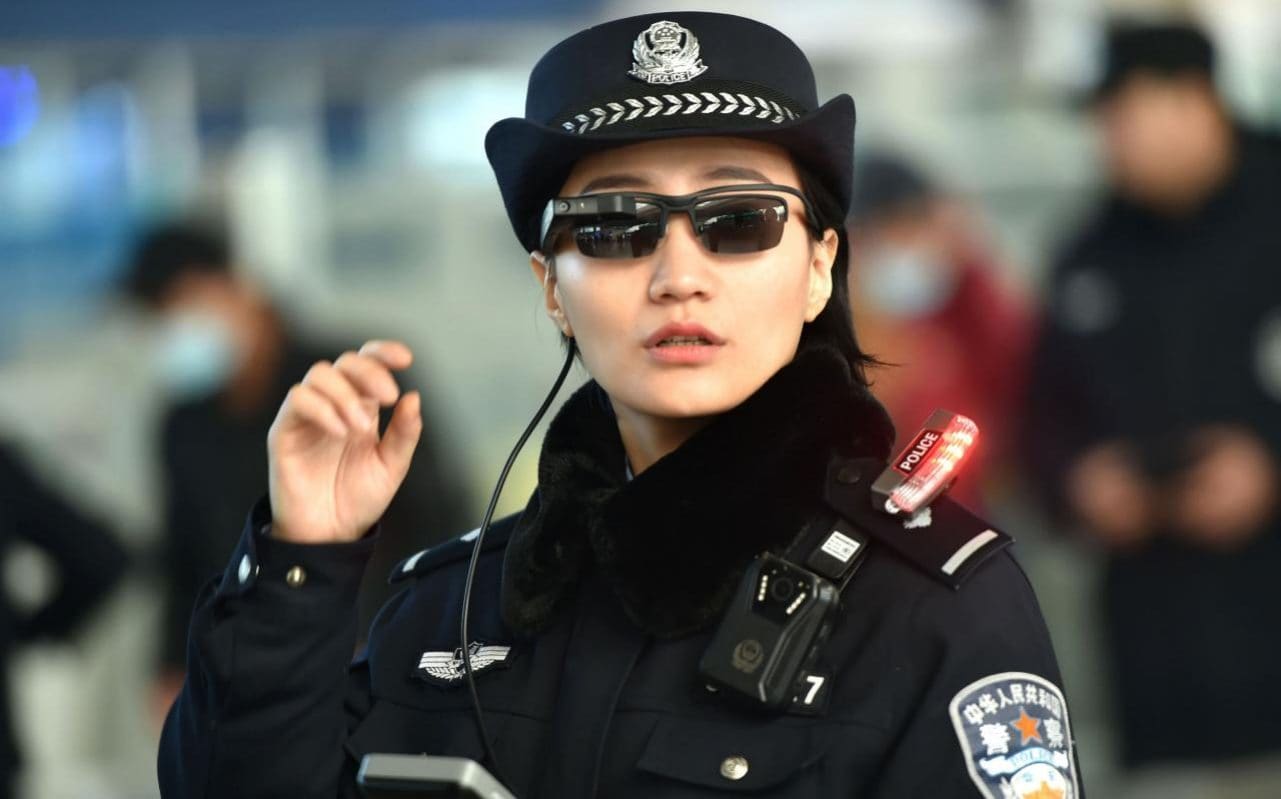
We are now on the brink of a “third revolution in warfare,” heralded by killer robots — the fully autonomous weapons that could decide who to target and kill… without human input.
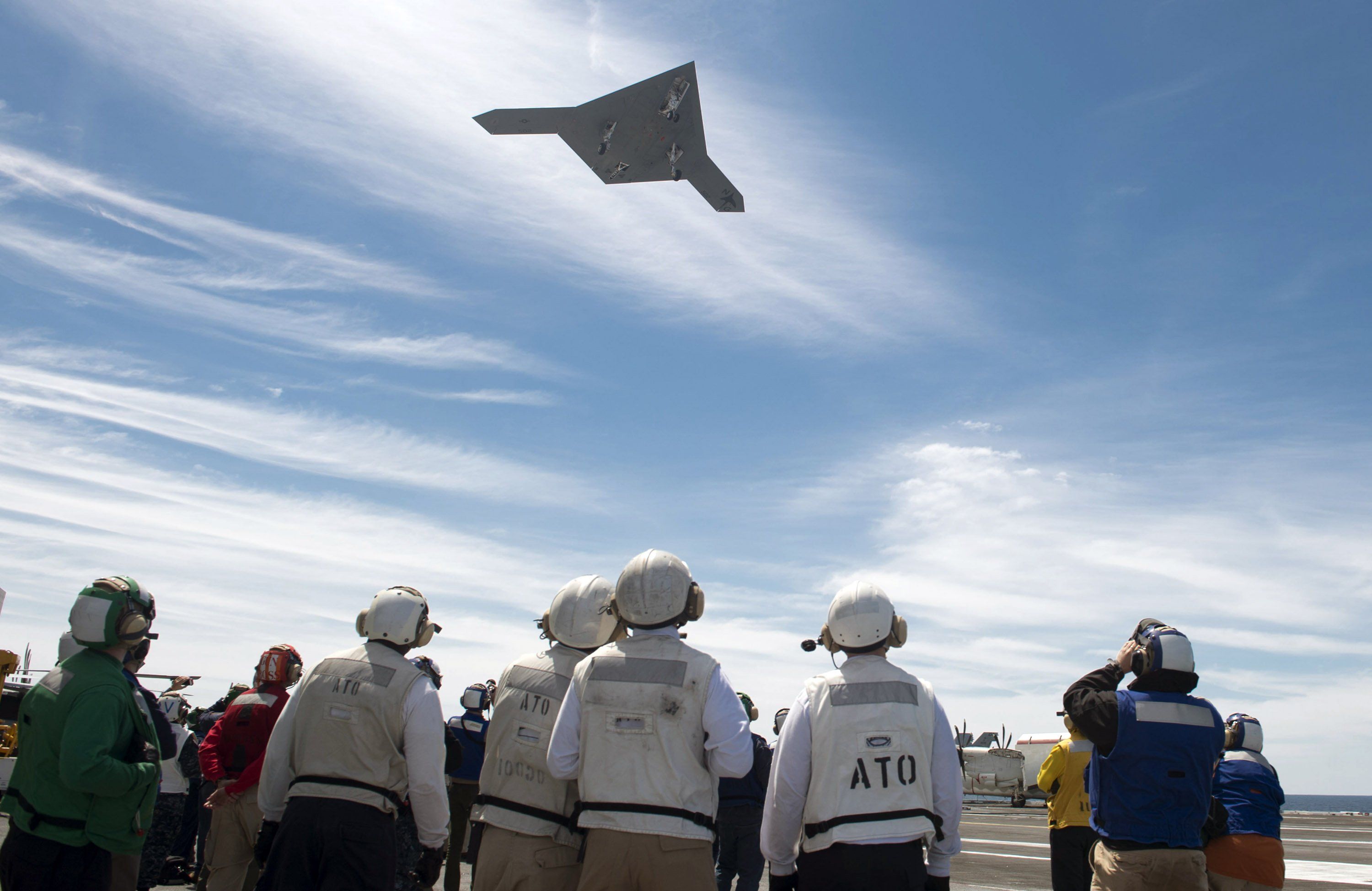
Over the weekend, experts on military artificial intelligence from more than 80 world governments converged on the U.N. offices in Geneva for the start of a week’s talks on autonomous weapons systems. Many of them fear that after gunpowder and nuclear weapons, we are now on the brink of a “third revolution in warfare,” heralded by killer robots — the fully autonomous weapons that could decide who to target and kill without human input. With autonomous technology already in development in several countries, the talks mark a crucial point for governments and activists who believe the U.N. should play a key role in regulating the technology.
The meeting comes at a critical juncture. In July, Kalashnikov, the main defense contractor of the Russian government, announced it was developing a weapon that uses neural networks to make “shoot-no shoot” decisions. In January 2017, the U.S. Department of Defense released a video showing an autonomous drone swarm of 103 individual robots successfully flying over California. Nobody was in control of the drones; their flight paths were choreographed in real-time by an advanced algorithm. The drones “are a collective organism, sharing one distributed brain for decision-making and adapting to each other like swarms in nature,” a spokesman said. The drones in the video were not weaponized — but the technology to do so is rapidly evolving.
This April also marks five years since the launch of the International Campaign to Stop Killer Robots, which called for “urgent action to preemptively ban the lethal robot weapons that would be able to select and attack targets without any human intervention.” The 2013 launch letter — signed by a Nobel Peace Laureate and the directors of several NGOs — noted that they could be deployed within the next 20 years and would “give machines the power to decide who lives or dies on the battlefield.”