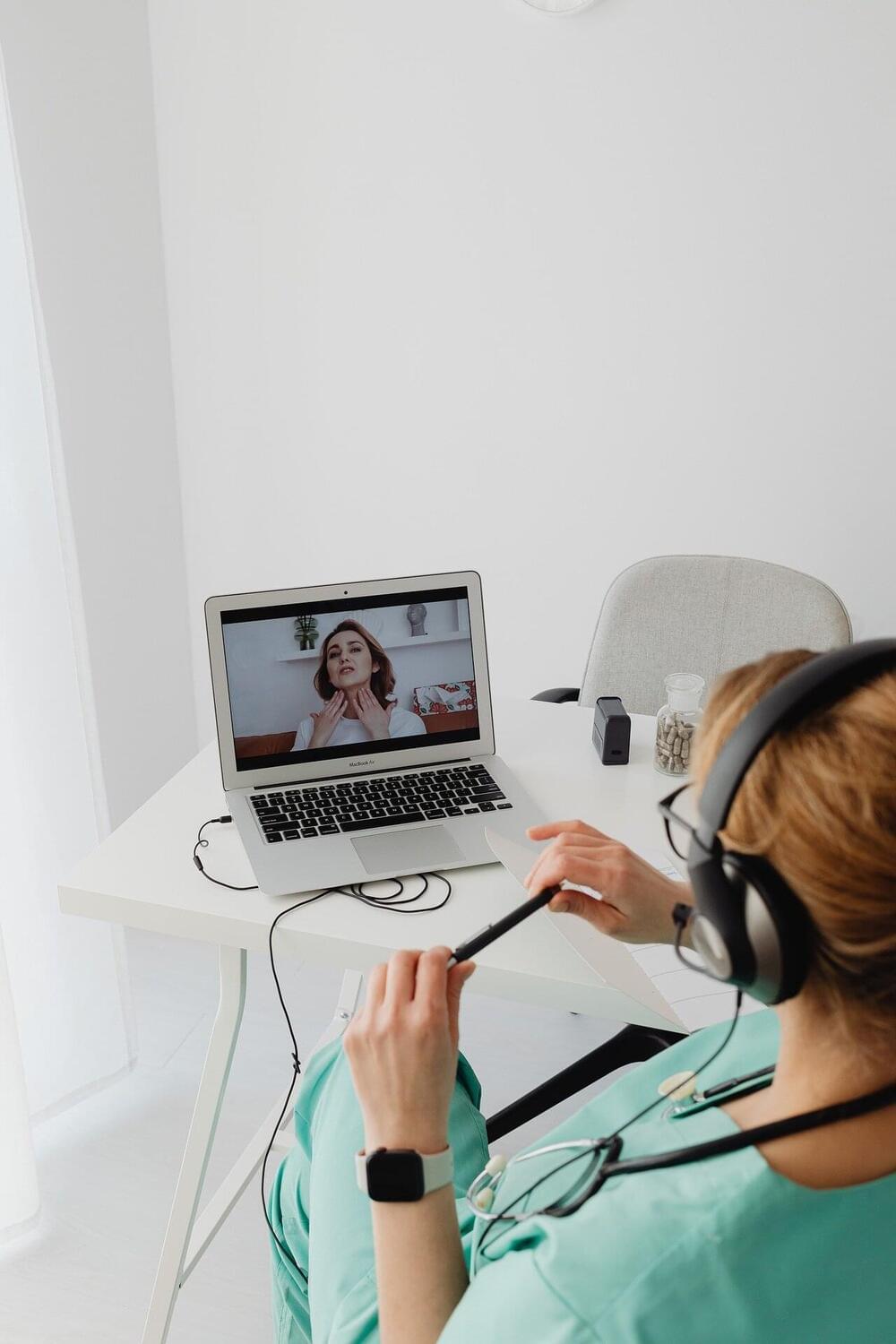
The expanded availability of opioid use disorder-related telehealth services and medications during the COVID-19 pandemic was associated with a lowered likelihood of fatal drug overdose among Medicare beneficiaries, according to a new study.
“The results of this study add to the growing research documenting the benefits of expanding the use of telehealth services for people with opioid use disorder, as well as the need to improve retention and access to medication treatment for opioid use disorder,” said lead author Christopher M. Jones, PharmD, DrPH, director of the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “The findings from this collaborative study also highlight the importance of working across agencies to identify successful strategies to address and get ahead of the constantly evolving overdose crisis.”
Published today in JAMA Psychiatry, this study is a collaborative research effort led by researchers at the National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, a part of CDC; the Office of the Administrator and the Center for Clinical Standards and Quality, both part of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS); and the National Institute on Drug Abuse, a part of the National Institutes of Health.