Medical/ Biocomputing will only continue to grow and advance as a result of the demand for more improved experiences by consumers and business in communications and entertainment, food, home life, travel, business, etc.
Today, we have seen early opportunities and benefits with 3D printing, BMI, early stage Gene/ Cell circuitry and computing. In the future, we will see these technologies more and more replaced by even more advance Biocomputing and gene circuitry technology that will ultimately transform the human experiences and quality of life that many like to call Singularity.
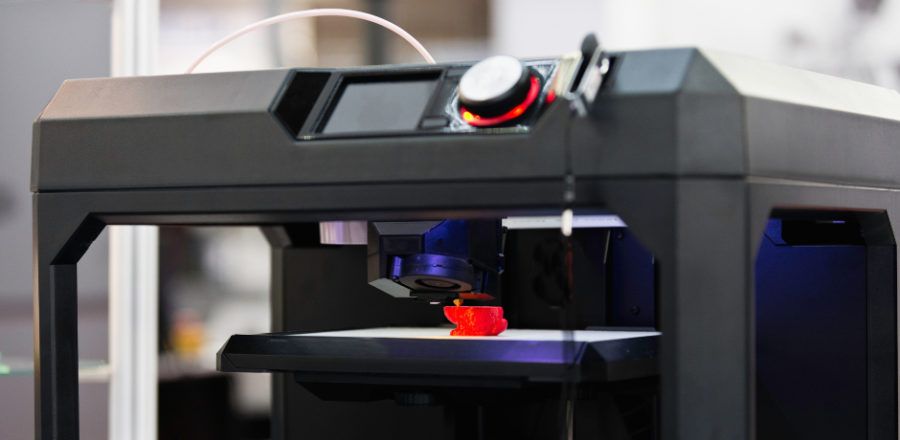
Printing technology has come a long way from screechy dot-matrix printers to 3D printers which can print real life objects from metals, plastics, chemicals and concrete. While, at first, 3D printers were being used to create just basic shapes with different materials, more recently, they have been used to create advanced electronics, bio-medical devices and even houses.
Aircraft manufacturer Airbus recently showcased the world’s first 3D-printed mini aircraft, Thor, at the International Aerospace Exhibition and Air Show in Berlin. Although Airbus and its competitor have been using 3D-printed parts for their bigger assemblies, recent attempt shows that aviation may be ready for a new future with much lighter and cheaper planes given 3D printing not only cuts down the costs with less wastage, it also makes the plane lighter, thereby making them faster and more fuel efficient. But planes and toys is not what 3D printing might be restricted to; though in the elementary stage at the moment, the technology is being used for creating complex electronics like phones and wearables and may be able to reduce costs for manufacturers like Samsung and Apple.
One of the most important uses for the technology comes in the field of medical sciences. While pharma companies have been working on producing medicines from 3D printers, with one winning approval from the US’s Food and Drug Administration earlier this year, the technology is also being used to create bones, cartilages and customisable prosthetic limbs. But the real test for the technology lies in bioprinting—creating living cells via a 3D printer. Doctors have been using 3D printed organs to practice on, but scientists at research institutes have been experimenting with printing stem cells, skin tissue, organs and DNA. Though this is still decades from being a reality, printing of regenerative tissues can help cure heart ailments. 3D printing is also helping in construction, with a printer being used to create the first office space in Dubai using concrete blocks. The city aims that 25% of its buildings will be 3D printed by 2030.