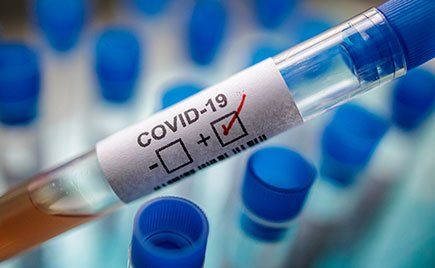
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first blood test that looks for the antibodies against the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19. This is different than assays that test for presence of the virus—those test to determine if a patient has COVID-19. These new antibody tests determine if the person was exposed to the virus, had COVID-19 and recovered. And it suggests, if positive, that the person is now immune to COVID-19 and can’t get it again.
Research Triangle Park, North Carolina-based Cellex was granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) on its test yesterday.
The test is performed on a blood sample taken from a patient’s vein and can be performed by laboratories certified under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA), the Health and Human Services division that oversees clinical diagnostic testing in the United States.