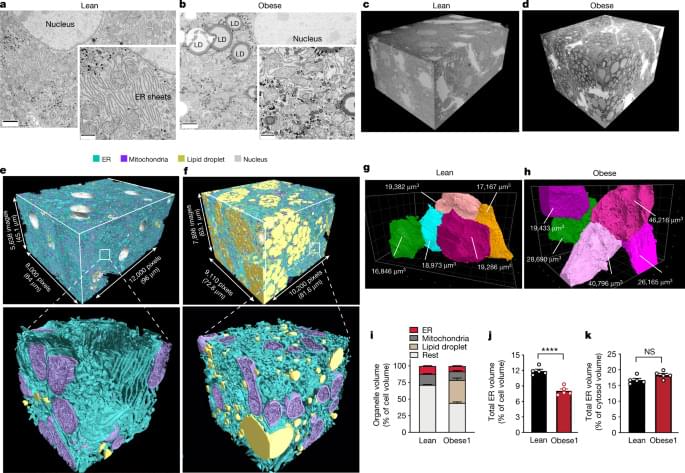
Fascinating 3D electron microscopy study by Parlakgül et al. wherein they compare the subcellular organization of liver tissue from lean and obese mice. The authors found substantial differences in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) organization. These ER differences were shown to directly influence metabolic health in a causal fashion, opening the doors to new ways of treating metabolic dysfunction. #electronmicroscopy #cellbiology #metabolism
Detailed reconstruction using enhanced focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy imaging and deep-learning-based automated segmentation demonstrates that hepatocyte subcellular organelle architecture regulates metabolism.