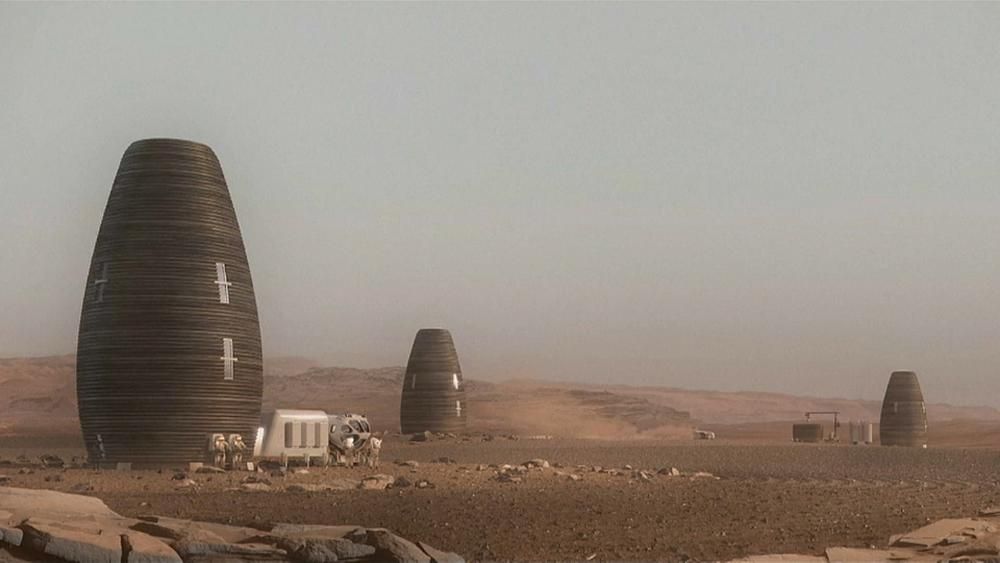
A self-assembling space habitat, a deep sleep chamber to shuttle astronauts on long journeys, and a protective magnetic force field are the latest projects NASA is embarking on.
NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concept (NIAC) Program is responsible for funding futuristic space concepts that could, as NASA puts it, “change the possible.” It’s not enough to merely be a cool concept, though—projects are also screened for technical plausibility. In its latest round of funding, NIAC’s Phase II program has selected eight projects to move ahead. Among the most promising ones are three focusing on how to build livable future habitats in space.