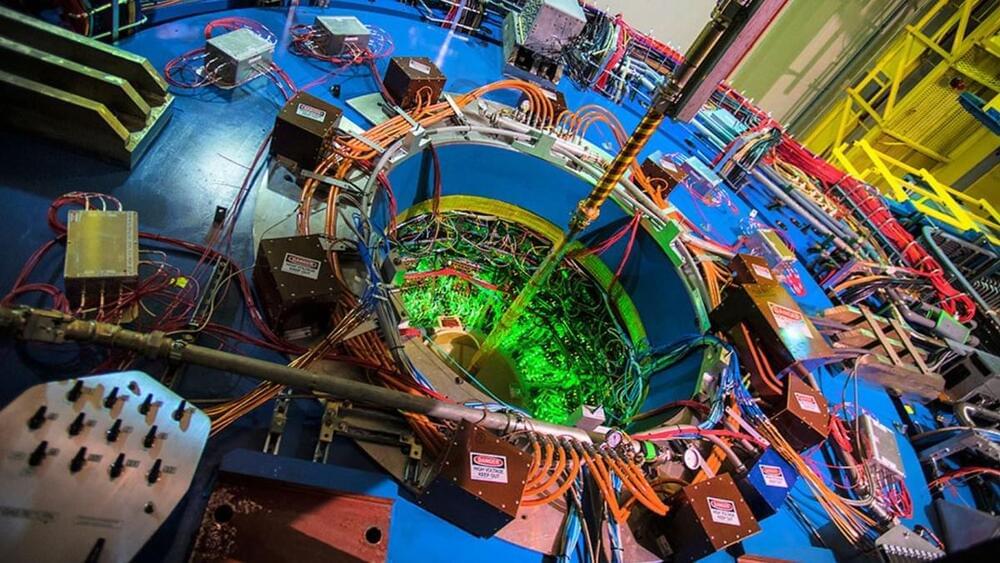
Scientists at Brookhaven National Laboratory have uncovered an entirely new kind of quantum entanglement, a phenomenon that causes particles to become weirdly linked, even across vast cosmic distances, reports a new study. The discovery allowed them to capture an unprecedented glimpse of the bizarre world inside atoms, the tiny building blocks of matter.
The mind-bending research resolves a longstanding mystery about the nuclei of atoms, which contain particles called protons and neutrons, and could help shed light on topics ranging from quantum computing to astrophysics.