are crucial because, if this interaction is comprehended, it may be possible to address various disorders that require stem cell therapy, heal wounds, and improve the durability of organ transplants.101 A recent study showed a connection between hematopoietic stem cells and the microbiome through altering metabolic stress.66 Therefore, the microbiota is crucial for maintaining microbial homeostasis, regulating metabolism, and the innate and adaptive immune systems.101 Furthermore, the study reveals that compositional alterations in the gut microbiome driven by dysbiosis are related to stem cell aging, metabolic dysregulations, stem cells’ epigenetic instability, and abnormal immune system activation.66
In the field of anti-aging, stem cells are regarded to have great potential. In numerous organs, it has been demonstrated that as we age, stem cells lose their capacity for self-renewal and differentiation and run out of resources.89 The emergence of anti-aging medications should address the dysregulation caused by aging that affects stem cells’ capacity for differentiation and self-renewal by re-regulating intrinsic and extrinsic variables. The host microbiome, hormones, local immune system, systemic inflammation, and niche structure are just a few examples of microenvironmental and systemic factors that influence stem cell aging.66
Endogenous ethanol is a class of microbiological metabolites. Proteobacteria, including E. coli and other Enterobacteriaceae, produce ethanol with bacterial origins. High endogenous ethanol levels in the human hippocampus inhibit proliferating stem cells and reduce progenitor and stem cells.102 Additionally, when more ethanol accumulates in the gut, it enhances the permeability of the gut by disrupting epithelial tight junctions, particularly zonula occludens. This enables the movement of pathogenic microbes, their endotoxins, and ethanol across the epithelial layer, causing more immediate and adverse effects on tissues. As a result, the stem cell reserve depletes, hastening the aging process and compensating for damaged tissues.103